Poverty and obesity: Difference between revisions
imported>Ross McEwan |
imported>Ross McEwan |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===The Relationship Between Energy Density and Energy Cost=== | ===The Relationship Between Energy Density and Energy Cost=== | ||
There is an apparent inverse relationship between the energy density of foods and the energy cost of food. This meaning that energy dense foods are cheaper for food consumption then the 'healthier' less energy dense food substances. | |||
Its is observed that diets which are high in fats, sugars and grains are associated with lower diet costs and are an effective way of saving money but still satisfying the need for food. | |||
French studies have shown that for every additional 100g of sweets and fats there was a 0.05 - 0.40 Euro per day reduction in the cost of diet in contrast to each 100g additional portion of fruit and vegetables there was a 0.18 - 0.29 Euro per day increase in dietary costs. | |||
Studies have also shown evidence that in America obesity is an economic issue, rather than a medical, education or genetic issue. | |||
===Pricing of Foods and Influence of Income/SES=== | ===Pricing of Foods and Influence of Income/SES=== | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 21 October 2011
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is 01 April 2012. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
Introduction
Poverty and obesity are very closely linked. In the USA, the highest rates of obesity occur in the poorest population groups. Poverty is associated with lower expenditure on food, and low consumption of fruit and vegetables, and energy-dense foods represent the lowest-cost option for consumers. However, the high energy density and palatability of sweets and fats are associated with higher energy intakes. [1]
Diet Quality
Dietary Energy Density
Influence on energy intakes
Energy dense foods result in higher energy intakes overall - list studies on this
Function of water content
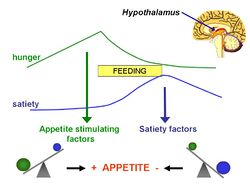
The energy density of foods is determined by their water content - energy dilute foods are well hydrated whereas energy dense foods are comparably dry. Affects satiety.
Palatability of energy dense foods
Sugar and fat stimulate reward centers in brain, resulting in human taste preference. List studies on whether this is innate or acquired.
Energy Costs
The Relationship Between Energy Density and Energy Cost
There is an apparent inverse relationship between the energy density of foods and the energy cost of food. This meaning that energy dense foods are cheaper for food consumption then the 'healthier' less energy dense food substances.
Its is observed that diets which are high in fats, sugars and grains are associated with lower diet costs and are an effective way of saving money but still satisfying the need for food.
French studies have shown that for every additional 100g of sweets and fats there was a 0.05 - 0.40 Euro per day reduction in the cost of diet in contrast to each 100g additional portion of fruit and vegetables there was a 0.18 - 0.29 Euro per day increase in dietary costs.
Studies have also shown evidence that in America obesity is an economic issue, rather than a medical, education or genetic issue.
Pricing of Foods and Influence of Income/SES
References
- ↑ Drewnowski A, Specter SE (2004) Poverty and obesity: the role of energy density and energy costs Am J Clin Nutr 79:6-16 PMID 14684391