Diabesity: Difference between revisions
imported>Luke Kennedy Burke |
imported>John Stephenson (some copyedit) |
||
| (45 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
The term '''diabesity''' was coined by [https://vpn.ucsf.edu/oby/journal/v19/n3/full/,DanaInfo=www.nature.com+oby2010334a.html Ethan Sims] in 1973, to describe the close relationship between [[diabetes mellitus type 2]] (T2DM) and [[obesity]]. Their findings suggested that by overfeeding young men with no previous family history of diabetes, the initial signs of diabetes were induced. This excess consumption led to increases in [[insulin]] production, plasma [[glucose]], [[triglycerides]] and eventually impaired glucose tolerance; all signs predisposing one to T2DM and obesity.<ref> | |||
Sims EAH ''et al.'' (1973) Endocrine and metabolic effects of experimental obesity in man, ''Recent Prog Horm Res'' 29:457–96</ref><ref>Haslam DW, James WP (2005) Obesity''Lancet'' 366:1197–209</ref> | |||
T2DM is a disorder where cells fail to take up glucose from the blood. Glucose is the fuel for respiration which produces energy for our cells to function properly. Diabetes mellitus is the foremost cause of kidney failure ([[diabetic nephropathy]]), blindness ([[diabetic retinopathy]]), and amputation in adults ([[diabetic neuropathy]]). People with this disease lack the ability to utilize the hormone [[insulin]]. Insulin is produced by the [[pancreas]] after a meal in response to increased concentrations of glucose in the blood. The insulin signal attaches to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, causing them to switch on their glucose-transporting machinery. People with T2DM have normal or even elevated levels of insulin in their blood, and normal insulin receptors, but the binding of insulin to its receptors does not turn on the glucose-transporting machinery. | |||
Proteins called [[IRS proteins]] (insulin receptor substrate) bind with the insulin receptor inside the cell. The receptor responds by adding a phosphate group onto the IRS molecules. This rouses the IRS molecules into action, and they activate a variety of processes, including an enzyme that turns on the glucose transporter machinery. When the IRS genes are deliberately inactivated in [[transgenic]] “knockout” mice, T2DM results. However, there are no IRS gene mutations in inherited T2DM; the IRS genes are normal. This suggests that in T2DM something is impeding with the action of the IRS proteins. An estimated 80% of those who develop T2DM are obese. | |||
When the IRS genes are deliberately | |||
This suggests that in | |||
==Visceral fat accumulation and type 2 diabetes== | ==Visceral fat accumulation and type 2 diabetes== | ||
Excess visceral adipose tissue increases the risk for T2DM. Excess fat within the [[abdomen]], known as [[visceral adiposity]], creates a serious health risk of metabolic complications independent from accumulation of adipose tissue in other regions: visceral adiposity is related with an increase in ''[[insulin resistance]]'', whereas abdominal subcutaneous fat is not. (''Insulin resistance'' describes the impaired ability of insulin to suppress hepatic glucose output and promote glucose disposal in the periphery.) As T2DM gets worse, patients have higher blood sugar levels ([[hyperglycaemia]]) because the [[pancreatic beta cells]] are unable to make enough insulin. In insulin resistance, normal amounts of insulin are unable to produce a normal response from adipose, muscle and liver cells. Cnop ''et al.'' showed that visceral fat is the best predictor of insulin sensitivity whilst subcutaneous fat establishes leptin levels <ref>Cnop''et al.'' (2002) The concurrent accumalation of intra-adominal and subcutaneous fat explains the association between insulin resistance and plasma leptin concentrations. ''Diabetes'' 51:1005-15</ref> | |||
In 1994, a new hormone was found, called [[leptin]], that provides feedback to the brain of the level of fat in the body. Leptin suppresses appetite, but most obese people have very high leptin levels, as leptin is secreted by adipose cells. Therefore, obesity is not generally caused by a deficiency in leptin; instead there seems to be a defect in leptin signalling. Adipocytes also produce an array of other peptides including [[adiponectin]], [[resistin]] and [[TNF alpha]]. They act on peripheral tissues and thereby affect insulin sensitivity and the processes involved in substrate metabolism. | |||
The lipoprotein profile related to obesity and insulin resistance is mostly due to intra-abdominal fat [4]. There are better measures of obesity (particularly visceral obesity) that can predict diabetes. These include ''waist circumference'', the ''waist-to-hip ratio'' and ''insulin resistance''. | |||
Fat cells show elevated hydrolysis of stored triglycerides and increased free fatty acids into the blood. Insulin resistance reduces the antilipolytic effect of insulin, which leads to reduced glucose uptake and increased release of free fatty acids and glycerol. [5] Excess free fatty acids are taken by the portal vein to the liver. The liver is then overwhelmed by the free fatty acids and starts up typical IR metabolic processes. The liver responds by increasing [[glyconeogenesis]] (production of glygogen), increasing [[triglyceride]], apolipoprotein B and [[very low density lipoprotein]] (VLDL) production. This in turn increases the production of [[low density lipoproteins]] and the reduction of [[high density lipoproteins]] (HDLs). This lipid profile is known as atherogenic dyslipidaemia as it eventually leads to [[atherosclerosis]]. Intramyocellular lipids (IMCL) are more closely associated to insulin resistance than to body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, or total body fat. High free fatty acid and VLDL levels are a key cause of fat accumulation in muscle cells and IMCL increases have been seen in patients with insulin resistance. Surgical removal of visceral fat had a positive effect on the hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity, and on leptin and TNFα levels. [6] | |||
Long term exposure of pancreatic beta cells to increased fatty acid levels causes damaging effects such as increased insulin secretion at low glucose concentrations, decreased proinsulin production, exhaustion of insulin reserves and reduced response to concentrations of glucose stimulus. Solomon and Mayer were first to associate [[glucocorticoid]]s as a required factor in genetic obesity, observing that obesity was avoided after bilateral [[adrenalectomy]] and completely restored by [[cortisol]] replacement. <ref>Solomon J, Mayer J (1973) The effect of adrenalectomy on the development of the obese- hyperglycemic syndrome in ob-ob mice ''Endocrinology'' 93:510–2</ref> | |||
===11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1=== | |||
[[11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1]] (11β-HSD-1) is an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of inactive [[cortisone]] to active cortisol, a potent glucocorticoid. It is found throughout the body and is a highly regulated enzyme that increases the ligand accessibility for glucocorticoid receptors. | |||
{{Image|Diabesity.jpg|right|500px|}} | |||
Excessive glucocorticoid exposure causes central obesity, [[hypertension]], and [[dyslipidaemia]] and insulin resistance, as seen in [[Cushing’s syndrome]]. Transgenic mice over-expressing 11β-HSD-1 in [[white adipose tissue]] have these features as well, while 11β-HSD-1 deficient mice are protected from these metabolic abnormalities. In [[human idiopathic obesity]], circulating cortisol levels are not elevated, but 11HSD1 mRNA and activity is increased in subcutaneous adipose tissue. The impact of increased adipose 11β-HSD-1 on pathways leading to metabolic complications remains unclear in humans. Pharmacological inhibition of 11HSD1 has been achieved in liver with [[carbenoxolone]], which enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity.] <ref>London E, Castonguay T (2009) Diet and the role of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 on obesity ''Nutr Biochem'' 20:485-93</ref> | |||
Visceral obesity may be secondary to enhanced local activation of cortisol via increased levels and activity of 11β-HSD-1 in adipose tissue that result in abnormally high levels of cortisol in adipose tissue. Obesity is distinct from Cushing's syndrome in that the source of the elevated glucocorticoids is adipose tissue rather than the [[adrenal cortex]]. | |||
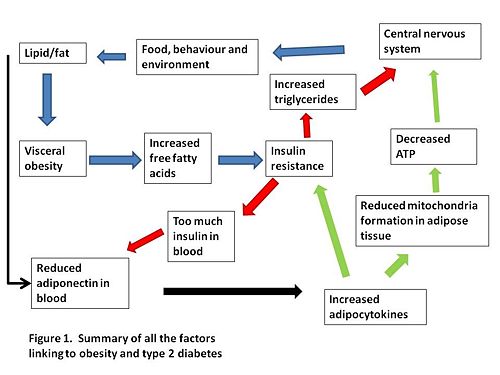
A summary of how we think visceral obesity causes insulin resistance and T2DM is shown in Figure 1. | |||
==Causes of type 2 diabetes in obese patients== | ==Causes of type 2 diabetes in obese patients== | ||
===Endoplasmic reticulum stress | ===Endoplasmic reticulum stress === | ||
Endoplasmic reticulum stress | [[Endoplasmic reticulum stress]] (ER stress) is a molecular-level link connecting obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Mice lacking X-box-binding protein-1 (XBP-1), a transcription factor used to modulate the body’s response to ER stress, as well as mice that had induced ER stress via pharmacological means, showed the development of insulin resistance. ER stress or down-regulation of XBP-1 causes the suppression of insulin receptor signaling in the body’s cells via activation of Jun kinases (JNKs). In mice, this insulin receptor suppression leads to increased insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. It is thought that increased activity of JNKs causes the phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) within important tissues such as liver, muscle and fat. As well as insulin resistance, JNK activity can result in the inhibition of insulin production in pancreatic β-cells. In mice which lack JNKs such as JNK1, obesity-induced obesity prevalence is reduced, and in general they also have reduced adiposity. | ||
ER stress or down-regulation of XBP-1 causes the suppression of insulin receptor signaling in the body’s cells via activation of Jun kinases (JNKs). In | |||
It is thought that increased activity of JNKs causes the phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) within important tissues such as liver, muscle and fat. As well as insulin resistance, | |||
In summary, there is a key process which controls the detection of obesity-induced ER stress, causing an inhibition of insulin action that leads to insulin resistance and T2DM. It is thought that ER stress is a precursor to cell inflammation as a result of obesity. This then leads to complete breakdown of glucose homeostasis. | |||
===Dysfunction of the pancreatic β-cells=== | |||
If insufficient insulin is secreted by the pancreatic β-cells, then adequate glucose uptake cannot occur. In mice fed a high fat diet, subsequent T2DM is at least partly due to reduced insulin secretion. Analysis of insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets of these mice found dysfunction in the production and/or secretion of insulin. An increase in glucagon-positive cells within the islets was also discovered in these mice. Similar changes are present in human cases of T2DM. | |||
It is also possible that there is increased pancreatic β-cell [[apoptosis]], induced by increasing obesity, reducing the level of insulin secretion. This reduced insulin secretion cannot then cope with the insulin resistance caused by obesity. Dysfunction and death of the pancreatic β-cells may be a result of cell inflammation due to hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and increased levels of adipokines. | |||
===Resistin=== | |||
The discovery of [[resistin]] came about through the development of a new class of anti-diabetic drugs called [[thiazolidinediones]] (TZDs). These act by increasing a target tissue’s sensitivity to insulin. They are ligands for a nuclear receptor called [[peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-ϒ ]] (PPARϒ) which is abundant in adipocytes. Tests showed a high correlation between TZD/PPARϒ binding and glucose lowering ''in vivo''. However, the target genes of TZD-bound PPARϒ are unknown. To try and discover whether IR might be controlled by a TZD-controlled, adipocyte-originating substance, a genetic screen was carried out for genes induced by adipocyte formation but downregulated when treated with TZDs. This produced evidence of a TZD-regulated protein, called ''resistin''.<ref>Steppan CM ''et al.''(2001) The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. ''Nature'' 409:307-312</ref><ref>Qatanani M ''et al.'' (2009) Macrophage-derived human resistin exacerbates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. ''J Clin Invest'' 119:531-9</ref> Resistin expression increases when adipocytes differentiate, and decreases with administration of TZD drugs such as [[rosiglitazone]], [[pioglitazone]] and [[troglitazon]]. In mice, resistin is expressed almost exclusively in white adipose tissue, with highest expression in female gonadal fat. An amino acid sequence expressed in humans with a large similarity to resistin was also found. In mice, serum levels of resistin decrease with fasting and are restored with re-feeding. In mice fed on a 45% fat content diet for 8 weeks, the levels of resistin in serum are greatly elevated, initially increasing within four weeks of the diet being adopted, the same point as when the mice become obese and insulin resistant. Higher than normal resistin levels can also be detected in leptin-deficient (''ob/ob'') mice and in leptin receptor deficient (''db/db'') mice, both of which are genetically predisposed to obesity and T2DM. | |||
Intraperitoneal administration of resistin to mice results in impaired insulin sensitivity, while insulin levels remain normal. Both ''in vitro'' and ''in vivo'' studies show that neutralization of resistin causes enhanced insulin action and glucose uptake. In obese, diabetic mice, resistin neutralization causes reduced levels of hyperglycemia by increasing insulin sensitivity. | |||
In humans, resistin is thought to be secreted by macrophages not adipocytes. Despite this, there is still a strong correlation in humans between | Resistin is believed to modulate at least one step in the insulin signaling pathway. At present it is unclear whether levels of resistin have a major effect on insulin activity in humans. In humans, resistin is thought to be secreted by [[macrophages]] not [[adipocytes]]. Despite this, there is still a strong correlation in humans between high levels of resistin, obesity, and T2DM. | ||
==The immunology of obesity== | ==The immunology of obesity== | ||
T2DM has long been considered as primarily a metabolic disease, but recent studies have challenged this, and implicated an unlikely candidate system in the promotion of disease onset - the immune system. Mild inflammation of fat tissue in obese patients reportedly acts through immune-cell processes to impair insulin signalling in adipocytes. | |||
[[Adipocytes]] have a dual role as both a fat storage depot and an endocrine organ. Obesity can induce a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation (Feuerer et al., 2009), and, unlike other forms of inflammation, fat inflammation appears to escape immune regulation. Depending on its state, adipose tissue will activate various phenotypes of [[T-cell]]s (‘non-obese’ CD4 or ‘obese’ CD8), which in turn regulate (or fail to regulate) the infiltration of [[macrophage]]s. This permeation of macrophages and their production of proinflammatory cytokines results in chronic inflammation. This impairs insulin signalling in the adipocytes, which leads to lipolysis and the release of non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) into the circulation. These fatty acids induce insulin resistance in the liver and skeletal muscles, and impair B-cell function. | |||
Depending on its state, adipose tissue will activate various phenotypes of T- | |||
Several groups have recently targeted the different T-cell populations and both reversed and prevented the onset of obesity-induced T2DM. Feuerer ''et al.'' (2009) isolated a specific phenotype of T-cell, CD4, which is enriched in the adipose tissue of lean mice but reduced in that of obese, insulin-resistant mice. Through loss-of-function experiments, it was shown that CD4 cells are functionally active and their absence results in inflammatory cytokine production and reduced glucose uptake. Importantly, CD4 T-cells were only shown to behave in this manner in visceral fat stores, which, unlike subcutaneous stores, are associated with the development of T2DM. A complementary study, performed by Winer ''et al.'' (2009), demonstrated that CD4 T-cell transfer reverses weight gain and IR in null mutants. Nevertheless, because the mice lost weight after the CD4 T-cell transfer, it makes conclusive interpretation of the data difficult. This data led the authors to conclude that obesity-associated metabolic abnormalities are under the pathophysiological control of CD4 T-cells, which inversely control the infiltration of problematic macrophages . | |||
A separate study by Nishimura ''et al.'' (2009) revealed that a different type of T-cell, CD8, are increased in obese mice and precede chronic inflammation observed in adipose tissue. Similarly, the adoptive transfer of CD8 T-cells resulted in adipose inflammation. Together this evidence led the authors to propose that obese adipose tissue activates CD8+ T-cells, which drive the recruitment of macrophages and their differentiation into an inflammatory rather than anti-inflammatory phenotype. | |||
Another aspect of the immune system that has been implicated in T2DM onset is [[mast cell]] function. Mast cells respond to allergic and parasitic challenge by releasing inflammatory mediators, playing an integral protective role. An excess of mast cells can lead to mast cell instability and inflammation. Shi ''et al.'' observed that the white adipose tissue of obese mice possesses a significantly more mast cells than lean equivalents. This led them to ask whether the manipulation of mast cell number, through genetic reduction and pharmacological equalization, can reduce the onset of obesity and T2DM. In the first set of experiments, genetically mast cell-deficient mice and control mice were fed on a Western-diet for three months. Loss of mast cell function appeared to have the effect of lowering serum leptin, increasing glucose tolerance and increasing insulin sensitivity. In the second strand of experimentation, mice were treated with mast cell-stabilizing medication to ask whether diet-induced obesity and diabetes could be inhibited. After two months on a Western-diet, mice were either switched to a healthy diet, supplied with mast-cell stabilizing medication, or a combination of both. While the dietary adjustment caused minor improvements, the medication stimulated significant restitution and the combination of both allowed a near full recovery in comparison to control group who continued on a Western-diet. | |||
Both of these drugs are already used to treat other medical conditions and are therefore both safe and available, however the question that remains to be answered is do Zaditor and cromolyn offer similar protection against diabetes in humans? A study into T-cell concentration in human abdominal fat tissue by Winer ''et al.'' (2009) has revealed an abundance of protective CD4 T-cells in normal weight individuals when compared to that of obese, diabetic patients, as well a reflection of inverse number of macrophages. | |||
==Treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes== | ==Treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes== | ||
Lifestyle changes provide the basis of treatment in all obese patients, but when these fail to reduce the weight in obese patients, anti-obesity drugs are used. There are few well-tolerated drugs which have long term efficacy in maintaining weight loss. Current available medications include [[sibutramine]] and [[orlistat]]. | |||
[2 | '''[[Sibutramine]]''' reduces body weight and appetite and increases satiety. Prospective randomised controlled trials have shown it to be effective, with one trial finding that patients on sibutramine lost 4.3kg or 4.6% more weight than those taking the placebo. The most common adverse effects are dry mouth, constipation and insomnia. '''Orlistat''' acts by inhibiting pancreatic and gastrointestinal lipases, preventing absorption of about 30% of dietary fat. Randomized controlled trials have shown that patients taking this have lost 2.7kg or 2.9% more weight than controls. As orlistat reduces LDL and cholesterol levels independently of reductions in body weight, it also retards the progression to a diabetic state and aids glycemic control in patients with diabetes. Side effects include fecal urgency and abdominal cramping.<ref>Chaputy JP, Tremblay A (2006) Current and novel approaches to the drug therapy of obesity. ''Eur J Clin Pharmacol'' 62 </ref> | ||
Patients with impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose and obesity are all at a high risk of developing T2DM, so combination therapy for glycaemic control and weight management is often required. Several strategies are used, including the promotion of weight loss through lifestyle modifications and anti-obesity drugs, improving glycemic control through the reduction of insulin resistance and the treatment of common associated risk factors such as hypertension and dyslipidaemia to improve cardiovascular prognosis <ref>ScheenAJ (2000) Treatment of diabetes in patients with severe obesity. ''Biomed Pharmacother'' 54:74-79</ref> | |||
When treating T2DM, main aims are to return metabolic disturbances to normal, achieve good glycemic control and assist with weight management. Dietary management is particularly important, to reduce the cardiovascular risks associated with central obesity. Patients with T2DM need to restrict carbohydrate and total calorific intake and eat foods of low glycemic index, to reduce the post prandial rise in blood glucose. When dietary management is not successful, pharmacological intervention is added, including anti-diabetic drugs to prevent hyperglycaemia, ACE inhibitors to treat hypertension and statins or fibrates to treat hyperlipidaemia.<ref>Lean MEJ ''et al.'' (1990) Obesity, weight loss and prognosis in type 2 diabetes. ''Diabetic Med'' 7:228-233</ref> | |||
[ | '''[[Metformin]]''' is recommended as first-line treatment in T2DM patients. When this fails, other agents are added to provide combination therapy. Most T2DM patients require combination therapy, because monotherapy with metformin usually only maintains good metabolic control in the short term. Treatments which can be added include [[sulphonylurea]]s, [[acarbose]], [[glucagon-like peptide-1]] (GLP-1) analogues, [[thiazolidinedione]]s, glinides, or insulin. <ref>Monami M ''et al.'' (2008) Comparison of different drugs as add-on treatments to metformin in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. ''Diabetes Res Clin Pr'' 79:196–203</ref> | ||
Physical exercise and weight loss are among the most effective methods for preventing the onset of diabetes, and a large randomised study concluded that lifestyle intervention was more effective that metformin. However lifestyle modification is often found to be difficult to sustain by obese patients. <ref>Jermendy G (2005) Can type 2 diabetes mellitus be considered preventable? ''Diabetes Res Clin Pract'' 68:S73-S81</ref><ref>Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group(2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin ''New Eng J Med'' 346:393–403</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}} | |||
Latest revision as of 23:57, 24 February 2012
The term diabesity was coined by Ethan Sims in 1973, to describe the close relationship between diabetes mellitus type 2 (T2DM) and obesity. Their findings suggested that by overfeeding young men with no previous family history of diabetes, the initial signs of diabetes were induced. This excess consumption led to increases in insulin production, plasma glucose, triglycerides and eventually impaired glucose tolerance; all signs predisposing one to T2DM and obesity.[1][2]
T2DM is a disorder where cells fail to take up glucose from the blood. Glucose is the fuel for respiration which produces energy for our cells to function properly. Diabetes mellitus is the foremost cause of kidney failure (diabetic nephropathy), blindness (diabetic retinopathy), and amputation in adults (diabetic neuropathy). People with this disease lack the ability to utilize the hormone insulin. Insulin is produced by the pancreas after a meal in response to increased concentrations of glucose in the blood. The insulin signal attaches to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, causing them to switch on their glucose-transporting machinery. People with T2DM have normal or even elevated levels of insulin in their blood, and normal insulin receptors, but the binding of insulin to its receptors does not turn on the glucose-transporting machinery.
Proteins called IRS proteins (insulin receptor substrate) bind with the insulin receptor inside the cell. The receptor responds by adding a phosphate group onto the IRS molecules. This rouses the IRS molecules into action, and they activate a variety of processes, including an enzyme that turns on the glucose transporter machinery. When the IRS genes are deliberately inactivated in transgenic “knockout” mice, T2DM results. However, there are no IRS gene mutations in inherited T2DM; the IRS genes are normal. This suggests that in T2DM something is impeding with the action of the IRS proteins. An estimated 80% of those who develop T2DM are obese.
Visceral fat accumulation and type 2 diabetes
Excess visceral adipose tissue increases the risk for T2DM. Excess fat within the abdomen, known as visceral adiposity, creates a serious health risk of metabolic complications independent from accumulation of adipose tissue in other regions: visceral adiposity is related with an increase in insulin resistance, whereas abdominal subcutaneous fat is not. (Insulin resistance describes the impaired ability of insulin to suppress hepatic glucose output and promote glucose disposal in the periphery.) As T2DM gets worse, patients have higher blood sugar levels (hyperglycaemia) because the pancreatic beta cells are unable to make enough insulin. In insulin resistance, normal amounts of insulin are unable to produce a normal response from adipose, muscle and liver cells. Cnop et al. showed that visceral fat is the best predictor of insulin sensitivity whilst subcutaneous fat establishes leptin levels [3]
In 1994, a new hormone was found, called leptin, that provides feedback to the brain of the level of fat in the body. Leptin suppresses appetite, but most obese people have very high leptin levels, as leptin is secreted by adipose cells. Therefore, obesity is not generally caused by a deficiency in leptin; instead there seems to be a defect in leptin signalling. Adipocytes also produce an array of other peptides including adiponectin, resistin and TNF alpha. They act on peripheral tissues and thereby affect insulin sensitivity and the processes involved in substrate metabolism.
The lipoprotein profile related to obesity and insulin resistance is mostly due to intra-abdominal fat [4]. There are better measures of obesity (particularly visceral obesity) that can predict diabetes. These include waist circumference, the waist-to-hip ratio and insulin resistance.
Fat cells show elevated hydrolysis of stored triglycerides and increased free fatty acids into the blood. Insulin resistance reduces the antilipolytic effect of insulin, which leads to reduced glucose uptake and increased release of free fatty acids and glycerol. [5] Excess free fatty acids are taken by the portal vein to the liver. The liver is then overwhelmed by the free fatty acids and starts up typical IR metabolic processes. The liver responds by increasing glyconeogenesis (production of glygogen), increasing triglyceride, apolipoprotein B and very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) production. This in turn increases the production of low density lipoproteins and the reduction of high density lipoproteins (HDLs). This lipid profile is known as atherogenic dyslipidaemia as it eventually leads to atherosclerosis. Intramyocellular lipids (IMCL) are more closely associated to insulin resistance than to body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, or total body fat. High free fatty acid and VLDL levels are a key cause of fat accumulation in muscle cells and IMCL increases have been seen in patients with insulin resistance. Surgical removal of visceral fat had a positive effect on the hepatic and peripheral insulin sensitivity, and on leptin and TNFα levels. [6]
Long term exposure of pancreatic beta cells to increased fatty acid levels causes damaging effects such as increased insulin secretion at low glucose concentrations, decreased proinsulin production, exhaustion of insulin reserves and reduced response to concentrations of glucose stimulus. Solomon and Mayer were first to associate glucocorticoids as a required factor in genetic obesity, observing that obesity was avoided after bilateral adrenalectomy and completely restored by cortisol replacement. [4]
11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1
11β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11β-HSD-1) is an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of inactive cortisone to active cortisol, a potent glucocorticoid. It is found throughout the body and is a highly regulated enzyme that increases the ligand accessibility for glucocorticoid receptors.
Excessive glucocorticoid exposure causes central obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia and insulin resistance, as seen in Cushing’s syndrome. Transgenic mice over-expressing 11β-HSD-1 in white adipose tissue have these features as well, while 11β-HSD-1 deficient mice are protected from these metabolic abnormalities. In human idiopathic obesity, circulating cortisol levels are not elevated, but 11HSD1 mRNA and activity is increased in subcutaneous adipose tissue. The impact of increased adipose 11β-HSD-1 on pathways leading to metabolic complications remains unclear in humans. Pharmacological inhibition of 11HSD1 has been achieved in liver with carbenoxolone, which enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity.] [5]
Visceral obesity may be secondary to enhanced local activation of cortisol via increased levels and activity of 11β-HSD-1 in adipose tissue that result in abnormally high levels of cortisol in adipose tissue. Obesity is distinct from Cushing's syndrome in that the source of the elevated glucocorticoids is adipose tissue rather than the adrenal cortex.
A summary of how we think visceral obesity causes insulin resistance and T2DM is shown in Figure 1.
Causes of type 2 diabetes in obese patients
Endoplasmic reticulum stress
Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) is a molecular-level link connecting obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Mice lacking X-box-binding protein-1 (XBP-1), a transcription factor used to modulate the body’s response to ER stress, as well as mice that had induced ER stress via pharmacological means, showed the development of insulin resistance. ER stress or down-regulation of XBP-1 causes the suppression of insulin receptor signaling in the body’s cells via activation of Jun kinases (JNKs). In mice, this insulin receptor suppression leads to increased insulin resistance and the development of type 2 diabetes. It is thought that increased activity of JNKs causes the phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrates (IRSs) within important tissues such as liver, muscle and fat. As well as insulin resistance, JNK activity can result in the inhibition of insulin production in pancreatic β-cells. In mice which lack JNKs such as JNK1, obesity-induced obesity prevalence is reduced, and in general they also have reduced adiposity.
In summary, there is a key process which controls the detection of obesity-induced ER stress, causing an inhibition of insulin action that leads to insulin resistance and T2DM. It is thought that ER stress is a precursor to cell inflammation as a result of obesity. This then leads to complete breakdown of glucose homeostasis.
Dysfunction of the pancreatic β-cells
If insufficient insulin is secreted by the pancreatic β-cells, then adequate glucose uptake cannot occur. In mice fed a high fat diet, subsequent T2DM is at least partly due to reduced insulin secretion. Analysis of insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets of these mice found dysfunction in the production and/or secretion of insulin. An increase in glucagon-positive cells within the islets was also discovered in these mice. Similar changes are present in human cases of T2DM.
It is also possible that there is increased pancreatic β-cell apoptosis, induced by increasing obesity, reducing the level of insulin secretion. This reduced insulin secretion cannot then cope with the insulin resistance caused by obesity. Dysfunction and death of the pancreatic β-cells may be a result of cell inflammation due to hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia and increased levels of adipokines.
Resistin
The discovery of resistin came about through the development of a new class of anti-diabetic drugs called thiazolidinediones (TZDs). These act by increasing a target tissue’s sensitivity to insulin. They are ligands for a nuclear receptor called peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-ϒ (PPARϒ) which is abundant in adipocytes. Tests showed a high correlation between TZD/PPARϒ binding and glucose lowering in vivo. However, the target genes of TZD-bound PPARϒ are unknown. To try and discover whether IR might be controlled by a TZD-controlled, adipocyte-originating substance, a genetic screen was carried out for genes induced by adipocyte formation but downregulated when treated with TZDs. This produced evidence of a TZD-regulated protein, called resistin.[6][7] Resistin expression increases when adipocytes differentiate, and decreases with administration of TZD drugs such as rosiglitazone, pioglitazone and troglitazon. In mice, resistin is expressed almost exclusively in white adipose tissue, with highest expression in female gonadal fat. An amino acid sequence expressed in humans with a large similarity to resistin was also found. In mice, serum levels of resistin decrease with fasting and are restored with re-feeding. In mice fed on a 45% fat content diet for 8 weeks, the levels of resistin in serum are greatly elevated, initially increasing within four weeks of the diet being adopted, the same point as when the mice become obese and insulin resistant. Higher than normal resistin levels can also be detected in leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mice and in leptin receptor deficient (db/db) mice, both of which are genetically predisposed to obesity and T2DM.
Intraperitoneal administration of resistin to mice results in impaired insulin sensitivity, while insulin levels remain normal. Both in vitro and in vivo studies show that neutralization of resistin causes enhanced insulin action and glucose uptake. In obese, diabetic mice, resistin neutralization causes reduced levels of hyperglycemia by increasing insulin sensitivity.
Resistin is believed to modulate at least one step in the insulin signaling pathway. At present it is unclear whether levels of resistin have a major effect on insulin activity in humans. In humans, resistin is thought to be secreted by macrophages not adipocytes. Despite this, there is still a strong correlation in humans between high levels of resistin, obesity, and T2DM.
The immunology of obesity
T2DM has long been considered as primarily a metabolic disease, but recent studies have challenged this, and implicated an unlikely candidate system in the promotion of disease onset - the immune system. Mild inflammation of fat tissue in obese patients reportedly acts through immune-cell processes to impair insulin signalling in adipocytes.
Adipocytes have a dual role as both a fat storage depot and an endocrine organ. Obesity can induce a state of chronic, low-grade inflammation (Feuerer et al., 2009), and, unlike other forms of inflammation, fat inflammation appears to escape immune regulation. Depending on its state, adipose tissue will activate various phenotypes of T-cells (‘non-obese’ CD4 or ‘obese’ CD8), which in turn regulate (or fail to regulate) the infiltration of macrophages. This permeation of macrophages and their production of proinflammatory cytokines results in chronic inflammation. This impairs insulin signalling in the adipocytes, which leads to lipolysis and the release of non-esterified fatty acids (NEFAs) into the circulation. These fatty acids induce insulin resistance in the liver and skeletal muscles, and impair B-cell function.
Several groups have recently targeted the different T-cell populations and both reversed and prevented the onset of obesity-induced T2DM. Feuerer et al. (2009) isolated a specific phenotype of T-cell, CD4, which is enriched in the adipose tissue of lean mice but reduced in that of obese, insulin-resistant mice. Through loss-of-function experiments, it was shown that CD4 cells are functionally active and their absence results in inflammatory cytokine production and reduced glucose uptake. Importantly, CD4 T-cells were only shown to behave in this manner in visceral fat stores, which, unlike subcutaneous stores, are associated with the development of T2DM. A complementary study, performed by Winer et al. (2009), demonstrated that CD4 T-cell transfer reverses weight gain and IR in null mutants. Nevertheless, because the mice lost weight after the CD4 T-cell transfer, it makes conclusive interpretation of the data difficult. This data led the authors to conclude that obesity-associated metabolic abnormalities are under the pathophysiological control of CD4 T-cells, which inversely control the infiltration of problematic macrophages .
A separate study by Nishimura et al. (2009) revealed that a different type of T-cell, CD8, are increased in obese mice and precede chronic inflammation observed in adipose tissue. Similarly, the adoptive transfer of CD8 T-cells resulted in adipose inflammation. Together this evidence led the authors to propose that obese adipose tissue activates CD8+ T-cells, which drive the recruitment of macrophages and their differentiation into an inflammatory rather than anti-inflammatory phenotype.
Another aspect of the immune system that has been implicated in T2DM onset is mast cell function. Mast cells respond to allergic and parasitic challenge by releasing inflammatory mediators, playing an integral protective role. An excess of mast cells can lead to mast cell instability and inflammation. Shi et al. observed that the white adipose tissue of obese mice possesses a significantly more mast cells than lean equivalents. This led them to ask whether the manipulation of mast cell number, through genetic reduction and pharmacological equalization, can reduce the onset of obesity and T2DM. In the first set of experiments, genetically mast cell-deficient mice and control mice were fed on a Western-diet for three months. Loss of mast cell function appeared to have the effect of lowering serum leptin, increasing glucose tolerance and increasing insulin sensitivity. In the second strand of experimentation, mice were treated with mast cell-stabilizing medication to ask whether diet-induced obesity and diabetes could be inhibited. After two months on a Western-diet, mice were either switched to a healthy diet, supplied with mast-cell stabilizing medication, or a combination of both. While the dietary adjustment caused minor improvements, the medication stimulated significant restitution and the combination of both allowed a near full recovery in comparison to control group who continued on a Western-diet.
Both of these drugs are already used to treat other medical conditions and are therefore both safe and available, however the question that remains to be answered is do Zaditor and cromolyn offer similar protection against diabetes in humans? A study into T-cell concentration in human abdominal fat tissue by Winer et al. (2009) has revealed an abundance of protective CD4 T-cells in normal weight individuals when compared to that of obese, diabetic patients, as well a reflection of inverse number of macrophages.
Treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes
Lifestyle changes provide the basis of treatment in all obese patients, but when these fail to reduce the weight in obese patients, anti-obesity drugs are used. There are few well-tolerated drugs which have long term efficacy in maintaining weight loss. Current available medications include sibutramine and orlistat.
Sibutramine reduces body weight and appetite and increases satiety. Prospective randomised controlled trials have shown it to be effective, with one trial finding that patients on sibutramine lost 4.3kg or 4.6% more weight than those taking the placebo. The most common adverse effects are dry mouth, constipation and insomnia. Orlistat acts by inhibiting pancreatic and gastrointestinal lipases, preventing absorption of about 30% of dietary fat. Randomized controlled trials have shown that patients taking this have lost 2.7kg or 2.9% more weight than controls. As orlistat reduces LDL and cholesterol levels independently of reductions in body weight, it also retards the progression to a diabetic state and aids glycemic control in patients with diabetes. Side effects include fecal urgency and abdominal cramping.[8]
Patients with impaired glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose and obesity are all at a high risk of developing T2DM, so combination therapy for glycaemic control and weight management is often required. Several strategies are used, including the promotion of weight loss through lifestyle modifications and anti-obesity drugs, improving glycemic control through the reduction of insulin resistance and the treatment of common associated risk factors such as hypertension and dyslipidaemia to improve cardiovascular prognosis [9]
When treating T2DM, main aims are to return metabolic disturbances to normal, achieve good glycemic control and assist with weight management. Dietary management is particularly important, to reduce the cardiovascular risks associated with central obesity. Patients with T2DM need to restrict carbohydrate and total calorific intake and eat foods of low glycemic index, to reduce the post prandial rise in blood glucose. When dietary management is not successful, pharmacological intervention is added, including anti-diabetic drugs to prevent hyperglycaemia, ACE inhibitors to treat hypertension and statins or fibrates to treat hyperlipidaemia.[10]
Metformin is recommended as first-line treatment in T2DM patients. When this fails, other agents are added to provide combination therapy. Most T2DM patients require combination therapy, because monotherapy with metformin usually only maintains good metabolic control in the short term. Treatments which can be added include sulphonylureas, acarbose, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues, thiazolidinediones, glinides, or insulin. [11]
Physical exercise and weight loss are among the most effective methods for preventing the onset of diabetes, and a large randomised study concluded that lifestyle intervention was more effective that metformin. However lifestyle modification is often found to be difficult to sustain by obese patients. [12][13]
References
- ↑ Sims EAH et al. (1973) Endocrine and metabolic effects of experimental obesity in man, Recent Prog Horm Res 29:457–96
- ↑ Haslam DW, James WP (2005) ObesityLancet 366:1197–209
- ↑ Cnopet al. (2002) The concurrent accumalation of intra-adominal and subcutaneous fat explains the association between insulin resistance and plasma leptin concentrations. Diabetes 51:1005-15
- ↑ Solomon J, Mayer J (1973) The effect of adrenalectomy on the development of the obese- hyperglycemic syndrome in ob-ob mice Endocrinology 93:510–2
- ↑ London E, Castonguay T (2009) Diet and the role of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase-1 on obesity Nutr Biochem 20:485-93
- ↑ Steppan CM et al.(2001) The hormone resistin links obesity to diabetes. Nature 409:307-312
- ↑ Qatanani M et al. (2009) Macrophage-derived human resistin exacerbates adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice. J Clin Invest 119:531-9
- ↑ Chaputy JP, Tremblay A (2006) Current and novel approaches to the drug therapy of obesity. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62
- ↑ ScheenAJ (2000) Treatment of diabetes in patients with severe obesity. Biomed Pharmacother 54:74-79
- ↑ Lean MEJ et al. (1990) Obesity, weight loss and prognosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Med 7:228-233
- ↑ Monami M et al. (2008) Comparison of different drugs as add-on treatments to metformin in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pr 79:196–203
- ↑ Jermendy G (2005) Can type 2 diabetes mellitus be considered preventable? Diabetes Res Clin Pract 68:S73-S81
- ↑ Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group(2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin New Eng J Med 346:393–403