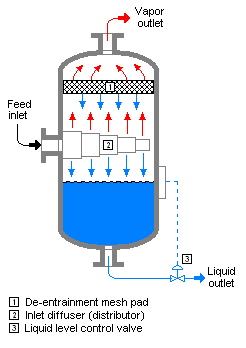
Flash evaporation
Flash evaporation is the partial or total vaporization that occurs when a saturated liquid stream undergoes a reduction in pressure by passing through a throttling valve or other throttling device. This process is one of the simplest unit operations. If the throttling valve or device is located at the entry into a pressure vessel so that the flash evaporation occurs within the vessel, then the vessel is often referred to as a flash drum.
If the saturated liquid is a single-component liquid (for example, liquid propane or liquid ammonia), a part of the liquid immediately "flashes" into vapor (i.e., evaporates). Both the vapor and the residual liquid are cooled to the saturation temperature of the liquid at the reduced pressure. This is often referred to as "auto-refrigeration" and is the basis of most conventional vapor-compression refrigeration systems.
If the saturated liquid is a multi-component liquid (for example, a mixture of propane, isobutane and normal butane), a part of the liquid will also immediately flash into a vapor and the flashed vapor will be richer in the more volatile components than is the remaining liquid.
Flash evaporation of a single-component liquid
The flash evaporation of a single-component liquid is an isenthalpic (i.e., constant enthalpy) process and is often referred to as an adiabatic flash, a flash distillation or a throttling expansion. The following equation, derived from a simple heat balance around the throttling valve or device, is used to predict how much of a single-component liquid is vaporized.
- X = 100 ( HuL – HdL ) ÷ ( HdV – HdL )
where: X = weight percent vaporized HuL = upstream liquid enthalpy at upstream temperature and pressure, J/kg HdV
= flashed vapor enthalpy at downstream pressure and corresponding saturation
temperature, J/kgHdL
= residual liquid enthalpy at downstream pressure and corresponding saturation
temperature, J/kg
If the enthalpy data required for the above equation is unavailable, then the following equation may be used.
- X = 100 · cp ( Tu – Td ) ÷ Hv
where: X = weight percent vaporized cp = liquid specific heat at upstream temperature and pressure, J/(kg · °C) Tu = upstream liquid temperature, °C Td = liquid saturation temperature corresponding to the downstream pressure, °C Hv
= liquid heat of vaporization at downstream pressure and corresponding
saturation temperature, J/kg
( Note: The words "upstream" and "downstream" refer to before and after the liquid passes through the throttling valve or device.)
This type of flash evaporation is used in the desalination of brackish water or ocean water by Multi-Stage Flash Distillation. The water is heated and then routed into a reduced-pressure flash evaporation "stage" where some of the water flashes into steam. This steam is subsequently condensed into salt-free water. The residual salty liquid from that first stage is introduced into a second flash evaporation stage at a pressure lower than the first stage pressure. More water is flashed into steam which is also subsequently condensed into more salt-free water. This sequential use of multiple flash evaporation stages is continued until the design objectives of the system are met. A large part of the world's installed desalination capacity uses multi-stage flash distillation. Typically such plants have 24 or more sequential stages of flash evaporation.
Equilibrium flash of a multi-component liquid
The equilibrium flash of a multi-component liquid is also an enthalpic process and may be visualized as a simple distillation process using a single equilibrium stage. It is very different and more complex than the flash evaporation of single-component liquid. For a multi-component liquid, calculating the amounts of flashed vapor and residual liquid in equilibrium with each other at a given temperature and pressure requires a trial-and-error iterative solution. Such a calculation is commonly referred to as an equilibrium flash calculation. It involves solving the following Rachford-Rice equation:[1][2][3][4][5]
- Overall material balance equation :
- Material balance equation for any component :
- Equation defining the vapor-liquid equilibrium constant :
where: = moles of total feed liquid = moles of flashed vapor = fraction of feed that is vaporized = = moles of residual liquid = vapor-liquid equilibrium constant = mole fraction of component in the feed liquid = mole fraction of component in the flashed vapor = mole fraction of component in the residual liquid
The mole fraction of a component in a multi-component mixture is the relative proportion of moles belonging to the component to the total moles of liquid or vapor. It is one way of measuring concentration. For each component , the mole fraction is the number of moles divided by the total number of moles in the mixture :
Newton's method (also known as the Newton-Raphson method) is an efficient iterative algorithm for solving the above Rachford-Rice equation. Alternatively, an Excel spreadsheet and the Excel Solver function can be used.
The equilibrium flash of multi-component liquids is very widely utilized in petroleum refineries, petrochemical and chemical plants and natural gas processing plants.
Spray drying
Spray drying is the rapid drying of a slurry of very small solids suspended in a liquid. The slurry is first atomized into very small liquid droplets which are then sprayed into a stream of hot dry air. The liquid rapidly evaporates leaving behind dry powder or dry solid granules. The dry powder or solid granules are recovered from the exhaust air by using cyclones, bag filters or electrostatic precipitators.
A brief explanation of spray drying has been included here because some readers may consider spray drying to be a form of flash evaporation. However, although it is a form of liquid evaporation, it is quite different from flash evaporation.
References
- ↑ McNeese University lecture (scroll down to Rachford-Rice Equation)
- ↑ Polynomial Objective Functions for Flash Calculations, John H. Warrent and Michael A. Adewumi, Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, Vol.32, pages 1528-1530
- ↑ "Complementarity Formulation for the Representation of Algebraic Systems Containing Conditional Equations", V. Rico-Ramírez and A. W. Westerberg Institute for Complex Engineered Systems, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Technical Report ICES 06-243-98
- ↑ Automatic Plotting of Multiple Phase Boundaries and Flash Calculations, Infochem Computer Services, United Kingdom
- ↑ Flash Calculations using the Soave-Redlich-Kwong equation of state (view full-size image)