Appetite
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
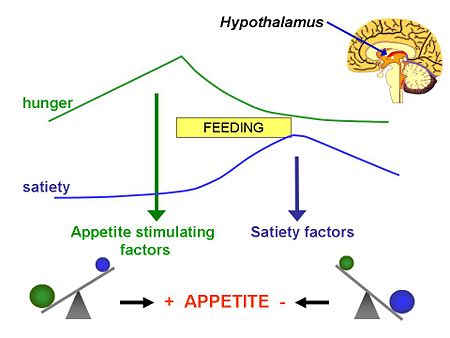
Appetite is the desire to eat food, and is experienced as hunger. Appetite in mammals is controlled by neural circuits in the hypothalamus which are influenced by hormonal and neural signals from the digestive tract, including the appetite-stimulating hormone ghrelin. The drive to eat is balanced by satiety signals from the digestive tract, and by feedback from adipose tissue - including by the hormone leptin. Appetite is also subject to sensory stimuli - the sight and smell of food, and is modulated by internal (circadian) rhythms; we are hungry at meal times. Appetite is also influenced by stress, by glucose concentrations in the blood, and by physiological state - appetite is stimulated after exercise, and is enhanced in pregnancy.
- Leptin [r]: Hormone secreted by adipocytes that regulates appetite. [e]
- Ghrelin [r]: A hormone produced by P/D1 cells lining the fundus of the human stomach that stimulate appetite. [e]