Prednisone: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett (fixed link) |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Replacing medical templates with CZMed) |
||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
{{CZMed}} | |||
Revision as of 00:24, 3 June 2009
Prednisone, also called dehydrocortisone, prednisona, or prednisonum (IUPAC name (8S,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-hydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-6,7,8,9,12,14,15,16-octahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,11-dione) is a synthetic anti-inflammatory glucocorticoid steroid designed as a mimic of the naturally occuring steroid cortisone. It is used to treat many inflammatory conditions. It is a prodrug that only becomes active after conversion to prednisolone, a glucocorticoid agonist, in the liver. Prednisolone binds to cytoplasmic receptors to control biosynthesis of prostaglandins and leukotrienes.
indications
Prednisone is use to treat allergies, carditis, systemic dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, psoriasis, acute adrenocortical deficiency, Addison's disease, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, hypercalcemia associated with neoplasms, thyroiditis, ulceratice colitis, Crohn's disease, anemias, erythroblastopenia,thrombocytopenia, bursitis, epicondylitis, tenosynovitis, lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin's or non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, primary brain tumors, nephrotic syndrome, tuberculous meningitis, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, cerebral edema, chorioretinitis, diffuse posterior choroiditis, allergic conjunctivitis, Herpes zoster ophthalmicus, iridocyclitis, iritis, keratitis, optoc neuritis, sympathetic ophthalmia, corneal marginal allergic ulcers, symptomatic sarcoidosis, Loeffler's syndrome, berylliosis, andpulmonary tuberculosis. This is not a complete list of conditions for which prednisone is used.
comparison to cortisone and prednisolone
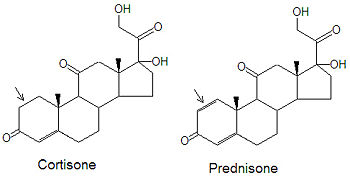
Prednisone's structure is based on that of the naturally-occuring corticosteroid cortisone. The only difference between them is the presence of a carbon-carbon double bond in the A ring of prednisone that is not present in cortisone (note arrows in the figure). The active form of the drug, prednisolone, as the name implies ("ol"), has a hydroxyl group on ring C in place of the carbonyl group present in prednisone.
Brand names
- Delta-cortelan
- Delta-cortisone
- Delta-cortone
- Delta-dome
- Adasone
- Ancortone
- Apo-prednisone
- Betapar
- Bicortone
- Cartancyl
- Colisone
- Cortan
- Cortancyl
- Cortidelt
- Cotone
- Dacorten
- Dacortin
- Decortancyl
- Decortin
- Decortisyl
- Dekortin
- Delcortin
- Dellacort
- Dellacort A
- Delta Cortelan
- Delta E
- Deltacortene
- Deltacortisone
- Deltacortone
- Deltasone
- Deltison
- Deltisona
- Deltisone
- Deltra
- Di-Adreson
- Diadreson
- Econosone
- Encorton
- Encortone
- Enkorton
- Fernisone
- Fiasone
- Hostacortin
- In-Sone
- Incocortyl
- Juvason
- Lisacort
- Me-Korti
- Metacortandracin
- Meticorten
- Nisona
- Nizon
- Novoprednisone
- Nurison
- Orasone
- Origen Prednisone
- Panafcort
- Panasol
- Paracort
- Parmenison
- Pehacort
- Precort
- Predeltin
- Prednicen-M
- Prednicorm
- Prednicort
- Prednicot
- Prednidib
- Prednilonga
- Prednison
- Prednisone Intensol
- Prednitone
- Prednizon
- Prednovister
- Presone
- Pronison
- Rectodelt
- Retrocortine
- Servisone
- Sone
- Sterapred
- Supercortil
- Ultracorten
- Ultracortene
- Winpred
- Wojtab
- Zenadrid
External Links
The most up-to-date information about Prednisone and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Prednisone - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Prednisone - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Prednisone - Detailed information from DrugBank.