Condensation (phase transition): Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok m (→Applications: Typo fixed) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{ | {{Image|Phase Changes.png|right|303px|The four major phases of matter. }} | ||
'''Condensation''' is a process in which the [[vapor]] phase of a substance is changed into the [[liquid]] phase by removing and transferring [[heat]] from the vapor to a cooling medium.<ref>{{cite book|author=Eduardo Cao|title=Heat Transfer in Process Engineering|edition=1st Edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill|year=2009|id=ISBN 0-07-162408-2}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=G.S. Sawhney|title=Heat and Mass Transfer|edition=|publisher=I.K. International Publishing House|year=2008|id=ISBN 81-906942-7-8}}</ref> For the process to take place, the vapor must be [[Boiling point#Saturated temperature and pressure|saturated]] and the [[heat of vaporization]] must be removed from the vapor.<ref>For a saturated liquid to boil, the heat of vaporization must be absorbed into the liquid. For a saturated vapor to condense, the latent heat of vaporization must be released from the vapor. When released by a condensing vapor, the heat of vaporization is sometimes referred to as the ''heat of condensation''.</ref> | '''Condensation''' is a process in which the [[vapor]] phase of a substance is changed into the [[liquid]] phase by removing and transferring [[heat]] from the vapor to a cooling medium.<ref>{{cite book|author=Eduardo Cao|title=Heat Transfer in Process Engineering|edition=1st Edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill|year=2009|id=ISBN 0-07-162408-2}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=G.S. Sawhney|title=Heat and Mass Transfer|edition=|publisher=I.K. International Publishing House|year=2008|id=ISBN 81-906942-7-8}}</ref> For the process to take place, the vapor must be [[Boiling point#Saturated temperature and pressure|saturated]] and the [[heat of vaporization]] must be removed from the vapor.<ref>For a saturated liquid to boil, the heat of vaporization must be absorbed into the liquid. For a saturated vapor to condense, the latent heat of vaporization must be released from the vapor. When released by a condensing vapor, the heat of vaporization is sometimes referred to as the ''heat of condensation''.</ref> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
* Condensation on direct contact of the saturated vapor with the cooling surface within a [[heat exchanger]] and that surface must be at a [[temperature]] cooler than of the saturated vapor. This is the most common type of condensation used in industry and there two modes in which it may occur:<ref name=Kandlikar>{{cite book|author=Satish G. Kandlikar. Masahiro Shoji and V.K. Dhir (Editors)| title=Handbook of Phase Change: Boiling and Condensation|edition=1st Edition|publisher=CRC Press|year=1999| id=ISBN 1-56032-634-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Donald R. Pitts and Leighton E. Sissom|title=Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Heat Transfer|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill|year=1998|id=ISBN 0-07-050207-2}}</ref> | * Condensation on direct contact of the saturated vapor with the cooling surface within a [[heat exchanger]] and that surface must be at a [[temperature]] cooler than of the saturated vapor. This is the most common type of condensation used in industry and there two modes in which it may occur:<ref name=Kandlikar>{{cite book|author=Satish G. Kandlikar. Masahiro Shoji and V.K. Dhir (Editors)| title=Handbook of Phase Change: Boiling and Condensation|edition=1st Edition|publisher=CRC Press|year=1999| id=ISBN 1-56032-634-4}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=Donald R. Pitts and Leighton E. Sissom|title=Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Heat Transfer|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=McGraw-Hill|year=1998|id=ISBN 0-07-050207-2}}</ref> | ||
** Filmwise condensation is characterized by a thin film of liquid forming over the entire cooling surface. This occurs when a clean, wettable surface, such as most metals, is in contact with the saturated vapor. The flow of the liquid film may be [[laminar]] (if the flow velocity along the cooling surface of the heat exchanger is relatively slow) and the [[heat transfer]] will occur by [[conduction (heat)]]. If the flow velocity is relatively fast, the flow of the liquid film may be [[turbulent]] and the heat transfer may occur by [[convection (heat)]] as well as conduction. | ** Filmwise condensation is characterized by a thin film of liquid forming over the entire cooling surface. This occurs when a clean, wettable surface, such as most metals, is in contact with the saturated vapor. The flow of the liquid film may be [[laminar]] (if the flow velocity along the cooling surface of the heat exchanger is relatively slow) and the [[heat transfer]] will occur by [[conduction (heat)|conduction]]. If the flow velocity is relatively fast, the flow of the liquid film may be [[turbulent]] and the heat transfer may occur by [[convection (heat)|convection]] as well as conduction. | ||
** Dropwise condensation occurs when the vapor is in contact with a non-wettable surface, such as [[Teflon]]. In this case, drops of condensed liquid (referred to as ''condensate'') form and grow in size until carried away by [[gravity]] or by the flowing motion of the vapor. In dropwise condensation, a portion of the cooling surface remains exposed to the vapor, and therefore results in much better heat transfer than does filmwise condensation. However, dropwise condensation is difficult to sustain reliably and, for that reason, most industrial heat exchangers are typically designed to operate in filmwise condensation mode. | ** Dropwise condensation occurs when the vapor is in contact with a non-wettable surface, such as [[Teflon]]. In this case, drops of condensed liquid (referred to as ''condensate'') form and grow in size until carried away by [[gravity]] or by the flowing motion of the vapor. In dropwise condensation, a portion of the cooling surface remains exposed to the vapor, and therefore results in much better heat transfer than does filmwise condensation. However, dropwise condensation is difficult to sustain reliably and, for that reason, most industrial heat exchangers are typically designed to operate in filmwise condensation mode. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 1 August 2024
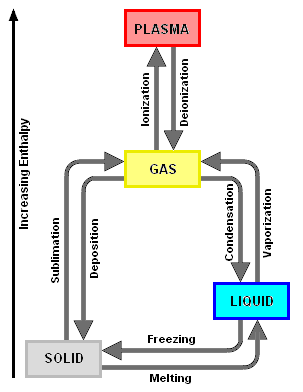
Condensation is a process in which the vapor phase of a substance is changed into the liquid phase by removing and transferring heat from the vapor to a cooling medium.[1][2] For the process to take place, the vapor must be saturated and the heat of vaporization must be removed from the vapor.[3]
The condensation of vapors, like the boiling of liquids, plays a very significant role in a great many commercial and industrial processes.
Types of condensation
There are several types of condensation:
- Condensation on direct contact of the saturated vapor with the cooling surface within a heat exchanger and that surface must be at a temperature cooler than of the saturated vapor. This is the most common type of condensation used in industry and there two modes in which it may occur:[4][5]
- Filmwise condensation is characterized by a thin film of liquid forming over the entire cooling surface. This occurs when a clean, wettable surface, such as most metals, is in contact with the saturated vapor. The flow of the liquid film may be laminar (if the flow velocity along the cooling surface of the heat exchanger is relatively slow) and the heat transfer will occur by conduction. If the flow velocity is relatively fast, the flow of the liquid film may be turbulent and the heat transfer may occur by convection as well as conduction.
- Dropwise condensation occurs when the vapor is in contact with a non-wettable surface, such as Teflon. In this case, drops of condensed liquid (referred to as condensate) form and grow in size until carried away by gravity or by the flowing motion of the vapor. In dropwise condensation, a portion of the cooling surface remains exposed to the vapor, and therefore results in much better heat transfer than does filmwise condensation. However, dropwise condensation is difficult to sustain reliably and, for that reason, most industrial heat exchangers are typically designed to operate in filmwise condensation mode.
- Condensation on direct contact of the saturated vapor with a liquid at a temperature cooler than that of the saturated vapor.[4]
Applications
Distillation: Condensation is an important component of all distillation processes in large scale industrial distillation systems such as those in chemical plants, petroleum refineries, petrochemical plants, natural gas processing and alcohol distilleries. It is an equally important component of the small scale distillation equipment used in chemical laboratories.
Refrigeration: The condensation process is also an important integral part of almost all residential, commercial and industrial refrigeration systems.
Electric power plants: Most thermal power plants have large condensers, known as surface condensers, to condense the exhaust steam from their steam turbines.
Sublimation and deposition
Although condensation is sometimes defined so as to include the vapor phase of a substance being changed into the solid phase, that process is more correctly referred to as deposition . The opposite process, namely changing from a solid phase into a vapor phase, is referred to as sublimation. Neither deposition or sublimation are discussed in this article.
References
- ↑ Eduardo Cao (2009). Heat Transfer in Process Engineering, 1st Edition. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-162408-2.
- ↑ G.S. Sawhney (2008). Heat and Mass Transfer. I.K. International Publishing House. ISBN 81-906942-7-8.
- ↑ For a saturated liquid to boil, the heat of vaporization must be absorbed into the liquid. For a saturated vapor to condense, the latent heat of vaporization must be released from the vapor. When released by a condensing vapor, the heat of vaporization is sometimes referred to as the heat of condensation.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Satish G. Kandlikar. Masahiro Shoji and V.K. Dhir (Editors) (1999). Handbook of Phase Change: Boiling and Condensation, 1st Edition. CRC Press. ISBN 1-56032-634-4.
- ↑ Donald R. Pitts and Leighton E. Sissom (1998). Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Heat Transfer, 2nd Edition. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-050207-2.
- ↑ Robert G. Fleagle and Joost A. Businger (1980). An Introduction to Atmospheric Physics, 2nd Edition. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-260355-9.