Foscarnet
|
| |||||||
| foscarnet | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | treatment of CMV retinitis, herpes and HIV. | ||||||
| Properties: | antiviral agent | ||||||
| Hazards: | renal toxicity, seizures | ||||||
| |||||||
Foscarnet is an antiviral drug used to treat retinitis due to cytomegalovirus (CMV) and acyclovir-resistant herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 & HSV-2) infections in patients with compromised immune systems, often associated with HIV/AIDS. Foscarnet is injected intravaneously, as the trisodium salt, due to poor absorption.
Mechanism of action
Foscarnet binds to pyrophosphate binding sites of DNA polymerases and thus inhibits the production of viral DNA by blocking the energy source (pyrophosphate) from reaching the viral polymerases. Cellular DNA polymerases are not effected by the dosages at which foscarnet is taken.
Warnings
Renal toxicity and impairment is a concern when using foscarnet. Associated changes in mineral and electrolyte concentrations may also cause seizures, so hydration must be ensured and serium creatinine levels monitored. Contact dermatitis in the genital area may occur following injections due to the high foscarnet concentrations in urine.
Chemistry
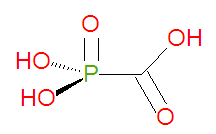
Foscarnet is a carboxylic acid-based organic mimic of the natural inorganic compound pyrophosphate. The chemical name of foscarnet is phosphonoformic acid and it has chemical formula CH3O5P, giving it a molecular mass of 126.0053 g/mol. However, the drug is administered as the hydrated trisodium salt, which has chemical formula Na3CO5P•6 H2O and molecular mass 300.1 g/mol. Being already phosphorylated, foscarnet does not need to be phosphorylated to become active. Because of this, viral strains resistant to acyclovir or ganciclovir, associated with thymidine kinase deficiency, may be treatable with foscarnet. Foscarnet and related compounds, like phosphonoacetic acid (PAA), can be synthesized by reacting chloroformic acid esters with phosphites[1], typical of an Arbuzov reaction.
Synonyms and brand names
Synonyms
- Carboxyphosphonic acid
- Dihydroxyphosphinecarboxylic acid oxide
- Foscarnet sodium
- Forscarnet sodium
- hydroxycarbonyl phosphonic acid
- PFA
- Phosphonocarboxylic acid
- Phosphonoformate
- Phosphonoformic acid
Brand names (company)
- Foscarnet Sodium® (Hospira, Inc)
- Foscavir® (Astrazeneca)
- Triapten® (Riemser)
External links
The most up-to-date information about Foscarnet and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Foscarnet - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Foscarnet - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Foscarnet - Detailed information from DrugBank.
References
- ↑ Noren, Helgstrand, Johansson, Misiorny and Stening (1983). "Synthesis of esters of phosphonoformic acid and their antiherpes activity". J. Med. Chem. 26 (2): 264-270. [e]