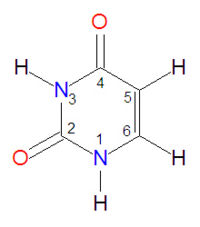
Uracil
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
|
| |||||||
| uracil | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | RNA base | ||||||
| Properties: | |||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Uracil is one of the bases found in RNA. In RNA, the H1 proton is removed and the N1-nitrogen atom is bound the the C1' carbon of ribose. It is analogous in structure to thymidine, which can be thought of as 5-methyl-uracil, and it usually forms base pairs with adenine (A) in RNA. In an adenine-uracil base pair, the O4 oxygen atom of uracil forms a hydrogen bond with one of the amino protons (H61) of adenine. A second hydrogen bond is formed between the uracil H3 proton and the adenine N1 nitrogen atom. Like other nucleotide bases, it is subject to oxidative damage.