Quinolone: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{TOC|left}} | |||
In [[medicine]], '''quinolones''' are [[antibiotic]]s that are "a group of derivatives of naphthyridine carboxylic acid, quinoline carboxylic acid, or nalidixic acid."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> [[Nadixilic acid]]'s effects are localized to the urinary tract, but it was the first quinolone in general use. The subsequent quinolones, with broader spectra, were fluorinated and are often called fluoroquinolones.<ref name=GG>{{citation | In [[medicine]], '''quinolones''' are [[antibiotic]]s that are "a group of derivatives of naphthyridine carboxylic acid, quinoline carboxylic acid, or nalidixic acid."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> [[Nadixilic acid]]'s effects are localized to the urinary tract, but it was the first quinolone in general use. The subsequent quinolones, with broader spectra, were fluorinated and are often called fluoroquinolones.<ref name=GG>{{citation | ||
| title = Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics | | title = Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics | ||
| edition = Ninth | | edition = Ninth | ||
| editor = Hardman JG, Limberd LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW, Alfred Goodman Gilman | | editor = Hardman JG, Limberd LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW, Alfred Goodman Gilman | ||
| publisher = McGraw-Hill | year = 1996}}, pp. 1065-1068 | | publisher = McGraw-Hill | year = 1996}}, pp. 1065-1068</ref> | ||
{{col-begin}} | |||
{{col-break|width=33%}} | |||
* [[Cinoxacin]] | |||
* [[Ciprofloxacin]] | |||
* [[Enoxacin]] | |||
* [[Gatifloxacin]] (respiratory quinolone) | |||
* [[Gemifloxacin]] | |||
* [[Grepafloxacin]] | |||
* [[Levofloxacin]] (respiratory quinolone) | |||
{{col-break|width=33%}} | |||
* [[Lomefloxacin]] | |||
* [[Moxifloxacin]] (respiratory quinolone | |||
* [[Norfloxacin]] | |||
* [[Ofloxacin]] | |||
* [[Pefloxacin]] | |||
* [[Sparfloxacin]] | |||
* [[Trovafloxacin]] | |||
{{col-break|width=33%}} | |||
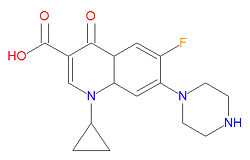
{{Image|Ciprofloxacin structure.jpg|right|250px|Ciprofloxacin, a simple fluoroquinolone}} | |||
{{col-end}} | |||
==Mode of action== | ==Mode of action== | ||
The mechanism of action for quinolones is different from that of [[macrolide]]s, beta-[[lactam]]s, [[aminoglycoside]]s, or [[tetracycline]]s, so organisisms resistant to those classes of antibiotic drugs may be susceptible to quinolones. In particular, the quinolones interfere with [[topoisomerase]] enzymes, including [[topoisomerase II]] (DNA gyrase) and [[topoisomerase IV]], which are vital to bacterial [[DNA]] [[DNA replication|replication]], [[DNA transcription|transcription]], [[DNA repair|repair]] and [[DNA recombination|recombination]]. | |||
==Classes== | ==Classes== | ||
===Non-fluorinated=== | |||
[[Nadixilic acid]] has no action beyond the urinary tract; it is not absorbed systemically. | |||
===Fluoroquinolones=== | |||
The first, unspecialized systemic quinolones included [[ciprofloxacin]], [[ofloxacin]] and [[norfloxacin]]. Of these, [[ciprofloxacin]] and [[levofloxacin]] have enhanced activity against [[Pseudomonas]]. | |||
'Respiratory quinolones' are [[levofloxacin]], [[gatifloxacin]], or [[moxifloxacin]]. However, gatifloxacin can cause dysglycemia.<ref name="pmid16510739">{{cite journal| author=Park-Wyllie LY, Juurlink DN, Kopp A, Shah BR, Stukel TA, Stumpo C et al.| title=Outpatient gatifloxacin therapy and dysglycemia in older adults. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2006 | volume= 354 | issue= 13 | pages= 1352-61 | pmid=16510739 | 'Respiratory quinolones' are [[levofloxacin]], [[gatifloxacin]], or [[moxifloxacin]]. However, gatifloxacin can cause dysglycemia.<ref name="pmid16510739">{{cite journal| author=Park-Wyllie LY, Juurlink DN, Kopp A, Shah BR, Stukel TA, Stumpo C et al.| title=Outpatient gatifloxacin therapy and dysglycemia in older adults. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2006 | volume= 354 | issue= 13 | pages= 1352-61 | pmid=16510739 | ||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16510739 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa055191 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> | | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16510739 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa055191 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> | ||
[[Enrofloxacin]] is marketed for veterinary use as Baytril. | |||
==Interactions== | |||
The group may compete with other drugs that are normally metabolized by the CYP P-450-1A2 pathway, thus increasing their blood levels. These include anticoagulants and theophylline. | |||
They can also decrease the blood levels, by less well-defined pathways, of anticonvulsants. | |||
==Side effects== | |||
Because the use of fluoroquinolones may lead to [[tendinitis]] or tendon rupture, especially in the [[Achilles tendon]], the FDA requires a "black box" warning for these medications. The cause of the tendon damage is not yet determined. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:33, 2 December 2010
In medicine, quinolones are antibiotics that are "a group of derivatives of naphthyridine carboxylic acid, quinoline carboxylic acid, or nalidixic acid."[1] Nadixilic acid's effects are localized to the urinary tract, but it was the first quinolone in general use. The subsequent quinolones, with broader spectra, were fluorinated and are often called fluoroquinolones.[2]
|
|
Mode of action
The mechanism of action for quinolones is different from that of macrolides, beta-lactams, aminoglycosides, or tetracyclines, so organisisms resistant to those classes of antibiotic drugs may be susceptible to quinolones. In particular, the quinolones interfere with topoisomerase enzymes, including topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are vital to bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair and recombination.
Classes
Non-fluorinated
Nadixilic acid has no action beyond the urinary tract; it is not absorbed systemically.
Fluoroquinolones
The first, unspecialized systemic quinolones included ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and norfloxacin. Of these, ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin have enhanced activity against Pseudomonas.
'Respiratory quinolones' are levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, or moxifloxacin. However, gatifloxacin can cause dysglycemia.[3]
Enrofloxacin is marketed for veterinary use as Baytril.
Interactions
The group may compete with other drugs that are normally metabolized by the CYP P-450-1A2 pathway, thus increasing their blood levels. These include anticoagulants and theophylline.
They can also decrease the blood levels, by less well-defined pathways, of anticonvulsants.
Side effects
Because the use of fluoroquinolones may lead to tendinitis or tendon rupture, especially in the Achilles tendon, the FDA requires a "black box" warning for these medications. The cause of the tendon damage is not yet determined.
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Quinolone (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Hardman JG, Limberd LE, Molinoff PB, Ruddon RW, Alfred Goodman Gilman, ed. (1996), Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (Ninth ed.), McGraw-Hill, pp. 1065-1068
- ↑ Park-Wyllie LY, Juurlink DN, Kopp A, Shah BR, Stukel TA, Stumpo C et al. (2006). "Outpatient gatifloxacin therapy and dysglycemia in older adults.". N Engl J Med 354 (13): 1352-61. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa055191. PMID 16510739. Research Blogging.