Melanocyte-stimulating hormone: Difference between revisions
imported>Gareth Leng No edit summary |
imported>Roger A. Lohmann m (add metadata & subpages) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
'''Melanocyte-stimulating hormones''' are a group of peptides produced via the cleavage of [[pro-opiomelanocortin]] (POMC). | '''Melanocyte-stimulating hormones''' are a group of peptides produced via the cleavage of [[pro-opiomelanocortin]] (POMC). | ||
Revision as of 08:43, 9 September 2020
Melanocyte-stimulating hormones are a group of peptides produced via the cleavage of pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC).
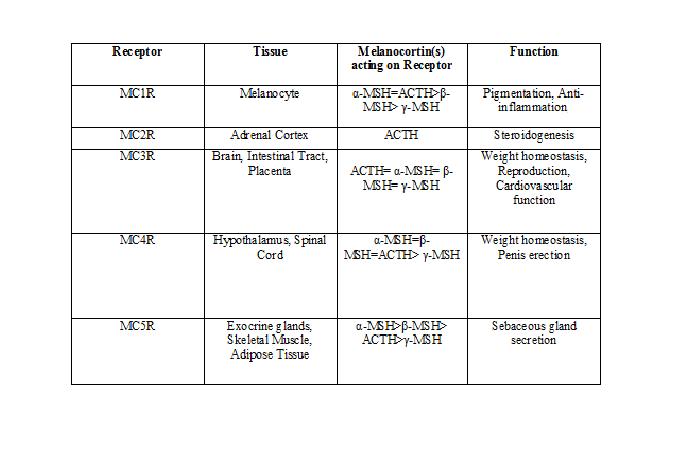
Inflammation α-MSH has potent anti-inflammatory effects although its precise mechanism is not fully understood, it is believed to influence vascular permeability and thus may act by decreasing it.
Cardiovascular Central application of γ- MSH (MC3R specific agonist, can induce tachycardia, while the bradychardia that occurs following electrical stimulation of the arcuate nucleus can be inhibited by the administration of SHU-9119 into the DVC. As it acts through MC4R this highlights a potential role for this receptor in mediating cardiovascular control.
Natriuresis γ-MSH acts on MC3R in the kidney to promote natriuresis, and hence a deficiency of this peptide, or a mutation of the receptor results in salt-sensitive hypertension in mice.
Sexual Function Activation of MC4R plays a role in erectile function in males while MC3R is believed to induce lordosis in females.
References
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedYang03