Dicloxacillin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (Chem infobox added) |
imported>Robert W King No edit summary |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Chem infobox | {{Chem infobox | ||
|align=right | |align=right | ||
|image=[[Image:Dicloxacillin structure.jpg| | |image=[[Image:Dicloxacillin structure.jpg|center|thumb|250px|{{#ifexist:Template:Dicloxacillin structure.jpg/credit|{{Dicloxacillin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}]] | ||
|width=250px | |width=250px | ||
|molname=dicloxacillin | |molname=dicloxacillin | ||
Revision as of 13:18, 3 April 2008
|
| |||||||
| dicloxacillin | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
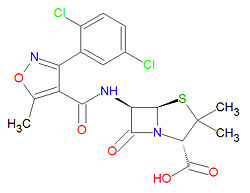
Dicloxacillin, (dichloro-oxacillin) is a beta-lactam based, penicillin-like, penicillinase-resistant antibiotic used to treat infections due to aerobic, Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. For more information about this drug, see the related pages for oxacillin and cloxacillin.
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name of dicloxacillin is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[[3-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, and it has molecular formula C19H17Cl2N3O5S, giving it a molecular mass of 470.3264 g/mol. It is susceptible to degradation in bacteria that express beta-lactamase.
External links
- Dicloxacillin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank