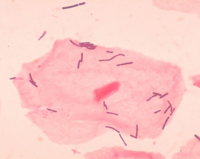
Lactobacillus acidophilus
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Lactobacillus acidophilus |
Description and significance
Lactobacillus acidophilus is a species of gram-positive bacteria commonly used in dairy production. L. acidophilus is also one of the most common forms of probiotics, which are "friendly bacteria".[1] L. acidophilus is found in the human and animal gut, mouth, and vagina. It functions as a lactic acid producer, by metabolizing lactose to lactic acid. The acid produced by L. acidophilus can control the growth of the fungus Candida albicans, which is the cause of Oral thrush and vaginal yeast infections.[2] The acid produced can also prevent unwanted organisms living in the gut. Common dairy products which use L. acidophilus in their production include Sweet acidophilus milk and yogurt. Sweet acidophilus milk and yogurt can be consumed by those who are lactose intolerant. Selected strains of L. acidophilus have shown significant reductions of cholesterol in humans, lowering the risk of coronary heart disease.[3]
Genome structure
Cell structure and metabolism
Ecology
Pathology
Application to Biotechnology
Current Research
References
http://www.umm.edu/altmed/articles/lactobacillus-acidophilus-000310.htm [1]