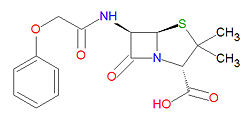
Penicillin V
|
| |||||||
| penicillin V | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antibiotic drug | ||||||
| Properties: | beta-lactam | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Penicillin V, or phenoxymethyl penicillin, is a broad-spectrum, beta-lactam-based antibiotic used to treat mild to severe infections due to Gram-positive bacteria. It is used to treat dental, ear, middle ear, respiratory tract and skin infections, and can also treat rheumatic and scarlet fevers. As opposed to penicillin G, it is resistant to digestive acids and is effective when administered orally.
Mechanism of action
Like other penicillin-like drugs, penicillin V works by binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins in bacterial cell walls and blocking the final cross-linking step in the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. This induces autolysis of the bactertial cells by autolysins.
Chemistry
Penicillin V is stable against degradation by beta-lactamases, including penicillinases, and cephalosporinases. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-[[2-(phenoxy)acetyl]amino]-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has molecular formula C16H18N2O5S (MM = 350.3895 g/mol).
Drug interactions
Tetracycline and its derivatives demeclocycline, doxycycline, methacycline, minocycline, oxytetracycline, rolitetracycline, and tetracycline are antagonists of penicillins. The effects of oral contraceptives, including [[ethinyl estradiol] and mestranol are decreased when using penicillin. Penicillins increases the effect and toxicity of methotrexate.[1]
Synonyms and brand names
|
synonyms
|
Brand names
|
Brand names
|
Brand Names
|
External links
The most up-to-date information about Penicillin V and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Penicillin V - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Penicillin V - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Penicillin V - Detailed information from DrugBank.