Oxidative stress
Chemists and biologists typically define oxidative stress as an imbalance, particularly in biological cells, between the rate of formation and/or concentration of 'oxygen free radicals' (or 'reactive oxygen species') — potent 'oxidizing' (electron capturing) atoms, ions or molecules — and their elimination or 'neutralization' by 'antioxidants' — 'reducing' (electron donating) molecules — the imbalance characterized by an excess of the former or a deficiency of the latter, leading to an alteration of a cell's 'redox' state towards the 'oxidized' state. The concept of oxidative stress occupies central importance in biology, as it applies, depending on circumstances, either to physiological phenomena essential for optimal functioning of organisms or to pathophysiological phenomenona, such as cardiovascular diseases, cancer and other clinical disease states, as well as to considerations of the mechanisms underlying aging.
In the definition of oxidative stress given above, the terms embraced by single quotes will require further discussion before any practical understanding of the concept can emerge. Accordingly, we will try to explicate those sub-concepts in turn, and relate them in a synthesis of the concept of oxidative stress.
Free radicals
In this section we elaborate on the following assertions about free radicals:
- A free radical is any chemical species (e.g., atoms, ions, molecules) capable of independent existence — hence the term ‘free’ — that contains one or more unpaired electrons.
- An unpaired electron is one that occupies a two-electron-capacity atomic or molecular orbital without an accompanying electron.
- A superscript dot is usually used to denote the unpaired electron.
- Radicals can form in many ways, in both industrial and biological systems, and in the latter, may form because of substances in food, water, pesticides, pollutants including tobacco smoke, drugs and radiation, because of normal responses to microbial infection, and as a byproduct of mitochondrial function.
- Because of their unpaired 'valence' electrons, radicals possess a high degree of chemical reactivity and potential for disrupting the structure and activity of biologically important molecules.
- A full understanding of free radical chemistry requires understanding many concepts from quantum mechanics and quantum chemistry, among which include:
- Atomic orbitals
- The Pauli principle
- Spin quantum numbering
- Covalent bonding
- Molecular orbitals
- Hund's rules
Chemists define a 'free radical' as an atom, ion or molecule that has one or more unpaired electrons, whereas all its other electrons, if it has others, exist in pairs that have 'opposite spin', technically opposite 'intrinsic angular momentum' or differing spin quantum numbers (+½ and -½).[1] The qualifier 'free' denotes the independent existence of the radical species, and many biological chemists drop the term as they consider only those radicals which can exist independently, however briefly.
ABCs of atomic structure
A little background on the structure of atoms will help explain the special properties of radicals. After British scientist J. J. Thompson discovered the negatively charged electron, the British physicist Ernest Rutherford (1871-1937) discovered the positively charged nucleus and conceived of an atom as low-mass negatively charged electrons in orbits around a more massive nucleus in the center, like planets orbiting a sun. Between 1913 and 1915 the Danish physicist Niels Bohr (1885-1962) developed a model of the atom that proposed that electron orbits could occupy only certain positions around the nucleus, and then in 1923 the French physicist Louis de Broglie (1892-1987), thinking about how one could view light as either particles (photons) or waves, proposed that electrons might have wave-like properties. The Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger (1887-1961) showed in 1926 that one could treat an electron as a wave occupying a so-called 'orbital', strictly a mathematical 'wave function' that gave the probability of the electron's location everywhere in the space around the nucleus. The modern description of the atom takes as fundamental that electrons occupy orbitals that have distinctive shapes indicating likely volumes of electron occupancy — mathematicians refer to them as spherical harmonic functions — the surfaces of the shapes enclose the region of space that likely contains the electron. Physicists and chemists designate the differently shaped orbitals with the lowercase letters s, p, d, f, and others.
In 1924, the Austrian-American physicist Wolfgang Pauli (1900-1958) inferred that only two electrons can occupy an orbital, formulating his 'exclusion principle'. In 1925, the Dutch-American physicists Uhlenbeck and Goudsmit, discovered that the two electrons must differ in a property interpreted in classical physics terms as spin, as if each electron rotated on a spherical axis, in one of two directions, one clockwise (↑), the other counterclockwise (↓). Soon after Pauli explained the quantum mechanical foundation of this discovery.
Given the two-electrons-only capacity of orbitals — Pauli's exclusion principle — the electrons of atoms with many electrons (e.g., carbon has 6, oxygen 8), arrange themselves in concentric shells about the nucleus with differing numbers of two-electron-capacity orbitals. The first shell, the innermost shell, has only one orbital, an orbital with the shape designated s (spherical), and the orbital itself designated a 1s orbital, in honor of its principal quantum number n = 1, giving it the 'first' shell label and the lowest energy level designation. The second shell has both s- and p-type orbitals, 1 s-type, 3 p-types labeled px, py, and pz. Thus an atom with electrons fully occupying the first and second shells would have two 1s electrons (1s2), two 2s electrons (2s2), and six 2p electrons (2p6), for a total of ten. With 10 balancing protons in the nucleus (atomic number, Z=10), that characterizes neon, an atom with a 'closed', or 'complete', set of shells, and therefore quite unreactive chemically.
The following table summarizes certain main features of atomic structure in relation to orbitals:
|
Table: Features of Atomic Structure in Relation to Orbitals
|
In the table, note that the different orbital types in each shell segregate as 'subshells'.
Consider the most common variety (also known as isotope) of hydrogen atom, which comprises a nucleus consisting of one proton, a positively charged particle, and one electron, a negatively charged particle, the latter occupying a surrounding electron shell, having no sub-shells, a shell that has the intrinsic capacity to hold two electrons. We can symbolize it as H•, or H•. For quantum mechanical reasons relating to a kind of stability, so to speak, the hydrogen atom tends to behaves as if it wanted two electrons in that shell, specifically a pair of electrons 'spinning' in opposite directions. Accordingly, the hydrogen atom tends to react with another hydrogen atom like itself, one with an oppositely spinning electron in its only electron shell, such that the two hydrogen nuclei share the two electrons in the shell, binding the two atoms together in what chemists refer to as a 'molecule' with a 'covalent bond' — in this case, a non-polar covalent bond, as no electrical asymmetry persists in the molecule because the equal positive charges on the two hydrogen nuclei means the orbiting electrons spend equal time near each nucleus. We can symbolize the hydrogen molecule as H:H, depicting the shared electrons between the two nuclei, or more simply, as H–H or H2. A hydrogen atom may satisfy its reluctance to possess an unpaired electron also by simply donating its electron to some other electron-eager atom or molecule, and continue its existence as a hydrogen ion, H+. In water, H2O, the medium of biological chemistry, some H+ can dissociate from the water molecule, leaving a hydroxyl ion, OH− in its wake.
Referring then to our definition of 'free radical', or just 'radical', we can recognize the hydrogen atom, H•, as a radical, and we can begin to appreciate the reactive nature of a radical eager to achieve electron pairing. We will see that other radicals, like H•, may through transfer or sharing, either lose an electron, or gain one, depending on circumstances.
- At this point we introduce a few helpful definitions:
|
Molecular structure
Consider next an atom with at least two more nuclei and electrons than the hydrogen atom. The additional electrons must locate in shells 2 and above (see Table: Features of Atomic Structure in Relation to Orbitals). The higher the shell the higher the energy levels of the electrons there, farther away from the positively charged nucleus. Each higher numbered shell successively has a greater number of orbitals of a greater number of orbital types.
To quote chemist Peter Atkins, "The central quantum mechanical idea on which the modern description of the structure of the atom is based is that its electrons occupy 'orbitals." The electrons occupying the outermost shell, whether the shell has only 1 electron or as many as it can carry, act as so-called 'valence' electrons, the electrons largely responsible for the determining whether the atom can form a bond with another atom, and the strength of the bond. In biological systems, the action in chemical reactions takes place with the valence electrons, in the outermost shell.
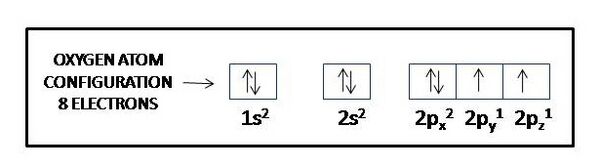
Consider specifically the oxygen atom, which plays a central role in oxidative stress. It has 8 protons and 8 electrons. An electron configuration table for the oxygen atoms reads as follows:
- 1s2
- 2s2 2p4
We interpret the table entry as indicating 2 electrons in the first shell, and 6 in the second. In the second shell, two electrons occupy an s-type orbital, and 4 occupy p-type orbitals. Given that a p-type orbital has a capacity of 6 electrons (viz., a 2 electron capacity each in px, py, and pz), oxygen falls short by two electrons of its 'wanting' to fill its outermost, or valence, shell, shell #2, to its full natural capacity. In biological systems an oxygen atom typically finds itself sharing two electrons originally fully owned by one or two other atoms, sharing them in covalent bonds. For example, it can share the eager-to-pair-up single 1s electrons in two hydrogen atoms, forming the covalent bonds that make up a water molecule, H:O:H, or H-O-H, or H2.
Unlike the case of the non-polar covalent bond forming a hydrogen molecule, discussed above, in the case of water, covalent bonds are polar covalent bonds, as the 8 protons in the oxygen nucleus has greater electrical attractive power for hydrogen's electrons than the two protons in the two hydrogen nuclei, 'polarizing' the molecule characterized by more electronegativity in the vicinity of the oxygen nucleus than in the vicinity of the hydrogen nuclei.
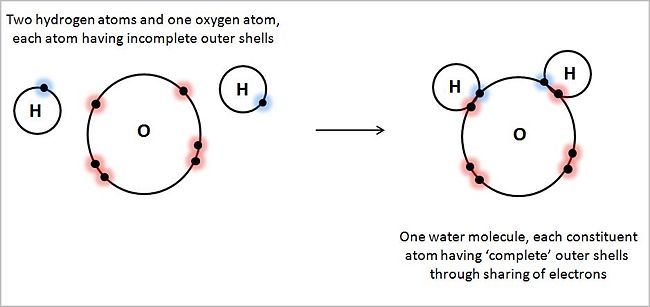
For simplicity, the illustration shows only those electrons of each atom located in its outer shell. Hydrogen atoms, with one electron each in their outer shell (1s1), behave as if they 'wanted' two electrons in their outer shell. Oxygen atoms, with six electrons in its outer shell (1s22s22p4), behave as if they 'wanted' eight electrons in their outer shell — the so-called 'octet rule'. By virtue of each hydrogen atom pairing its unpaired outer shell electron with an unpaired oxygen electron in its outer shell, sharing electrons, all three atoms approach their 'goal' of filing their valence shells to their natural full capacity, creating in the process two covalent bonds.
How can we know that an oxygen atom has two unpaired [(↑) (↑)] electrons in its six-electron outer shell? Could it not have two paired 2s electrons (2s2 [(↑↓)] and two paired electrons each in 2px [(↑↓)] and 2py [(↑↓)] and no electrons in 2py, as that would give it six paired electrons [(↑↓)] in its outer shell, two in the s subshell and 4 in the p subshell, in which case it would not have two unpaired electrons available to share electrons with two hydrogen atoms? The answer involves how electrons get added to orbitals in succession and to a rule called Hund’s rule. Electrons get added to orbitals in succession in a way that minimizes the total energy of the atom, as each orbital has its own energy level determined by a number of factors including the shape of the orbital (s-orbitals have lower energy than p-orbitals); the shell it finds itself in (shells more distant from the nucleus tend to have higher energy); and, the extent to which the electrons exert repulsive forces (repulsive forces between electrons raise their energy level). By Hund’s rule, for an oxygen atom the lowest total energy level emerges when its eight electrons arrange themselves successively in the single 1s orbital, the single 2s orbital, and the three 2p orbitals, no one orbital holding more than two electrons, paired [(↑↓)]. Hund’s rule then further applies to subshells that have more than one orbital, like the p subshell in the second shell of the oxygen atom, which has three p orbitals (see Table: Features of Atomic Structure in Relation to Orbitals). Hund’s rule specifies that electrons then arrange with parallel [(↑) (↑) spins to different orbitals in the multi-orbital subshell.
So, to comply with Hund’s rule an oxygen atom must arrange its electrons as follows:
Thus, an oxygen atom will have two unpaired, parallel-spin electrons in its outer shell, rendering it a radical, or more specifically, a di-radical.
Molecular orbitals
- ↑ Electron Spin and Electron Intrinsic Angular Momentum
- 'Note: The notion of spin for this intrinsic property of the electron arises from thinking about the property from the classical mechanics perspective.