Vietnam War
Template:TOC-right Since there is a current state and government of Vietnam, with full diplomatic representation including participation in international organizations, the final authorities on the definition of Vietnam War would appear to be the Vietnamese. They tend to refer to the Wars (plural) of Vietnam, often referring to a period starting sometime after 1959 and extending to 1975 as the "American War". While some see a period in which fighting in Southeast Asia merely was a proxy for what many Westerners believe was an existential battle between Western and Communist ideology, this is a view external to that of Vietnam. Unquestionably, the present government of Vietnam is Communist, but it is a Vietnamese communism, with a vibrant economy.
Vietnamese drives for independence begin, at least, in the 1st century C.E., with the Trung Sisters' revolt against the Chinese; the citation here mentions the 1968th anniversary of their actions.[1]
A useful perspective comes from retired U.S. lieutenant general Harold G. Moore (U.S. Army, retired) and journalist Joseph L. Galloway. Their book, We Were Soldiers once, and Young, as well as the movie made about the subject, part of the Battle of the Ia Drang, has been iconic, to many, of the American involvement. [2] Recently, they returned to their old battlefields and met with their old enemies, both sides seeking some closure. Some of their perspective may help.
Perspective and Naming
In 1990, one of their visits included the Vietnam Historic Museum in Hanoi.
The high point for us was not the exhibits but finding a huge mural that was both a timeline and a map of Vietnam's unhappy history dating back well over a thousand years...the Chinese section of the timeline stretched out for fifty feet or so. The section devoted to the French and their 150 years of colonial occupation was depicted in about twelve inches. The minuscule part that marked the U.S. war was only a couple of inches.[3]
So, while War in Vietnam goes back to to the rebellion, against China, of the Trung Sisters in the first century C.E., practical limits need to be set on the scope of this article. Many other articles can deal with other aspects, of the long history of Vietnam, than the period roughly from 1941 to 1975, all or part of which seems to form the Western concept of the Vietnam War.
From a Western concept that all post-WWII matters centered around Communism, it was the military effort of the Communist Party of Vietnam under Ho Chi Minh to defeat France (1946-54), and the same party, now in control of North Vietnam, to overthrow the government of South Vietnam (1958-75) and take control of the whole country, in the face of military intervention by the United States (1964-72). Vo Nguyen Giap refers to the Resistance War starting on December 19, 1946, and ending with the French exist.[4] Communists also use the term American War, although the dates are less clearly defined.
Others discuss the Viet Minh resistance, in the colonial period, to the French and Japanese, and the successful Communist-backed overthrow of the post-partition southern government, as separate wars. Unfortunately for naming convenience, there is a gap between the end of French rule and the start of partition in 1954, and the Northern decision to commit to controlling the South in 1959.
Background
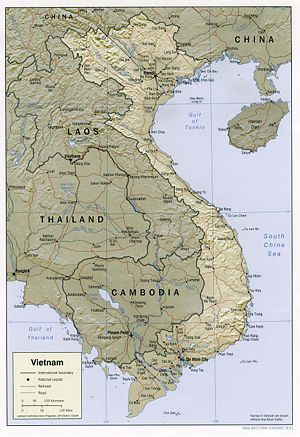
There are important background details variously dealing with the start of French colonization in Indochina, including the present countries of Vietnam and Laos, the expansion of Japan into Indochina and the U.S. economic embargoes as a result, and both the resistance to Japanese occupation and the Vichy French cooperation in ruling Indochina. A Japanese invasion in 1941 triggered U.S. export embargoes to Japan, which affected the Japanese decision to attack Western countries in December 1941; see Vietnam, war, and the United States .
In the West, the term is usually considered to have begun somewhere in the mid-20th century. There were at least two periods of hot war, first the Vietnamese war of independence from the French, including guerilla resistance starting during the Second World War and ending in a 1954 Geneva treaty that partitioned the country into the Communist North (NVN) (Democratic Republic of Vietnam, DRV) and non-Communist South (SVN) (Republic of Vietnam, RVN). A referendum on reunification had been scheduled for 1956, but never took place. Nevertheless, a complex and powerful United States Mission to the Republic of Vietnam was always present after the French had left and the Republic of Vietnam established.
While Communists had long had aims to control Vietnam, the specific decision to conquer the South was made, by the Northern leadership, in May 1959. The DRV had clearly defined political objectives, and a grand strategy, involving military, diplomatic, covert action and psychological operations to achieve those objectives. Whether or not one agreed with those objectives, there was a clear relationship between long-term goals and short-term actions. Its military first focused on guerilla and raid warfare in the south, simultaneously improving the air defensives of the north.
In contrast, the Southern governments from 1954 did not either have popular support or tight control over the populace. There was much jockeying for power as well as corruption. An assumption here is that while the U.S. and other countries had major roles, the thrust of the article is how it affected Vietnam and the Vietnamese. Issues of U.S. politics and opinion that affected it are in Vietnam, war, and the United States.
Eventually, following the Maoist doctrine of protracted war, the final "Phase III" offensive was by conventional forces, the sort that the U.S. had tried to build a defense against when the threat was from guerrillas. T-54 tanks that broke down the gates of the Presidential Palace in the southern capital, Saigon, were not driven by ragged guerrillas.
Fighting gradually escalated from that point, with a considerable amount of covert Western action in Vietnam and Laos. After the Gulf of Tonkin incident, in which U.S. President Lyndon Baines Johnson claimed North Vietnamese naval vessels had attacked U.S. warships, open U.S. involvement began in 1964, and continued until 1972. After the U.S. withdrawal based on a treaty in Paris, the two halves were to be forcibly united, by DRV conventional invasion, in 1975.
Without trying to name the wars, the key timeline events in modern history are:
- 1858-1862: French invasion and establishment of colonial government
- 1941: Japanese invasion of French Indochina
- 1945: End of World War II and return of Indochina to French authority; formal resistance starts circa 1946.
- 1954: End of French control and beginning of partition under the Geneva agreement; CIA covert operation started
- 1955: First overt U.S. advisors sent to the South
- 1959: North Vietnamese decision, in May 1959 to create the 559th (honoring the date) Transportation Group and begin infiltration of the South; U.S. advisory support begins to extend to tactical movement and fire support in roughly 1961
- 1964: Gulf of Tonkin incident and start of U.S. combat involvement; U.S. advisors and support, as well as covert operations, had been in place for several years
- 1969: Vietnamization policy starts
- 1972: Withdrawal of last U.S. combat forces as a result of negotiation
- 1975: Overthrow of the Southern government by regular Northern troops, followed by reunification under a Communist government.
Why we fight
While the title of this section draws from a U.S. movie, by John Ford, it is a question that applies to every war.
- Motivations in the Wars of Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description
- North Vietnamese cadre [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Vietnam, war, and the United States [r]: Add brief definition or description
- U.S. advisers in the Vietnam War [r]: U.S. military personnel who trained and assisted Army of the Republic of Viet Nam troops, originally in noncombat roles only but eventually side-by-side in battle [e]
- Competing U.S. military doctrine about unconventional warfare [r]: Add brief definition or description
How we fight
- Attrition [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Protracted war [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Vietnam War Ground Technology [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Air operations against North Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Air operations in South Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description (excludes
- Air assault [r]: Add brief definition or description)
French Indochina Background
- Vietnam, pre-colonial history [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Vietnam, French colonial period [r]: Add brief definition or description
At the time of the French invasion, during the Second French Revolution with Louis Napoleon III as President, there were four parts of what is now Vietnam:
- Cochinchina in the south, including the Mekong Delta and what was variously named Gia Dinh, Saigon, and Ho Chi Minh City
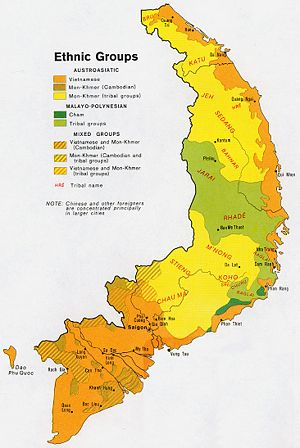
- Annam in the center, but the mountainous Central Highlands, the home of the Montagnard peoples, considered itself autonomous
- Tonkin in the North, including the Red River Delta, Hanoi, and Haiphong.
In 1858, France invaded Vietnam, and the ruling Nguyen dynasty accepted protectorate status. Cambodia and Laos also came under French control. Danang, then called Tourane, was captured in late 1858 and Gia Dinh (Saigon and later Ho Chi Minh City) in early 1859. In both cases Vietnamese Christian support for the French, predicted by the missionaries, failed to materialize.
Vietnamese resistance and outbreaks of cholera and typhoid forced the French to abandon Tourane in early 1860. They returned in 1861, with 70 ships and 3,500 men to reinforce Gia Dinh and. In June 1862, Emperor Tu Duc, signed the Treaty of Saigon.
French naval forces under Admiral de la Grandiere, the governor of Cochinchina (as the French renamed Nam Bo), demanded and received a protectorate status for Cambodia, on the grounds that the Treaty of Saigon had made France heir to Vietnamese claims in Cambodia. In June 1867, he seized the last provinces of Cochinchina. The Siamese government, in July, agreed to the Cambodian protectorate in return for receiving the two Cambodian provinces of Angkor and Battambang, to Siam. Siam was never under French control.
With Cochinchina secured, French naval and mercantile interests turned to Tonkin (as the French referred to Bac Bo).
Indochina under the Third French Republic
With the collapse of Napoleon III, in 1870, as a result of the Franco-Prussian War, the French Third Republic formed, and lasted until the Nazi conquest in 1940. Most of the key actions that set the context into which the Empire of Japan moved into the region happened during this period, and in the immediate aftermath under the Vichy goverment.
Few Frenchmen permanently settled in Indochina. Below the top layer of imperial control, the civil service comprised French-speaking Catholic Vietnamese; a nominal "Emperor" resided in Hue, the traditional cultural capital in north central Indonesia.
Little industry developed and 80% of the population lived in villages of about 2000 population; they depended on rice growing. Most were nominally Buddhist; about 10% were Catholic. Minorities included the Chinese merchants who controlled most of the commerce, and Montagnard tribesmen in the thinly populated Central Highlands. Vietnam was a relatively peaceful colony; sporadic independence movements were quickly suppressed by the efficient French secret police.
There were a variety of nationalist movements, non-Communist (e.g., Viet Nam Quoc Dan Dang) and Communist (e.g., Indochinese Communist Party. The French jailed (e.g., Vo Nguyen Giap,
In 1940 and 1941 the Vichy regime yielded control of Vietnam to the Japanese, and Ho returned to lead an underground independence movement (which received a little assistance from the O.S.S., the predecessor of the Central Intelligence Agency CIA).[5]
Indochina, a French colony in the spheres of influence of Japan and China, was destined to be drawn into the Second World War both through European and Asian events. See Vietnam War, World War II and immediate postwar. From 1946 to 1948, the French reestablished control, but, in 1948, began to explore a provisional government. While there is no clear start to what ended in 1954, the more serious nationalist movement was clearly underway by 1948.
First Indochinese War
- Vietnam War, First Indochina War [r]: The period, within the Vietnam War, between which France reasserted its colonial authority over Indochina in 1945, created a proto-state of Vietnam under a provisional government during which there was increasing insurgency, fought conventionally combat with the Viet-Minh starting in 1950, and ended in 1954. The end, militarily, involved the defeat of French forces at Dien Bien Phu and. politically, with the creation of North Vietnam and South Vietnam by the Geneva accords [e]
- Vietnam War, Partition and decisions [r]: Add brief definition or description
While there is no universally agreed name for this period in the history of Vietnam, it is the period between the formation of a quasi-autonomous government within the French Union, up to the eventual armed defeat of the French colonial forces by the Viet Minh. That defeat led to the 1954 Geneva accords that split Vietnam into North and South.
The French first created a provisional government under Bao Dai, then recognized Vietnam as a state within the French Union. In such a status, France would still control the foreign and military policy of Vietnam, which was unacceptable to both Communist and non-Communist nationalists.
Partition and decisions
- Vietnam War, Partition and decisions [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Vietnam, war, and the United States [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Vietnam War, Buddhist crisis and military coup of 1963 [r]: During the Vietnam War, a period of increasing domestic instability in the Republic of Viet Nam (South Vietnam), starting with harshly suppressed protests in April 1963 and ending with a military coup in November, during which President Ngo Dinh Diem and his brother, political advisor Ngo Dinh Nhu, were shot and killed shortly after being captured [e]
This period was begun by the military defeat of the French in 1954, with a Geneva meeting that partitioned Vietnam into North and South. Two provisions of the agreement never took place: a referendum on unification in 1956, and also banned foreign military support and intervention. G. Frederick Reinhardt was the first U.S. Ambassador accredited to the new Republic of Vietnam.
In the south, the Diem government was not popular, but there was no obvious alternative that would rise above factionalism, and also gain external support. Anti-Diem movements were not always Communist, although some certainly were.
The north was exploring its policy choices, both in terms of the south, and its relations with China and the Soviet Union. The priorities of the latter, just as U.S. and French priorities were not necessarily those of Diem, were not necessarily those of Ho. In 1959, North Vietnam made the explicit decision to overthrow the South by military means.
1959-to Gulf of Tonkin incident(1964)
- Vietnam war, Second Indochinese War, buildup before Gulf of Tonkin incident [r]: Add brief definition or description
To put the situation in a strategic perspective, remember that North and South Vietnam were artificial constructs of the 1954 Geneva agreements. While there had been several regions of Vietnam, when roughly a million northerners, of different religion and ethnicity than in the south, migrated into a population of five to ten million, there were identity conflicts. Communism has been called a secular religion, and the North Vietnamese government officials responsible for psychological warfare, as well as military operations, were part of a system of cadre. Communism, for its converts, was an organizing belief system that had no equivalent in the South. At best, the southern leadership intended to have a prosperous nation, although leaders were all too often focused on personal prosperity. Their Communist counterparts, however, had a mission of conversion by the sword — or the AK-47 assault rifle.
Between the 1954 Geneva accords and 1956, the two countries were still forming; the influence of major powers, especially France and the United States, and to a lesser extent China and the Soviet Union, were as much an influence as any internal matters. There is little question that in 1957-1958, there was a definite early guerilla movement against the Diem government, involving individual assassinations, expropriations, recruiting, shadow government, and other things characteristic of Mao's Phase I. The actual insurgents, however, were primarily native to the south or had been there for some time. While there was clearly communications and perhaps arms supply from the north, there is little evidence of any Northern units in the South, although organizers may well have infiltrated.
It is clear there was insurgency in the South from after the French defeat to the North Vietnamese decision to invade, but it is far more difficult to judge when and if the insurgency was clearly directed by the North. Given the two national sides both operated on the principle that their citizens were for them or against them, it is difficult to know how much neutralist opinion might actually have existed.
There is little doubt that there was some kind of Viet Minh-derived "stay behind" organization betweeen 1954 and 1960, but it is unclear that they were directed to take over action until 1957 or later. Before that, they were unquestionably recruiting and building infrastructure, a basic first step in a Maoist protracted war mode.
While the visible guerilla incidents increased gradually, the key policy decisions by the North were made in 1959. Early in this period, there was a greater degree of conflict in Laos than in South Vietnam. U.S. combat involvement was, at first, greater in Laos, but the activity of advisors, and increasingly U.S. direct support to South Vietnamese soldiers, increased, under U.S. military authority, in late 1959 and early 1960. Communications intercepts in 1959, for example, confirmed the start of the Ho Chi Minh trail and other preparation for large-scale fighting.
Guerilla attacks increased in the early 1960s, at the same time as the new John F. Kennedy administration made Presidential decisions to increase its influence. Diem, as other powers were deciding their policies, was clearly facing disorganized attacks and internal political dissent. There were unquestioned conflicts between the government, dominated by minority Northern Catholics, and both the majority Buddhists and minorities such as the Montagnards, Cao Dai, and Hoa Hao. These conflicts were exploited, initially at the level of propaganda and recruiting, by stay-behind Viet Minh receiving orders from the North.
Republic of Vietnam strategy
Quite separate from its internal problems, South Vietnam faced an unusual military challenge. On the one hand, there was a threat of a conventional, cross-border strike from the North, reminiscent of the Korean War. In the fifties, the U.S. advisors focused on building a "mirror image" of the U.S. Army, designed to meet and defeat a conventional invasion. [6]
Diem (and his successors) were primarily interested in using the ARVN as a device to secure power, rather than as a tool to unify the nation and defeat its enemies. Province and District Chiefs in the rural areas were usually military officers, but reported to political leadership in Saigon rather than the military operational chain of command. The 1960 "Counterinsurgency Plan for Vietnam (CIP)" from the U.S. MAAG was a proposal to change what appeared to be a dysfunctional structure. [6]
By 1962, the Diem government focused on the Strategic Hamlet Program as the main means of dealing with rural issues, whether of security or power.
Further analysis showed the situation was not only jockeying for power, but also reflected that the province chief indeed had security authority that could conflict with that of tactical military operations in progress, but also had responsibility for the civil administration of the province. That civil administration function became more and more intertwined, starting in 1964 and with acceleration in 1966, of the "other war" of rural development.[7]
Communist strategy
The Communist side had clearly defined political objectives, and a grand strategy, involving military, diplomatic, covert action and psychological operations to achieve those objectives. Whether or not one agreed with those objectives, there was a clear relationship between long-term goals and short-term actions, within the theory of dau trinh.
Especially under the French, there was also a broad-front nationalist aspect, involving non-communist groups such as the VNQDD. Arguably, some of the later southern insurgency was more anti-Diem rather than pro-communist. After the overthrow of Diem, Cao Dai and other factions broke away from the National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam; at least briefly, they regarded the absence of Diem as liberation. The hard-line Comunists, of course, disagreed.
Its military, or what the model called "armed dau trinh" first focused on guerilla and raid warfare in the south (i.e., Mao's "Phase I"), simultaneously improving the air defensives of the north. By the mid-sixties, they were operating in battalion and larger military formation that would remain in contact as long as the correlation of forces was to their advantage, and then retreat — Mao's "Phase II".
Eventually, following the Maoist doctrine of protracted war, the final "Phase III" offensive was by conventional forces, the sort that the U.S. had tried to build a defense against when the threat was from guerrillas. T-54 tanks that broke down the gates of the Presidential Palace in Saigon were not driven by ragged guerrillas.
Gulf of Tonkin incident
President Johnson asked for, and received, Congressional authority to use military force in Vietnam after the Gulf of Tonkin incident, which was described as a North Vietnamese attack on U.S. warships. After much declassification and study, much of the incident remains shrouded in what Clausewitz called the "fog of war", but serious questions have been raised of whether the North Vietnamese believed they were under attack, who fired the first shots, and, indeed, if there was a true attack. Congress did not declare war, which is defined as its responsibility in the Constitution of the United States; nevertheless, it launched what effectively was the longest war in U.S. history -- and even longer if the covert actions before the August 1964 Gulf of Tonkin situation is considered.
South Vietnamese government
There was a gradual transition from overt military government to at least the appearance of democratic government, but South Vietnam neither developed a true popular government, nor rooted out the corruption that caused a lack of support. Ngo Dinh Diem ruled from 1954 to 1963, with some coup attempts put down, but reasonably constant
Power constantly shifted in 1964 to 1967. This was not, as some have suggested, purely a series of struggles among military juntas. There were multiple Buddhist and other factions competing from outside the government. William Colby, then chief of the Central Intelligence Agency Far Eastern Division, observed that civilian politicians "divided and sub-divided into a tangle of contesting ambititions and claims and claims to power and participation in the government."[8] Some of these contests were simple drives for political power or wealth, while other reflected feeling of seeking to avoid preference for some groups, Catholic vs. Buddhist in the Diem Coup. Not all the competing groups, such as the Buddhists, were monolithic, and had their own internal struggles.
Vietnamese and U.S. goals were also not always in complete agreement. Certainly up to 1969, the U.S. was generally anything opposed to any policy, nationalist or not, which might lead to the South Vietnamese becoming neutralist rather than anticommunist. The Cold War containment policy was in force through the Eisenhower, Kennedy, and Johnson Administrations, while the Nixon administration was supportive of a more multipolar model of detente.
While there were still power struggles and internal corruption, there was much more stability between 1967 and 1975. Still, the South Vietnamese government did not enjoy either widespread popular support, or even an enforced social model of a Communist state. It is much easier to disrupt a state without common popular or decisionaker goals.
U.S. policy changes after 1964 election
- Vietnam, war, and the United States [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Joint warfare in South Vietnam 1964-1968 [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Air operations against North Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description
Although the combination of the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution and the political authority granted to Lyndon Johnson by being elected to the presidency rather than succeeding to it gave him more influence, and there was certainly an immense infusion of U.S. and allied forces into the theater of operations, never forget the chief participants in the war were Vietnamese.
Johnson's motives were different from Kennedy's, just as Nixon's motivations would be different from Johnson's. Of the three, Johnson was most concerned with U.S. domestic policy. He probably did want to see improvements in the life of the Vietnamese, but the opinions of his electorate were most important. His chief goal was implementing the set of domestic programs that he called the "Great Society". He judged actions in Vietnam not only on their own merits, but how they would be perceived in the U.S. political system. [9] To Johnson, Vietnam was a "political war" only in the sense of U.S. domestic politics, not a political settlement for the Vietnamese. He also saw it political in the sense of both his personal, and the U.S., position vis-a-vis the resto of the world.
Johnson and McNamara directed a three-part strategy, the first two developed by the civilian policymakers in Washington, and the third selected by them from different concepts by American leaders in Vietnam. Note that the initiative was coming from Johnson; the admittedly unstable South Vietnamese government was not part of defining their national destiny. The strategy they selected focused on the defeat of Communist forces in the field as the center of gravity, rather than the center of gravity being the stability of the rural population and, to modify Mao's metaphor, dry up the sea of people in which the guerilla swims, much as the fish swims in the sea. The Communist opponents saw the center of gravity as first population control, and then political and psychological dominance over the opposing alliance. Without judging its morality, the latter was closer to a unified grand strategic view. At best, the noncommunist view saw the matter in terms of a global grand strategy of containment, rather than the latter Nixon administration grand stragegy of detente.
Johnson chose Westmoreland's plan as most likely to succeed in the relatively near term. See Joint warfare in South Vietnam 1964-1968, and Competing U.S. military doctrine about unconventional warfare. Certainly by 1968, and perhaps in 1967, McNamara had increasingly less faith in the Johnson-Westmoreland model. McNamara quotes GEN William DuPuy, Westmoreland's chief planner, as recognizing that as long as the enemy could fight from the sanctuaries of Cambodia, Laos, and North Vietnam, it was impossible to bring adequate destruction on the enemy, and the model was inherently flawed.[10]
Also fundamental to Johnson was protecting his domestic legacy. Karnow quotes his comment to his biographer, Doris Kearns, as
I knew fro the start that I was bound to be crucified either way I moved. If I left the woman I really loved — the Great Society — in order to get invoved with that bitch of a war on the other side of the world, then i would lose everything at home. All my programs. All my hopes to feed the hungry and shelter the homeess. All my dreams to provide education and medical care to the browns and the blacks and the lame and the poor. But if I left that war and let the Communists take over South Vietnam, I would be seen as a coward and my nation seen as an apeaser, and we would both find it impossible to accomplish anything for anybody anywhere on the entire globe.[11]
See also Vietnam, war, and the United States for Johnson's belief of how a loss of South Vietnam would trigger domestic political attacks from right-wing ideologues that considered him the greatest of the dominoes.
Nixon, in contrast, saw resolution not just in Indochina, in a wider scope. He sough Soviet suppot, saying that if the Soviet Union helped bring the war to an honorable conclusion, the U.S. would "do something dramatic" to improve U.S.-Soviet relations. [12]
Vietnamization after Nixon's election
- Vietnamization [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Air operations against North Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Air campaigns against Cambodia and Laos [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Operation LINEBACKER I [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Operation LINEBACKER II [r]: Add brief definition or description
Westmoreland's approach, however, did not stop infiltration, which rose from 3,000 a month in 1965 to 8,000 a month throughout 1966 and 1967, and then 10,000 in 1968. By November 1965 the enemy had 110 battalions in the field, with 64,000 combat troops, 17,000 in combat support, and 54,000 part- time militia. With the Viet Cong forces depleted, Hanoi sent in its own PAVN troops, and had to supply them over the Ho Chi Minh Trail despite systematic bombing raids by the B-52s. American pressure forced Hanoi to reduce its level of activity in the South.
After the election of Richard M. Nixon, U.S. policy changed to one of turning ground combat over to South Vietnam, a process called Vietnamization.
Allied ground troops depart
- Operation LINEBACKER II [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Operation LINEBACKER I [r]: Add brief definition or description
- South Vietnam's ground war, 1972-1975 [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Northern Eastertide of 1972 [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Paris ceasefire talks [r]: Add brief definition or description
In the transition to full "Vietnamization," U.S. and third country ground troops turned ground combat responsibility to the Army of the Republic of Vietnam. Air and naval combat, combat support, and combat service support from the U.S. continued.
There were two unprecedented bombing campaigns. To stop the logistical support of the Eastertide invasion, Nixon launched Operation LINEBACKER I, which had the operational goal of disabling the infrastructure of infiltration.
When the North refused to return to negotiations in late in 1972, Nixon, in mid-December, ordered bombing at an unprecedented level of intensity, Operation LINEBACKER II. This was at the strategic and grand strategic levels, not so much attacking the infiltration infrastructure, but North Vietnam's physical ability to import supplies, its internal transportation and logistics, command and control, and integrated air defense system. Within one month of the start of the operation, a peace agreement was signed.
Peace accords and invasion, 1973-75
- Paris Peace talks [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Fall of South Vietnam [r]: Add brief definition or description
Peace accords were finally signed on 27 January 1973, in Paris. U.S combat troops immediately began withdrawal, and prisoners of war were repatriated. U.S. supplies and limited advise could continue. In theory, North Vietnam would not reinforce it troops in the south. The North, badly damaged by the bombings of 1972, recovered quickly and remained committed to the destruction of its rival. There was little U.S. popular support for new combat involvement, and no Congressional authorizations to expend funds to do so.
North Vietnam launched a new conventional invasion in 1975 and seized Saigon on April 30.[13]
No American combat units were present until the final days, when Operation FREQUENT WIND was launched to evacuate Americans and 5600 senior Vietnamese government and military officials, and employees of the U.S. The 9th Marine Amphibious Brigade, under the tactical commmand of Alfred M. Gray, Jr., would enter Saigon to evacuate the last Americans from the American Embassy to ships of the Seventh Fleet. Ambassador Graham Martin was among the last civilians to leave. [14] In parallel, Operation EAGLE PULL evacuated U.S. and friendly personnel from Phnom Penh, Cambodia, on April 12, 1975, under the protection of the 31st Marine Amphibious Unit, part of III MAF.
Vietnam was unified under Communist rule, as nearly a million refugees escaped by boat. Saigon was renamed Ho Chi Minh City.
References
- ↑ "Ha Noi celebrates Trung sisters 1,968th anniversary", Viet Nam News, 14 March 2008
- ↑ Moore, Harold G. (Hal) & Joseph L. Galloway (1999), We ere Soldiers Once...and Young: Ia Drang - the Battle That Changed the War in Vietnam, Random House
- ↑ Moore, Harold G. (Hal) & Joseph L. Galloway (2008), We are soldiers still: a journey back to the battlefields of Vietnam, Harper Collins
- ↑ Vo Nguyen Giap (1962), People's war, People's Army, Praeger, p. 88
- ↑ Patti, Archimedes L. A (1980). Why Viet Nam? Prelude to America's Albatross. University of California Press. , p. 477
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 , Chapter 6, "The Advisory Build-Up, 1961-1967," Section 1, pp. 408-457, The Pentagon Papers, Gravel Edition, Volume 2
- ↑ Eckhardt, George S. (1991), Vietnam Studies: Command and Control 1950-1969, Center for Military History, U.S. Department of the Army, pp. 68-71
- ↑ William Colby, Lost Victory, 1989, p. 173, quoted in McMaster, p. 165
- ↑ McMaster, H.R. (1997), Dereliction of Duty : Johnson, McNamara, the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and the Lies That Led to Vietnam, HarperCollins, ISBN 0060187956
- ↑ Gen. William E Dupuy, august 1, 1988 interview, quoted by McNamara, pages 212 and 371.
- ↑ Doris Kearns and Merle Miller, quoted in Karnow, p. 320
- ↑ Henry Kissinger (1973), Ending the Vietnam War: A history of America's Involvment in and Extrication from the Vietnam War, Simon & Schuster, p. 103
- ↑ Duiker, The Communist Road to Power, 341-49; David Butler, Fall of Saigon, (1986); Military History Institute of Vietnam, Victory in Vietnam: The Official History of the People's Army of Vietnam, 1954-1975 (2002), Hanoi's official historyexcerpt and text search
- ↑ Shulimson, Jack, The Marine War: III MAF in Vietnam, 1965-1971, 1996 Vietnam Symposium: "After the Cold War: Reassessing Vietnam" 18-20 April 1996, Vietnam Center and Archive at Texas Tech University