Metabolism/Citable Version
Metabolism (from Greek μεταβολισμός "metabolismos") is the biochemical modification of chemical compounds in living organisms and cells. Metabolism has two distinct divisions: anabolism, in which a cell uses energy and reducing power to construct complex molecules and perform other life functions such a creating cellular structure; and catabolism, in which a cell breaks down complex molecules to yield energy and reducing power. Cell metabolism involves extremely complex sequences of controlled chemical reactions called metabolic pathways.
History

The first controlled experiments in human metabolism were published by Santorio Santorio in 1614 in his book Ars de statica medecina that made him famous throughout Europe. He describes his long series of experiments in which he weighed himself in a chair suspended from a steelyard balance (see image), before and after eating, sleeping, working, sex, fasting, depriving from drinking, and excreting. He found that by far the greatest part of the food he took in was lost from the body through perspiratio insensibilis (insensible perspiration). At around the same time Jan Baptist van Helmont made the first observations regarding photosynthesis, when he discovered that plant growth required (almost) no soil nutrients. In the XVIII century, Priestley concluded that green plants use CO2 and release O2. In 1804, Nicolas de Saussure discovered that the increase in carbon content of plants (i.e. plant growth) arises from the fixation of atmospheric CO2. Between 1854 and 1864, Louis Pasteur discovered that glucose fermentation is due to microorganisms, and in 1897 Eduard Buchner proved that cell-free yeast extracts could also perform these reactions, and therefore the ability to ferment was not limited to living creatures. Subsequent investigations showed that (with a few exceptions) all living organisms metabolize glucose using the same mechanism.
Overview
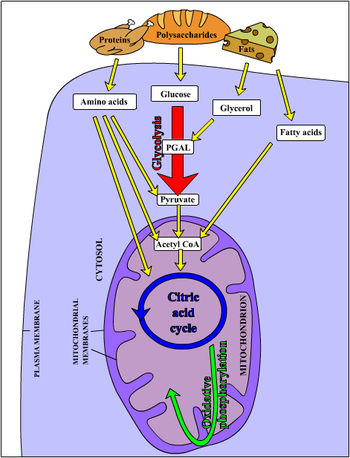
Molecules obtained by the cells from the environment (as food) must be converted into cell components, and these transformations usually require energy and reducing power.
Metabolic pathways
Important metabolic pathways are:
General pathways
Anabolism
Anabolic pathways that create building blocks and compounds from simple precursors:
- Glycogenesis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Porphyrin synthesis pathway
- HMG-CoA reductase pathway, leading to cholesterol and isoprenoids.
- Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction, but that usually have ecological function.
- Photosynthesis
- Light-dependent reaction (light reaction)
- Light-independent reaction (dark reaction)
- Calvin cycle
- Carbon fixation
- Glyoxylate cycle
Catabolism
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenolysis
- Citric acid cycle
- Beta-oxidation of fatty acids
Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism pathways, the modification or degradation of drugs and other xenobiotic compounds through specialized enzyme systems:
Nitrogen metabolism
Nitrogen metabolism includes the pathways for turnover and excretion of nitrogen in organisms as well as the biological processes of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle:
- Urea cycle, important for excretion of nitrogen as urea.
- Biological nitrogen fixation
- Nitrogen assimilation
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
Other
See also
- Cell metabolism
- Metabolomics
- Metabolome
- Metabolite
- Basal metabolic rate
- Thermic effect of food
- Iron-sulfur world theory, a "metabolism first" theory of the origin of life.
- Biodegradation
- Calorimetry
- Respirometry
- Microbial metabolism
- Metabolic network modelling
- dynamic energy budget
External links
- Interactive Flow Chart of the Major Metabolic Pathways
- Metabolism, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis - The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
- The Biochemistry of Metabolism at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
- Flow Chart of Metabolic Pathways at ExPASy
- Santorio Santorio's experiments
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes