Acupuncture
(from Latin acus, "needle" (noun), and pungere, "prick" (verb)) or in Standard Mandarin, zhēn jiǔ (針灸, needle therapy) Acupuncture involves inserting and manipulating needles into 'acupuncture points' on the body. with the aim of restoring health and well-being, and is particularly good at treating pain. The definition of these points is standardized by the World Health Organization [4]. Acupuncture is thought to have originated in China and is most commonly associated with Traditional Chinese medicine. Other types of acupuncture (Japanese, Korean, and classical Chinese acupuncture) are practiced and taught throughout the world.
Reviews of clinical trials according to the protocols of evidence-based medicine found evidence that acupunture can be efficacious for headache, low back pain and nausea, but for most conditions there is not enough reliable evidence to determine whether or not acupuncture is effective. The World Health Organisation (WHO), the National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) of the National Institute of Health (NIH), the American Medical Association (AMA) and various government reports have also commented on the efficacy of acupuncture. There is general agreement that acupuncture is safe when administered by well-trained practitioners, and that further research is warranted.
History
In China, acupuncture can perhaps be traced as far back as the 1st millennium BCE, and archeological evidence has been identified with the period of the Han dynasty (202 BCE to 220 CE). Forms of it are also described in the literature of traditional Korean medicine where it is called chimsul. It is also important in Kampo, the traditional medicine system of Japan.
Recent examinations of Ötzi, a 5000-year-old mummy found in the Alps, identified over fifty tattoos on his body, some of which are on acupuncture points that would today be used to treat ailments Ötzi suffered from. Some scientists believe that this is evidence that practices similar to acupuncture were practiced elsewhere in Eurasia during the early bronze age. [5], [6].
The Chinese medical text that first describes acupuncture is The Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine (History of Acupuncture), compiled around 305–204 BCE. Some hieroglyphics have been found dating to 1000 BCE that may indicate an early use of acupuncture. Bian stones, sharp pointed stones used to treat diseases in ancient times have also been discovered in China; some scholars believe that the bloodletting for which these stones were probably used presages certain acupuncture techniques [7].
The early Chinese Communist Party expressed antipathy towards classical forms of Chinese medicine, ridiculing it as superstitious, irrational and backward.[1] Reversing this position, Communist Party Chairman Mao later said that "Chinese medicine and pharmacology are a great treasure house and efforts should be made to explore them and raise them to a higher level"[8]. Representatives were sent across China to collect information about Chinese medicine. Traditional Chinese Medicine or TCM is the formalized system that resulted; it combines Acupuncture, Chinese herbal medicine, tui na and other modalities. After the Cultural Revolution, TCM instruction was incorporated into university medical curricula under the "Three Roads" policy, wherein TCM, biomedicine and a synthesis of the two would all be encouraged. After this time, forms of classical Chinese medicine other than TCM were outlawed, and some practitioners left China. The first forms of acupuncture to reach the USA were brought by non-TCM practitioners, many employing styles handed down in family lineages, or from master to apprentice (collectively known as "Classical Chinese Acupuncture").
Traditional theory
The traditional theory of acupuncture treats the human body as a whole that involves several 'systems of function' that are often associated with physical organs, although some, such as the 'triple heater' (San Jiao, also called the 'triple burner') have no corresponding physical organ. Disease is understood as a loss of homeostasis, and is treated by modifying the activity of one or more systems of function through the activity of needles, pressure, heat etc. on sensitive parts of the body traditionally called 'acupuncture points' in English, or 'xue' (穴, cavities) in Chinese. This is referred to as treating 'patterns of disharmony'.
The acupoints used may not be in the same area of the body as the targeted symptom. Some acupuncturists, particularly in Japan, reply on palpation for tender points, called 'ashi' (signifying 'that's it' or 'ouch!') points. The TCM theory is that such points work by stimulating the meridian system to bring about relief by rebalancing yin, yang and qi (also spelled "chi"). This theory is based on the paradigm of TCM, not that of science.
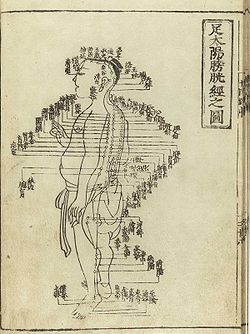
Treatment of acupuncture points may be performed along the twelve main or eight extra meridians, located throughout the body, or on 'ashi' points. Of the eight extra meridians, only two have acupuncture points of their own, the other six are 'activated' by using a master and couple point technique which involves needling the acupuncture points on the twelve main meridians that correspond to the particular extra meridian. Ten of the main meridians are named after organs of the body (Heart, Liver, etc.), and the other two are named after so-called body functions (Heart Protector or Pericardium, and San Jiao). The meridians are capitalized to avoid confusion with a physical organ (for example, we write the 'Heart meridian' as opposed to the 'heart meridian'). The two most important of the eight 'extra' meridians are situated on the midline of the anterior and posterior aspects of the trunk and head. The twelve primary meridians run vertically, bilaterally, and symmetrically and every channel corresponds to and connects internally with one of the twelve Zang Fu ('organs'). This means that there are six yin and six yang channels. There are three yin and three yang channels on each arm and on each leg.
The three yin channels of the hand (Lung, Pericardium, and Heart) begin on the chest and travel along the inner surface (mostly the anterior portion) of the arm to the hand.
The three yang channels of the hand (Large Intestine, San Jiao, and Small Intestine) begin on the hand and travel along the outer surface (mostly the posterior portion) of the arm to the head.
The three yin channels of the foot (Stomach, Gallbladder, and Bladder) begin on the face, in the region of the eye, and travel down the body and along the outer surface (mostly the anterior and lateral portion) of the leg to the foot.
The three yang channels of the foot (Spleen, Liver, and Kidney) begin on the foot and travel along the inner surface (mostly posterior and medial portion) of the leg to the chest or flank.
The movement of qi through each of the twelve channels is comprised of an internal and an external pathway. The external pathway is what is normally shown on an acupuncture chart and it is relatively superficial. All the acupuncture points of a channel lie on its external pathway. The internal pathways are the deep course of the channel where it enters the body cavities and related Zang-Fu organs. The superficial pathways of the twelve channels describe three complete circuits of the body.
The distribution of qi through the meridians is said to be as follows: Lung channel of hand taiyin to Large Intestine channel of hand yangming to Stomach channel of foot yangming to Spleen channel of foot taiyin to Heart channel of hand shaoyin to Small Intestine channel of hand taiyang to Bladder channel of foot taiyang to Kidney channel of foot shaoyin to Pericardium channel of hand jueyin to San Jiao channel of hand shaoyang to Gallbladder channel of foot shaoyang to Liver channel of foot jueyin then back to the Lung channel of hand taiyin.
Chinese medical theory holds that acupuncture works by normalizing the free flow of qi (a difficult-to-translate concept that pervades Chinese philosophy and is commonly translated as 'vital energy') throughout the body. Pain or illnesses are treated by attempting to remedy local or systemic accumulations or deficiencies of qi. Pain is considered to indicate stagnation of the flow of qi, and an axiom of acupuncture is no pain, no blockage; no blockage, no pain.
Many patients claim to experience the sensations of stimulus known in Chinese as 'deqi' (得氣, 'arrival of the qi'). This was considered to be evidence of locating the desired point.
The acupuncturist decides which points to treat by observing and questioning the patient. In TCM, there are four diagnostic methods: inspection, auscultation and olfaction, inquiring, and palpation. Inspection focuses on the face and particularly the tongue, including analysing its size, shape, tension, color and coating, and the absence or presence of teeth marks around the edge. Auscultation and olfaction refer, respectively, to listening for particular sounds (such as wheezing) and attending to unusual body odor. Inquiring focuses on the 'seven inquiries': chills and fever; perspiration; appetite, thirst and taste; defecation and urination; pain; sleep; and menses and leukorrhea. Palpation includes feeling the body for tender 'ashi' points, and palpation of the left and right radial pulses at two levels of pressure (superficial and deep) and three positions (immediately proximal to the wrist crease, and one and two fingers' breadth proximally, usually palpated with the index, middle and ring fingers). Other forms of acupuncture employ additional diagnosic techniques. In many forms of classical Chinese acupuncture, as well as Japanese acupuncture, palpation of the muscles and the hara (abdomen) are central to diagnosis.
Categories of acupuncture points
Certain acupuncture points are ascribed different functions according to different systems within the TCM framework.
- Five Transporting Points system describes the flow of qi in the channels using a river analogy; it describes qi bubbling up from a spring and gradually growing in depth and breadth like a river flowing from a mountain to the sea.
- Jing-well points are where the qi 'bubbles up'. These are always the first points on the yang channels or last points on the yin channels and with the exception of Kid-1 YongQuan, all are located on the tips of fingers and toes. They are indicated for 'fullness below the heart' (feeling of fullness in the epigastric or hypochondrium regions) and disorders of the zang organs (yang organs).
- Ying-spring points are where the qi 'glides' down the channel; they are indicated for heat in the body and changes in complexion.
- Shu-stream points are where the qi 'pours' down the channel; they are indicated for heaviness in the body and pain in the joints, and for intermittent diseases.
- Jing-river points are where the qi 'flows' down the channel; they are indicated for cough and dyspnoea, chills and fever, diseases manifesting as changes in voice, and for diseases of the sinews and bones.
- He-sea points are where the qi collects and begins to head deeper into the body; they are indicated for counterflow qi and diarrhea, and for disorders resulting from irregular eating and drinking.
- Five Phase Points ascribe each of the five phases - wood, fire, earth, metal and water - to one of the Five Transporting points. On the yin channels, the jing-well points are wood points, the ying-spring points are fire, shu-stream points are earth, jing-river points are metal, he-sea points are water points. On the yang channels, the jing-well points are metal, ying-spring are water, shu-stream are wood, jing-river points are fire and he-sea points are earth points. These point categories are then implemented according to Five Phase theory in order to approach the treatment of disease.
- Xi-cleft points are on the channel where the qi and blood gather and plunge more deeply; they are indicated in acute situations and for painful conditions.
- Yuan-source points are on the channel from where the yuan qi can be accessed.
- Luo-connecting points are at the point on the channel where the luo meridian diverges. Each of the twelve meridians have a luo point that diverges from the main meridian. There are also three extra luo channels that diverge at Sp-21, Ren-15 and Du-1.
- Back-shu points lie on the paraspinal muscles either side of the spine. Theory says that the qi of each organ is transported to and from these points, and can be influenced by them.
- Front-mu points are close to the respective organ. They have a direct effect on the organ itself but not on the associated channel.
- Hui-meeting points are considered to have a "special effect" on certain tissues and organs. The hui-meeting points are:
- zang organs - Liv-13 Zhang Men
- fu organs - Ren-12 Zhong Fu
- qi - Ren-17 Shang Fu
- blood - Bl-17 Ge Shu
- sinews - GB-34 Yang Ling Quan
- vessels - Lu-9 Tai Yuan
- bone - Bl11 Da Zhu
- marrow - GB-39 Xuan Zhong
TCM perspective on treatment of disease
Acupuncture has been used to treat a number of conditions. Typically, acupuncture treatment is highly-individualized and based on subjective and intuitive impressions, rather than on controlled scientific research. [9]. Although TCM is based on the treatment of "patterns of disharmony" rather than biomedical diagnoses, practitioners familiar with both systems have commented on relationships between the two. A given TCM pattern of disharmony may be reflected in a certain range of biomedical diagnoses: thus, the pattern called Deficiency of Spleen Qi could manifest as chronic fatigue, diarrhea or uterine prolapse. Likewise, a population of patients with a given biomedical diagnosis may have varying TCM patterns. These observations are encapsulated in the TCM aphorism One disease, many patterns; one pattern, many diseases. [2]
Criticism of TCM theory
TCM theory predates use of the scientific method, and has been criticised on that basis. A report for CSICOP said: "A few Chinese scientists we met maintained that although qi is merely a metaphor, it is still a useful physiological abstraction (e.g. that the related concepts of Yin and Yang parallel modern scientific notions of endocrinologic and metabolic feedback mechanisms). They see this as a useful way to unite Eastern and Western medicine. Their more hard-nosed colleagues quietly dismissed qi as bearing no tangible relationship to modern physiology and medicine."[10]
In 1995, George A. Ulett, Clinical Professor of Psychiatry, University of Missouri School of Medicine, stated that "devoid of metaphysical thinking, acupuncture becomes a rather simple technique that can be useful as a nondrug method of pain control." He believes that the traditional Chinese variety is primarily a placebo treatment, but electrical stimulation of about 80 acupuncture points has been proven useful for pain control.[11]
Ted Kaptchuk, author of The Web That Has No Weaver, refers to acupuncture as "prescientific". About TCM theory, Kaptchuk says: "These ideas are cultural and speculative constructs that provide orientation and direction for the practical patient situation. There are few secrets of Oriental wisdom buried here. When presented outside the context of Chinese civilization, or of practical diagnosis and therapeutics, these ideas are fragmented and without great significance. The 'truth' of these ideas lies in the way the physician can use them to treat real people with real complaints."
According to the NIH consensus statement on acupuncture:
- Despite considerable efforts to understand the anatomy and physiology of the 'acupuncture points', the definition and characterization of these points remains controversial. Even more elusive is the basis of some of the key traditional Eastern medical concepts such as the circulation of qi, the meridian system, and the five phases theory, which are difficult to reconcile with contemporary biomedical information but continue to play an important role in the evaluation of patients and the formulation of treatment in acupuncture. [12]
Legal and political status
Acupuncturists may also practice herbal medicine or tui na, or may be medical acupuncturists, who are trained in allopathic medicine but also practice acupuncture in a simplified form. License is regulated by the state or province in many countries, and often requires passage of a board exam.
In the USA, acupuncturists are generally known as 'Licensed Acupuncturists' (L.Ac.). The "Diplomate of Acupuncture" (Dipl. Ac.) means that the holder is board-certified by the National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine. Professional degrees include 'M.Ac.' (Master of Acupuncture), 'M.S.Ac.' (Master of Science in Acupuncture), "M.S.O.M" (Master of Science in Oriental Medicine), 'M.A.O.M.' (Master of Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine). 'O.M.D.' signifies Oriental Medical Doctor, and may be used by graduates of Chinese medical schools, or by American graduates of postgraduate programs, but the the OMD degree is not currently recognized by the Accreditation Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine which accredits American educational programs in acupuncture. Other healthcare providers such as physicians, dentists and chiropractors sometimes also practice acupuncture, though they may often receive less training than L.Ac.'s, who generally receive 2500-4000 hours of training in Chinese medical theory, acupuncture, and basic biosciences. Some also receive training in Chinese herbology and/or bodywork. The amount of training required for healthcare providers who are not L.Ac.'s varies from none to a few hundred hours, and in Hawaii the practice of acupuncture requires full training as a licensed acupuncturist. The National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine tests practitioners to ensure they are knowledgeable about Chinese medicine and appropriate sterile technique. Many states require this test for licensing, but each has its own laws and requirements. In some, acupuncturists are required to work with an MD in a subservient relationship. Over fifteen million Americans in 1994 tried acupuncture, and in 2005 a poll of American doctors showed that 60% of them believe acupuncture was at least somewhat effective, with the percentage increasing to 75% if acupuncture is considered as a complement to conventional treatment [13]. In 1996, the Food and Drug Administration changed the status of acupuncture needles from Class III to Class II medical devices, meaning that needles are regarded as safe and effective when used appropriately by licensed practitioners [14] [15].
In Australia, the legalities of practicing acupuncture also vary by state. In 2000, an independent government agency was established to oversee the practice of Chinese Herbal Medicine and Acupuncture in the state of Victoria. The Chinese Medicine Registration Board of Victoria [16] aims to protect the public, ensuring that only appropriately experienced or qualified practitioners are registered to practice Chinese Medicine. The Parliamentary Committee on the Health Care Complaints Commission in the Australian state of New South Wales commissioned a report investigating TXM practice. [17] They recommended the introduction of a government appointed registration board that would regulate the profession by restricting use of the titles "acupuncturist", "Chinese herbal medicine practitioner" and "Chinese medicine practitioner". The aim of registration is to protect the public by ensuring a high baseline level of competency and education of registered acupuncturists, enforcing guidelines regarding continuing professional education and investigating complaints of practitioner conduct. Victoria is the only state of Australia with an operational registration board. [18] Acupuncturists in NSW are bound by the guidelines in the Public Health (Skin Penetration) Regulation 2000 [19]which is enforced at local council level.
Clinical practice
Most modern acupuncturists use fine, disposable stainless steel needles (of diameter 0.18-0.51 mm), sterilized with ethylene oxide or by autoclave. The upper third of these needles is wound with a thicker wire (typically bronze), or covered in plastic, to stiffen the needle and provide a handle for the acupuncturist to grasp while inserting. The size and type of needle used, and the depth of insertion, depend on the acupuncture style being practiced.
Warming an acupuncture point, typically by moxibustion (the burning of mugwort), is a different treatment to acupuncture itself and is often used as a supplementary treatment. The Chinese term zhēn jǐu (針灸), commonly used to refer to acupuncture, comes from zhen meaning "needle", and jiu meaning "moxibustion". Moxibustion is still used in the 21st century to varying degrees among the schools of oriental medicine. For example, one technique is to insert the needle at the desired acupuncture point, attach dried mugwort to the external end of an acupuncture needle, and then ignite the mugwort. The mugwort will then smolder for several minutes and conduct heat through the needle to the tissue surrounding the needle in the patient's body. Another common technique is to hold a large glowing stick of moxa over the needles. Moxa is also sometimes burned at the skin surface, usually by applying an ointment to the skin to protect from burns.
An example of acupuncture treatment
In western medicine, vascular headaches (the kind that are accompanied by throbbing veins in the temples) are typically treated with analgesics such as aspirin and/or by the use of agents such as niacin that dilate the affected blood vessels in the scalp, but in acupuncture a common treatment for such headaches is to stimulate the sensitive points that are located roughly in the center of the webs between the thumbs and the palms of the patient, the hé gǔ points. These points are described as 'targeting the face and head' and are considered to be the most important point when treating disorders affecting the face and head. The patient reclines, and the points on each hand are first sterilized with alcohol, and then thin, disposable needles are inserted to a depth of approximately 3-5 mm until a characteristic 'twinge' is felt by the patient, often accompanied by a slight twitching of the area between the thumb and hand. Most patients report a pleasurable tingling sensation and a feeling of relaxation while the needles are in place. The needles are retained for 15-20 minutes while the patient rests, and then are removed.
In the clinical practice of acupuncturists, patients often report one or more of certain kinds of sensation associated with this treatment, sensations stronger than those felt by a patient not suffering from a vascular headache:
- Extreme sensitivity to pain at the points in the webs of the thumbs.
- In bad headaches, a feeling of nausea that persists for roughly the same period as the stimulation being administered to the webs of the thumbs.
- Simultaneous relief of the headache. (See Zhen Jiu Xue, p. 177f et passim.)
Indications according to acupuncturists in the West
According to the American Academy of Medical Acupuncture (2004), acupuncture may be considered as a complementary therapy for a wide range of conditions:[20]
- * Also included in the World Health Organization list of acupuncture indications.[21]
Scientific theories and mechanisms of action
The "gate control theory of pain", developed by Ronald Melzack and Patrick Wall, proposed that pain perception is not simply a direct result of activating pain fibers, but involves the synthesis of many different types of sensory information some of which can block (or "gate") the signals that come from the pain receptors. Accordingly, the perception of pain can be altered by a number of means physiologically, psychologically and pharmacologically. [3]
Pain transmission can also be modulated at many levels in the brain, including the periaqueductal gray, thalamus, and the feedback pathways from the cortex to the thalamus. Each of these brain structures processes different aspects of the pain — from experiencing emotional pain to the perception of what the pain feels like, to the recognition of how harmful the pain is, and to localizing where the pain is coming from. Pain blockade at some of these locations is mediated by neurohormones, especially those that bind to opioid receptors. The opiate drug morphine relieves pain by acting on the same type of opioid receptor as endorphins and enkephalins, naturally occurring opiate-like substances that the brain produces and releases.
Most importantly for understanding how acupuncture might work, it was shown that mild sensory stimulation (rubbing) relieves the feeling of pain because the activity of 'touch' receptors can partly inhibit the activity of pain receptors. Accordingly, it was recognised that this might provide a basis for understanding how one type of stimulation (by acupuncture needles) might block pain signals.
Research into efficacy
There is scientific agreement that an evidence-based medicine (EBM) framework should be used to assess health outcomes and that systematic reviews with strict protocols are important.[4] Organisations such as the Cochrane Collaboration publish such reviews. For many conditions, the Cochrane Collaboration concluded there is insufficient evidence that acupuncture is beneficial, often because of the paucity and poor quality of the research and that further research would be needed to support claims for efficacy [5]
For headache, Cochrane concluded (2006) that "evidence supports the value of acupuncture for the treatment of idiopathic headaches." [22]. For nausea and vomiting: the Cochrane review (2006) on the use of the P6 acupoint for the reduction of post-operative nausea and vomiting concluded that "compared with anti emetic prophylaxis, P6 acupoint stimulation seems to reduce the risk of nausea but not vomiting" [23]. Cochrane also stated: "Electroacupuncture is effective for first day vomiting after chemotherapy, but trials considering modern antivomiting drugs are needed." [24].Bandolier said "P6 acupressure in two studies showed 52% of patients with control having a success, compared with 75% with P6 acupressure"(1999) and that one in five adults, but not children showed reduction in early postoperative nausea(2000).
NIH consensus statement
According to the NIH:[6]
- Preclinical studies have documented acupuncture's effects, but they have not been able to fully explain how acupuncture works within the framework of the Western system of medicine that is commonly practiced in the United States.
In 1997, the NIH issued a consensus statement on acupuncture that concluded that
- there is sufficient evidence of acupuncture's value to expand its use into conventional medicine and to encourage further studies of its physiology and clinical value[25].
The consensus statement said thatthe data in support of acupuncture are as strong as those for many accepted Western medical therapies and added that there is clear evidence that needle acupuncture is efficacious for adult postoperative and chemotherapy nausea and vomiting and probably for the nausea of pregnancy... There is reasonable evidence of efficacy for postoperative dental pain... reasonable studies (although sometimes only single studies) showing relief of pain with acupuncture on diverse pain conditions such as menstrual cramps, tennis elbow, and fibromyalgia... The statement concluded:
- Acupuncture as a therapeutic intervention is widely practiced in the United States. While there have been many studies of its potential usefulness, many of these studies provide equivocal results because of design, sample size, and other factors. The issue is further complicated by inherent difficulties in the use of appropriate controls, such as placebos and sham acupuncture groups. However, promising results have emerged, for example, showing efficacy of acupuncture in adult postoperative and chemotherapy nausea and vomiting and in postoperative dental pain. There are other situations such as addiction, stroke rehabilitation, headache, menstrual cramps, tennis elbow, fibromyalgia, myofascial pain, osteoarthritis, low back pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and asthma, in which acupuncture may be useful as an adjunct treatment or an acceptable alternative or be included in a comprehensive management program. Further research is likely to uncover additional areas where acupuncture interventions will be useful.
The NIH's National Center For Complementary And Alternative Medicine continues to abide by the recommendations of the NIH Consensus Statement [26].
American Medical Association statement
In 1997, the following statement was adopted as policy of the AMA after a report on a number of alternative therapies including acupuncture:[27]
"There is little evidence to confirm the safety or efficacy of most alternative therapies. Much of the information currently known about these therapies makes it clear that many have not been shown to be efficacious. Well-designed, stringently controlled research should be done to evaluate the efficacy of alternative therapies."
A common criticism of studies that appear to show that acupuncture is effective is that most have methodological weaknesses. Many are not double blinded and are not randomised. However, in acupuncture: it is difficult to design studies in which the person providing treatment is blinded as to the treatment being given. The same problem arises in double-blinding procedures used in biomedicine, including virtually all surgical procedures, dentistry, physical therapy, etc.; the NIH Consensus Statement notes such issues with regard to sham acupuncture, a technique often used in studies purporting to be double-blinded. See also Criticism of evidence-based medicine. Tonelli, a critic of EBM, argues that complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) cannot be EBM-based unless the definition of evidence is changed. [28].
Safety and risks
Some forms of acupuncture such as the Japanese Tōyōhari and Shōnishin often use non-invasive techniques, in which specially-designed needles are rubbed or pressed against the skin. These methods are common in Japanese pediatric use. However, many forms of acupuncture are invasive procedures, and therefore not without risk. Injuries are rare among patients treated by trained practitioners.[29][30]
A survey of more than 400 patients receiving more than 3500 acupuncture treatments[31] found that the most common adverse effects were:
- Minor bleeding after removing the needles, affects about 3% of patients. Holding a cotton ball for about one minute over the site is usually sufficient to stop the bleeding.
- Hematoma, (bruises) affects about 2% of patients. These usually go away after a few days.
- Dizziness affects about 1% of patients. Some patients have a fear of needles which can produce dizziness and other symptoms of anxiety. Patients are usually treated lying down to reduce the likelihood of fainting.
The survey concluded: "Acupuncture has adverse effects, like any therapeutic approach. If it is used according to established safety rules and carefully at appropriate anatomic regions, it is a safe treatment method."[32]
- Infection is a risk that may arise due to use of unsterile or re-used needles. Reused needles can transfer blood-borne diseases such as HIV and hepatitis. Accordingly, the use of sterile, single-use-only needles is mandated by law in some countries, including the USA. Use of sterile needles is also mandated in parts of Australia (cf. above), but poorly enforced. [33]
Some western doctors believe that receiving any form of alternative medical care without also receiving orthodox western medical care is inherently risky, since undiagnosed disease may go untreated and could worsen. For this reason many acupuncturists and doctors prefer to consider acupuncture a complementary therapy rather than an alternative therapy. Critics also express concern that unethical or naive practitioners may induce patients to exhaust financial resources by pursuing ineffective treatment. [34]
Commenting on the safety of acupuncture, the NIH consensus panel stated that "(a)dverse side effects of acupuncture are extremely low and often lower than conventional treatments." They also stated:
- "the incidence of adverse effects is substantially lower than that of many drugs or other accepted medical procedures used for the same condition. For example, musculoskeletal conditions, such as fibromyalgia, myofascial pain, and tennis elbow... are conditions for which acupuncture may be beneficial. These painful conditions are often treated with, among other things, anti-inflammatory medications (aspirin, ibuprofen, etc.) or with steroid injections. Both medical interventions have a potential for deleterious side effects but are still widely used and are considered acceptable treatments."
In a Japanese survey of 55,291 acupuncture treatments given over 5 years by 73 acupuncturists, 99.8% of them had no significant minor adverse effects and there were no major adverse incidents [7]. Two combined studies in the UK of 66,229 acupuncture treatments yielded only 134 minor adverse events. [8]. The total of 121,520 treatments with acupuncture therapy were given with no major adverse incidents (for comparison, a single such event would have indicated a 0.002% incidence).
External links
International Standards
Professional organizations
- Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine Alliance (AOMAlliance) - U.S. organization representing L.Ac.'s and other AOM practitioners, e.g. M.D.'s and D.C.'s
- American Association of Oriental Medicine (AAOM) - U.S. organization representing L.Ac.'s exclusively
- Council of Colleges of Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (CCAOM) - U.S. organization representing acupuncture schools; also administers Clean Needle Technique (CNT) course required for American board certification
- National Acupuncture Detoxification Association - U.S. organization advocating use of auricular (ear) acupuncture for treating addiction
- The British Acupuncture Council (BAcC) - U.K. organization representing acupuncturists
Regulatory organizations
- National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (NCCAOM) - U.S. organization that administers board certification exams in acupuncture and Oriental medicine
- Accreditation Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (ACAOM) - National accrediting agency recognized by the U.S. Department of Education to accredit Master's-level programs in the acupuncture and Oriental medicine profession in the U.S.
- Federation of Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine Regulatory Agencies (FAOMRA) - State regulatory agency forum in the U.S.
Historical Images
Bibliography
- B. Brinkhaus, et al (2005} Acupuncture in Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Randomised Trial. The Lancet, Vol 366,
- Chen, J.D.Z., Ouyang, H. Review article: therapeutic roles of acupuncture in functional gastrointestinal disorders. Aliment Pharmacol Therapy 2004; 20:831-841
- Kaptchuk, Ted. The Web That Has No Weaver. Congdon and Weed, (1983) ISBN 0-86553-109-9
- Premier. EBSCO. 30 January 2006 <http://search.epnet.com/>
- Health Professions Regulatory Advisory Council, Minister’s Referral Letter January 18, 2006 – Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) <http://www.hprac.org/english/projects.asp> 20 March 2006
- Porkert, Manfred "The Theoretical Foundations of Chinese Medicine" MIT Press, 1974 ISBN 0-262-16058-7
References
- ↑ Crozier RC (1968) 'Traditional medicine in modern China' Harvard University Press
- ↑ (Kaptchuk, 1982)
- ↑ Wall PD, Melzack R (1962) On nature of cutaneous sensory mechanisms, Brain 85:331; Melzack R, Wall PD (1965) Pain mechanisms: A new theory, Science 150:171-9; Melzack R (1976) Acupuncture and pain mechanisms Anaesthesist 25:204-7
- ↑ In practice, EBM does not demand that doctors ignore research outside its "top-tier" criteria [1].
- ↑ For the following conditions, the Cochrane Collaboration concluded there is insufficient evidence that acupuncture is beneficial: Giving up smoking
Chronic asthma
Bell's palsy
Shoulder pain
Lateral elbow pain
Acute stroke
Rheumatoid arthritis
Depression
Induction of labour
For low back pain, a Cochrane review (2006) stated:
- Thirty-five RCTs covering 2861 patients were included in this systematic review. There is insufficient evidence to make any recommendations about acupuncture or dry-needling for acute low-back pain. For chronic low-back pain, results show that acupuncture is more effective for pain relief than no treatment or sham treatment, in measurements taken up to three months. The results also show that for chronic low-back pain, acupuncture is more effective for improving function than no treatment, in the short-term. Acupuncture is not more effective than other conventional and 'alternative' treatments. When acupuncture is added to other conventional therapies, it relieves pain and improves function better than the conventional therapies alone. However, effects are only small.[2]
- ↑ Get the Facts, Acupuncture, (2006). National Institute of Health.
- ↑ (Yamashita, Tsukayama, Tanno, Nishijo, JAMA)
- ↑ British Medical Journal 2001

