Metabolism/Citable Version
Metabolism (from Greek μεταβολισμός "metabolismos") is the biochemical modification of chemical compounds by living organisms and cells. In common usage, the word is often used to refer to the basal metabolic rate, the "set point" that each person has in breaking down food energy and building up their own body. In multicellular creatures like humans, its meaning encompasses the overall ingestion of food and excretion of wastes, as well as the building up of muscles and the growth of the body. In terms of the whole organism, metabolism includes the chemical conversion of ingested items other than food, like drugs and poisons (see Drug metabolism). This article describes the actual biology of metabolism at a cellular level, which explains just how those processes are carried out.
Metabolism includes: (1) anabolism, in which a cell uses chemical energy and reducing power to construct complex molecules, and perform life functions such as creating cellular structure; and (2) catabolism, in which a cell breaks down complex molecules to yield the chemical energy and reducing power. Cell metabolism involves complex sequences of controlled chemical reactions called metabolic pathways. Just as the word metabolism can be used to describe processes in a whole organism, the terms "anabolism" and "catabolism" can similarly be used in this way. For example, anabolic processes can also refer to building up muscle and adding body weight, while catabolic processes can refer to the loss of muscle mass and body fat.
History

The first controlled experiments on human metabolism were published by Santorio Santorio in 1614 in his book Ars de statica medecina, that made him famous throughout Europe. Santorio described his long series of personal experiments: in which he weighed himself in a chair suspended from a steelyard balance (see image), before and after eating, sleeping, working, sex, fasting, depriving from drinking, and excreting. He found that by far the greatest part of the food he took in was lost from the body through perspiratio insensibilis (insensible perspiration). In medicine and the health sciences today, the term "insensible losses" is still used to refer to the amount of fluid lost from the body through perspiration and processes that (unlike urine or feces) do not yield any obvious portion that can be weighed or measured.
At about the same time, Jan Baptist van Helmont made the first observations regarding photosynthesis, when he discovered that plant growth required (almost) no mass from the soil. The physical source of the new part of the plant was not initially obvious, but a series of further discoveries led to a basic understanding of the metabolic processes, photosynthesis, that create the newly grown portion of the plant. In the 18th century, Joseph Priestley discovered that green plants released a substance (later found to be oxygen) that could sustain the life of a mouse in an enclosed chamber. Jan Ingenhousz extended Priestley's experiments to show that it was the influence of light on the plant that enabled it to rescue the mouse ( that is, give off oxygen) and then Jean Senebier showed that CO2 was taken up by plants during photosynthesis. In 1804, the final piece was put into place by Nicolas de Saussure who discovered that the increase in plant mass (i.e. plant growth) arises not only from the fixation of atmospheric CO2, but also from the incorporation of water.
Between 1854 and 1864, Louis Pasteur discovered that glucose fermentation is due to microorganisms, and, in 1897, Eduard Buchner proved that cell-free yeast extracts could also perform these reactions, and so the ability to ferment was not limited to entire living creatures (cells)- but included certain portions of their physical contents. Subsequent investigations showed that living organisms, with few exceptions, metabolize glucose using the same mechanism, a biochemical pathway that breaks down sugar.
Overview: Harnessing energy and making chemical bonds
Living things, like all matter, obey the laws of thermodynamics. That means that energy and matter cannot be created from nothing. That means that cool things always get colder and not warmer, and it means each fragment of something is always smaller than the thing itself. But, unlike inanimate things, cells and tissues are able to harness energy and matter to change in ways that give the illusion of defying those laws. A baby does grow. A walrus' body is warmer than its icy surroundings. An amoeba can divide and shortly be two amoebas, each one the same size of the original cell that split. The metabolism of the baby, the walrus, and the amoeba is responsible for all these processes. Of course, rather than defy the laws of thermodynamics, the chemical reactions that make up metabolic processes always obey them.
Enzymes present in cells can catalyze a large variety of chemical reactions with exquisite specificity. Sometimes these enzymes are floating free in the cytoplasm of the cell, other times they are corralled together within a compartment of the cell, a special organelle. For example, the mitochondrion of cells contains enzymes for oxidative phosphorylation (a catabolic process). The Golgi apparatus of cells contains the of the enzymes used for protein posttranslational modification (an anabolic process).
Often, the chemical reactions needed to synthesize useful cell components require energy. Chemists describe these reactions as involving a positive change in free energy. Such chemical transformations are not spontaneous, but "uphill", requiring more than just the mixing together of the susbtrates. In these cases, specific enzymes may couple each "uphill" (non-spontaneous or energy requiring) reaction to a second, steep "downhill" (very spontaneous or energy releasing) reaction. Thus, thermodynamically favorable reactions can be used to "drive" each thermodynamically unfavorable one such that the the overall process goes on its own, as a spontaneous series of reactions.
ATP:the energy currency of cells
There is one particular energetically favourable reaction that is repeatedly used to drive "uphill" reactions in metabolism. This reaction, the hydrolysis of ATP into ADP and a phosphate ion, occurs again and again in metabolic pathways. ATP is sometimes called "the energy currency" (money) of cells due to this critical role and, consequently, it is vital for a cell to reconstitute the ATP pool. To restore the supply of ATP, it must be reformed from the ADP and phosphate group by coupling this "uphill" reaction to other "downhill" reactions. ATP synthesis is one of the major tasks faced by cells and is so ubiquitous that organisms can be classified according to how they derive energy for ATP synthesis. Organisms can be classified as:
Phototrophic
Phototrophic organisms can obtain energy from light. In these reactions, excitation of a photosynthetic reaction centre is caused by the absorption of a light photon. During the process, the reaction center loses an electron that excites (reduces) an electron acceptor, such as pheophytin, initiating a flow of electrons down an electron transport chain present in the thylakoid membrane. The energy released in the electron transfer steps serves to create a proton gradient across the membrane; its dissipation is used by ATP Synthase as the energy to synthesise ATP from ADP and a phosphate anion (see Chemiosmotic hypothesis). Depending on the organism, the reaction center regains the lost electron by either recycling the excited electrons or taking one from an electron donor. In plants, a water molecule serves as the electron donor through a process called photolysis, that releases oxygen gas as a waste product.
Chemotrophic
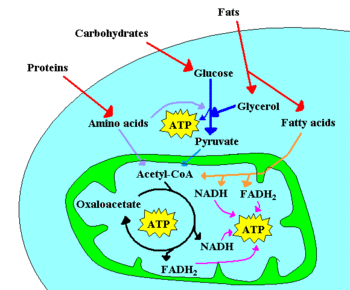
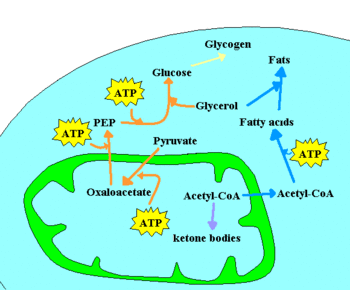
Chemotrophic organisms obtain energy from chemical reactions. For example, glucose can be oxidized to pyruvate through glycolysis. This process yields two molecules of ATP for each molecule of glucose, and releases four electrons, which reduce NAD+ to NADH. As the NAD+ molecules are scarce, the electrons present in NADH must be transferred to another molecule in order to regenerate NAD+ and to allow the degradation of more glucose molecules. NADH may donate its electrons to pyruvate (or to a pyruvate derivative), in which case a fermentation is said to occur. Alternatively, the electron acceptor may be a molecule totally unrelated to the metabolic pathway that released the electrons now present in NADH, in which case a respiration is said to occur. In the presence of NAD+, pyruvate dehydrogenase may decarboxylate pyruvate into acetyl-CoA, a pivotal molecule in metabolism. Acetyl-CoA can also be formed through β-oxidation of fatty acids or through the catabolism of amino acids, and is oxidized to CO2 through the Krebs cycle. The Krebs cycle releases eight electrons from each acetyl-CoA molecule, which are used to reduce three NAD+ to three NADH and one FAD to FADH2. The energy released in electron transfer from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen (in aerobic organisms) or other electron acceptor (in organisms that perform anaerobic respiration) may be used to create a proton gradient across a membrane, and to synthesize ATP through dissipation of this gradient (see Chemiosmotic hypothesis).
Reducing Power: obtaining electrons for chemical bonds
Reducing power is an important input into many anabolic pathways, including the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis, the biosynthesis of amino acids, and the biosynthesis of fatty acids. Reducing power is usually supplied as hydrogen equivalents carried by NADPH. Organisms can be classified according to the primary source of this reducing power as:
Organotrophic
These organisms use organic compounds (e.g. glucose) as the primary electron source.
Lithotrophic
These organisms use inorganic compounds (e.g. Fe2+, (iron ions)) as primary electron source.
Regulation of metabolism in animals
In animals, metabolism is controlled by the endocrine system through the secretion of a wide range of hormones. Some hormones have anabolic actions on the body, others have mainly catabolic actions. For example, testosterone is an anabolic hormone, and synthetic steroids that produce the anabolic actions are known as anabolic steroids. Cortisol on the other hand, which is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland, is a catabolic hormone.
In mammals, and other warm blooded animals, metabolic process are ultimately controlled by the central nervous system, which regulates the endocrine system. They are influenced by the balance between the energy demands of the organism, and the energy stores (see also Hunger). For example, fat stores secrete a hormone called leptin that acts at the hypothalamus to regulate hormone secretion. The hypothalamus is also sensitive to circulating concentrations of glucose, and to body temperature. When the ambient temperature is low, the metabolic rate of an endothermic animal will increase in order to generate more body heat (thermogenesis). In animals that hibernate, the body temperature drops down enough that the basal metabolic rate is quite low. This conserves resources over a winter period of inactivity.
Some ectothermic animals, like reptiles, regulate their body tempertaure by behavior. These "cold blooded" creatures, including lizards, snakes, and turtles, keep at an optimum body tempertaure by heating up in the sun (basking) and cooling down in the shade or the cool earth of a burrow. The metabolism of these animals also changes with body temperature, and explain the sluggish movements of an ectotherm in colder seasons or times of day.
Links to subtopics dealing with metabolism
General pathways
- Carbohydrate metabolism
- Fatty acid metabolism
- Protein synthesis
- Nucleic Acid metabolism
- Central metabolism
Anabolism
Anabolic pathways that create building blocks and compounds from simple precursors:
- Biosynthesis of amino acids and nucleotides
- Glycogenesis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Porphyrin synthesis pathway
- HMG-CoA reductase pathway, leading to cholesterol and isoprenoids.
- Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction, but that usually have ecological function.
- Photosynthesis
- Light-dependent reaction (light reaction)
- Light-independent reaction (dark reaction)
- Calvin cycle
- Carbon fixation
- Glyoxylate cycle
Catabolism
- Glycolysis
- Glycogenolysis
- Citric acid cycle
- Beta-oxidation of fatty acids
Drug metabolism
Drug metabolism pathways, the modification or degradation of drugs and other xenobiotic compounds through specialized enzyme systems:
Nitrogen metabolism
Nitrogen metabolism includes the pathways for turnover and excretion of nitrogen in organisms as well as the biological processes of the biogeochemical nitrogen cycle:
- Urea cycle, important for excretion of nitrogen as urea.
- Biological nitrogen fixation
- Nitrogen assimilation
- Nitrification
- Denitrification
Other
See also
- Metabolomics
- Metabolome
- Metabolite
- Basal metabolic rate
- Thermic effect of food
- Iron-sulfur world theory, a "metabolism first" theory of the origin of life.
- Biodegradation
- Calorimetry
- Respirometry
- Microbial metabolism
- Metabolic network modelling
- dynamic energy budget
External links
- Interactive Flow Chart of the Major Metabolic Pathways
- Metabolism, Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis - The Virtual Library of Biochemistry and Cell Biology
- The Biochemistry of Metabolism at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
- Flow Chart of Metabolic Pathways at ExPASy
- Santorio Santorio's experiments
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- Cell Metabolism academic journal home page
