Revision as of 13:44, 21 April 2009 by imported>Alice Chang
All unapproved Citizendium articles may contain errors of fact, bias, grammar etc. A version of an article is unapproved unless it is marked as citable with a dedicated green template at the top of the page, as in this version of the 'Biology' article. Citable articles are intended to be of reasonably high quality. The participants in the Citizendium project make no representations about the reliability of Citizendium articles or, generally, their suitability for any purpose.
 
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is May 21, 2009. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed.
Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration!
|
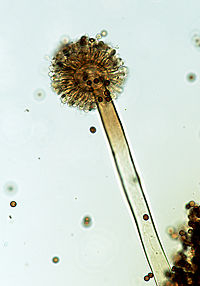
| Aspergillus niger
|
|
| Scientific classification
|
| Superkingdom:
|
Eukaryota
|
| Kingdom:
|
Fungi
|
| Subkingdom:
|
Dikarya
|
| Phylum:
|
Ascomycota
|
| Subphylum:
|
Pezizomycotina
|
| Class:
|
Eurotiomycetes
|
| Subclass:
|
Eurotiomycetidae
|
| Order:
|
Eurotiales
|
| Family:
|
Trichocomaceae
|
| Genus:
|
Aspergillus
|
| Species:
|
A. niger
|
|
| Binomial name
|
Aspergillus niger
|
Description and significance
Aspergillus niger is a fungus; it is an eukaryotic organism that has a membership in the Fungi [kingdom]]. The presence of A. niger causes plants, fruits and vegetables to grow black mold.
Genome structure
Cell structure and metabolism
Ecology
Pathology
Application to Biotechnology
Current Research
References
