Vibrio cholerae
Articles that lack this notice, including many Eduzendium ones, welcome your collaboration! |
 | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Vibrio cholerae |
Description and significance
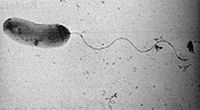
Vibrio Cholerae is a gram-negative, curved rod-shaped bacterium that has a single polar flagellum. It is an aerobic organism and thrives best in alkaline mediums.
Genome structure
The Cholera genome sequencing started in 1997 and was completed several years ago which revealed the bacterium`s two circular chromosomes with the larger of the chromosome having approximately 3 million base pairs. The smaller of the pair chromosomes have approximately one million.
According to the authors Kaper et. al at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Vibrio cholerae`s familial species seized a megaplasmid which was a sizable circular piece of DNA.
Cell structure and metabolism
Describe any interesting features and/or cell structures; how it gains energy; what important molecules it produces.
Ecology
Vibrio cholerae resides in aquatic habitats and are able to thrive in both fresh water and marine environments. In fresh water environments, the bacteria will inhabit lakes, ponds, and rivers. Marine environments such as oceans and seas are also places where V. cholerae can be found. V. cholerae are also readily found in costal areas where there are significant amounts of algal bloom.
Pathology
Vibrio cholerae is the causative agent of a serious epidemic disease Cholera. Cholera is a harmful bacterial ailment that often causes severe diarrhea which is usually procurred by drinking contaminated water. When ingested, Vibrio cholerae adapts itself to colonize in the human intestinal tract, mainly the small intestine. It then attaches to the mucosal surface which the Vibrio cholerae would produce an extoxin, the cholera toxin. The cholera toxin would then act on the intestinal mucosal cells by altering the ion transport pumps that control ion fluxes. Since water freely passes through membranes, the only way to control the movement of water into and out of tissue is to control the concentration of ions in the body. The cholera toxin diminishes the net flow of sodium into the tissue and generates a net flow of chloride and water out of the tissue and into the lumen. This causes an electrolyte imbalance in the system which in consequence, bring about copious amounts of diarrhea. If left untreated, death may ensue within a matter of hours.
Since the advancement of modern sewages and water treatment facilities, Cholera have been reduced tremendously in industrialized countries. However, Cholera is still substantially present in other parts of the world such as Asia, the Middle East, Latin America, and Sub-Saharan Africa. Social and environmental factors in these areas such as poverty, war, or natural disasters foster cholera outbreaks because people are forced to live in congested conditions with poor and insufficient sanitation.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required
