Metre (unit)
The metre (American meter) is the basic unit of length measurement in the International System of Units (SI) commonly known as the metric system. The metre is abbreviated as m, appearing after the quantity. The metre has been adopted as the fundamental unit of length in almost all countries of the world, with the United States being a notable exception.
Currently, the SI units define the metre in terms of the speed of light and the second, such that the metre is the length traveled by light in the reference medium of classical vacuum in the time interval of 1/299 792 458 second.[1][2] According to this definition, lengths may be determined in wavelengths λ of a standard source and converted to metres using the relation λ= c0 / f , where c0 = 299 792 458m/s is the defined speed of light in classical vacuum and f is the frequency of the source. As a consequence of this relation, measurement errors in frequency are mirrored in the wavelengths. A list of standard sources and measurement uncertainties is maintained by the BIPM.[3]
An easily realized and reproducible measurement is a major goal of metrology. The practicality of adoption of a time of flight as a measure of length depends critically upon the experimental fact that the speed of light in vacuum is a universal constant to within experimental error. As a result of the present definition, aside from the error in measuring transit times or frequencies, length measurements are subject only to the uncertainty in relating the medium used in a particular measurement to a reference vacuum, taken in SI units to be the classical vacuum.
The metre is also the basis of the SI units of area and volume, which are the square metre (m2) and cubic metre (m3), respectively.
History
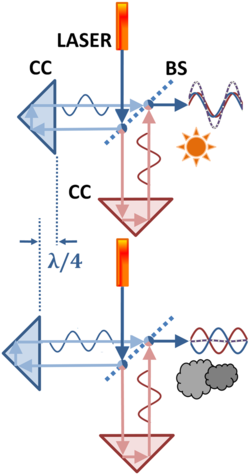
Measuring a length in wavelengths of light using a Michelson interferometer.
The metre was initially adopted as a unit of measure in France in 1790, during the French Revolution.
The original definition of the metre was the length of a pendulum with a half-period of 1 second, but was changed in 1791 to be the length of a prototype bar which was supposed to be 1/10 000 000 of the length of the meridian of Paris from the north pole to the equator. Since then, the metre has been redefined a number of times.[5]
After 1960 and before the switch to the transit-time definition in 1983, lengths were measured in terms of the number of wavelengths of light that could be fitted into them. The figure shows schematically how length was determined: the two panels show a laser source emitting a light beam split to travel two paths by a beam splitter (BS). The light is recombined by bouncing the two components off a pair of corner cubes (CC) that return the two components to the beam splitter again to be reassembled. The distance between the left-hand corner cube and the beam splitter is compared to that separation on the fixed leg as the left-hand spacing is adjusted to match the length of the object to be measured.[6]
In the top panel the path is such that the two beams reinforce each other after reassembly, leading to a strong light pattern (sun). The bottom panel shows a path that is made a half wavelength longer by moving the left-hand mirror a quarter wavelength further away, increasing the path difference by a half wavelength. The result is the two beams are in opposition to each other at reassembly, and the recombined light intensity drops to zero (clouds). Thus, as the spacing between the mirrors is adjusted, the observed light intensity cycles between reinforcement and cancellation as the number of wavelengths of path difference changes, and the observed intensity alternately peaks (sun) and dims (clouds). This behavior is called interference and the machine is called an interferometer. By counting fringes it is found how many wavelengths long the measured path is compared to the fixed leg.
This methodology for length determination requires a careful specification of the wavelength of the light used, and is one reason for employing a laser source. The precise definition of the metre was established in the 11th CGPM of 1960 as 1 650 763.73 wavelengths of the 2p10−5d5 line of krypton-86.[7] The measurement also requires careful specification of the medium in which the light propagates, which must be related to a reference medium of ideal vacuum.
This interferometer methodology had an experimental uncertainty related to determining the precise frequency of the source[8] and the careful measuring of the interference pattern that led in 1983 (along with other considerations spelled out in the final decision) to the switch to the (in principle) more exact procedure based upon the transit time of light.
In any event, precision measurement of lengths still are made in units of wavelengths of light using Michelson interferometry, with today's difference being that the wavelength unit is converted to metres using λ = c0 / f, rather than by the older more error-prone method involving a comparison with a selected standard source with a wavelength defined in metres. If a comparison of sources is to be made, it is more accurately done by comparing frequencies than by comparing wavelengths. An added advance, unrelated to the change in definition, is that today's sources are much more stable and their frequencies are better known.
Perhaps the main benefit of the change in definition was to define the metre in a manner that did not require further revision as light sources and measurement methodology advanced.
Practical measurement
Transit time measurement underlies most radio navigation systems for boats and aircraft, for example, radar and the nearly obsolete Long Range Aid to Navigation LORAN-C. For example, in one radar system, pulses of electromagnetic radiation are sent out by the vehicle (interrogating pulses) and trigger a response from a responder beacon. The time interval between the sending and the receiving of a pulse is monitored and used to determine a distance. In the global positioning system a code of ones and zeros is emitted at a known time from multiple satellites, and their times of arrival are noted at a receiver along with the time they were sent. Assuming the synchronized clocks on the satellites can be related to the receiver clock, the transit time can be found and used to provide the distance to each satellite. Receiver clock error is corrected by combining the data from four satellites.[9]
Such techniques vary in accuracy according to the distances over which they are intended for use. For example, LORAN-C is accurate to about 6km, GPS about 10m, enhanced GPS, in which a correction signal is transmitted from terrestrial stations (that is, differential GPS (DGPS)) or via satellites (that is, Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS)) can bring accuracy to a few meters or < 1 meter, or, in specific applications, centimeters. Time-of-flight systems for robotics (for example, Light Detection and Ranging LIDAR and Laser Detection and Ranging LADAR) aim at lengths of 10-100m and have an accuracy of about 5-10 mm[10]
In many practical circumstances, and for precision work, measurement of dimension using transit time measurements is used only as an initial indicator of length and is refined using an interferometer.[11][12] Measurements are made in units of wavelengths λ at a known frequency f, and related to the metre using λ = c0 / f. By using sources of several wavelengths to generate sum and difference beat frequencies, absolute distance measurements become possible. Multiple frequencies are used also to make corrections for the non-ideal properties of the medium (departures from classical vacuum), for example, by adding frequencies sensitive to the presence of water vapor.
For small objects, different methods are used that also depend upon determining size in units of wavelengths. For instance, in the case of a crystal, atomic spacings can be determined using X-ray diffraction.[13] The present best value for the lattice parameter of silicon, denoted a, is:[14]
- a = 543.102 064(14) × 10−12 m.
Similar techniques can provide the dimensions of small structures repeated in large periodic arrays like a diffraction grating.[15]
Such measurements allow the calibration of electron microscopes, extending measurement capabilities. For non-relativistic electrons in an electron microscope, the de Broglie wavelength is:[16]
with V the electrical voltage drop traversed by the electron, me the electron mass, e the elementary charge, and h the Planck constant. This wavelength can be measured in terms of inter-atomic spacing using a crystal diffraction pattern, and related to the metre through an optical measurement of the lattice spacing on the same crystal.
Measuring dimensions of localized structures (as opposed to large arrays of atoms like a crystal), as in modern integrated circuits, is done using the scanning electron microscope. This instrument bounces electrons off the object to be measured in a high vacuum enclosure, and the reflected electrons are collected as a photodetector image that is interpreted by a computer. These are not transit time measurements, but are based upon comparison of Fourier transforms of images with theoretical results from computer modeling. Such elaborate methods are required because the image depends on the three-dimensional geometry of the measured feature, for example, the contour of an edge, and not just upon one- or two-dimensional properties. The underlying limitations are the beam width and the wavelength of the electron beam (determining diffraction), determined, as already discussed, by the electron beam energy.[17] The calibration of these scanning electron microscope measurements is tricky, as results depend upon the material measured and its geometry. A typical wavelength is 0.5 Å, and a typical resolution is about 4 nm.
Another small dimension technique is the atomic force microscope. Calibration is attempted using standard samples measured by transmission electron microscopy.[18]
Other systems of units
In some systems of units, unlike the current SI system, lengths are fundamental units (for example, wavelengths in the older SI units and bohrs in atomic units) and are not defined by times of transit. Even in such units, however, the comparison of two lengths can be made by comparing the two transit times of light along the lengths. Such time-of-flight methodology may or may not be more accurate than the determination of a length as a multiple of the fundamental length unit.
Traditional units
The foot has been defined in the United States to equal exactly 0.3048 m, though an earlier definition of the survey foot was 1200/3937 m, which is different than the current definition by about one part in 500,000. The inch, being 1/12 foot, is exactly 0.0254 m, or 2.54 cm.
The modern Chinese chǐ (市尺), or "Chinese foot", has been defined to equal exactly one-third of a meter. The Hong Kong chek (尺) is exactly 0.371475 m. The Japanese kanejaku (曲尺) was defined as 10/33 m in 1891.
The Spanish vara was fixed at about 835.9 mm in 1801; however, the vara was defined in California as 838.2 mm (33 inches), and in Texas as 846.666 mm (33 1/3 inches).
References
- ↑ Resolution 1 of the 17th meeting of the Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) (1983). 1983 definition of the metre. International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Retrieved on 2011-03-19.
- ↑ The classical vacuum as a reference medium is described in Werner S. Weiglhofer and Akhlesh Lakhtakia (2003). “§ 4.1 The classical vacuum as reference medium”, Introduction to complex mediums for optics and electromagnetics. SPIE Press, 28, 34, 65. ISBN 9780819449474. and Tom G. MacKay (2008). “Electromagnetic Fields in Linear Bianisotropic Mediums”, Emil Wolf: Progress in Optics, Volume 51. Elsevier. ISBN 9780444520388.
- ↑ For example, see TJ Quinn (1999). "Practical realization of the definition of the metre (1997)". Metrologia vol 36: pp. 211-244. A web site listing current recommendations and uncertainties is maintained by the BIPM at Recommended values of standard frequencies. BIPM (2010-09-09). Retrieved on 2011-04-10. along with links to update documentation as updates occur.
- ↑ A conversion table for the SI units is maintained by NIST: Ambler Thompson and Barry N Taylor (March, 2008). Length. NIST guide for the use of the international system of units; Section B.9: Factors for units listed by kind of quantity or field of science. NIST. Retrieved on 2011-04-09. Advice on rounding conversions is provided here.
- ↑ For a brief history, see Historical context of the SI. The NIST reference on constants, units and uncertainty. NIST. Retrieved on 2011-03-08.
- ↑ The corner cube reflects the incident light in a parallel path that is displaced from the beam incident upon the corner cube. That separation of incident and reflected beams reduces some technical difficulties introduced when the incident and reflected beams are on top of each other. For a discussion of this version of the Michelson interferometer and other types of interferometer, see Joseph Shamir (1999). “§8.7 Using corner cubes”, Optical systems and processes. SPIE Press, pp. 176 ff. ISBN 0819432261.
- ↑ Resolution 6 of the 11th meeting of the CGPM (1960). 1960 definition of the metre. International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). Retrieved on 2011-03-19.
- ↑ An atomic transition is affected by disturbances, such as collisions with other atoms, leading to a range of frequencies for the transition referred to as a linewidth. Corresponding to the uncertainty in frequency is an uncertainty in wavelength. In contrast, the speed of light in ideal vacuum is not dependent upon frequency at all.
- ↑ A brief rundown is found at Donald Clausing (2006). “Receiver clock correction”, The Aviator's Guide to Navigation, 4rth ed. McGraw-Hill Professional. ISBN 9780071477208.
- ↑ Robert B Fisher and Kurt Konolige (2008). “§22.1.4: Time-of-flight range sensors”, Bruno Siciliano, Oussama Khatib, eds.: Springer handbook of robotics. Springer, pp. 528 ff. ISBN 354023957X.
- ↑ For an overview, see for example, Walt Boyes (2008). “Interferometry and transit time methods”, Instrumentation reference book. Butterworth-Heinemann, p. 89. ISBN 0750683082.
- ↑ An example of a system combining the pulse and interferometer methods is described by Jun Ye (2004). "Absolute measurement of a long, arbitrary distance to less than an optical fringe". Optics Letters vol. 29 (No. 10): p. 1153.
- ↑ Peter J. Mohr, Barry N. Taylor, David B. Newell (2008). "CODATA recommended values of the fundamental physical constants: 2006". Rev Mod Phys vol. 80: pp. 633-730. See section 8: Measurements involving silicon crystals, p. 46.
- ↑ Lattice parameter of silicon. The NIST reference on constants, units and uncertainty. National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved on 2011-04-04.
- ↑ A discussion of various types of gratings is found in Abdul Al-Azzawi (2006). “§3.2 Diffraction gratings”, Physical optics: principles and practices. CRC Press, pp. 46 ff. ISBN 0849382971.
- ↑ (2009) “Electron wavelength and relativity”, High-resolution electron microscopy, 3rd ed. Oxford University Press, p. 16. ISBN 0199552754.
- ↑ Michael T. Postek (2005). “Photomask critical dimension metrology in the scanning electron microscope”, Syed Rizvi: Handbook of photomask manufacturing technology. CRC Press, pp. 457 ff. ISBN 0824753747. and Harry J. Levinson (2005). “Chapter 9: Metrology”, Principles of lithography, 2nd ed. SPIE Press, pp. 313 ff. ISBN 0819456608.
- ↑ NG Orji et al. (2007). "TEM calibration methods for critical dimension standards". Proc. of SPIE vol. 6518. DOI:10.1117/12.713368. Research Blogging.
