Kazakhstan: Difference between revisions
John Leach (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Turkmenistan" to "Turkmenistan") |
John Leach (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "Kyrgyzstan" to "Kyrgyzstan") |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
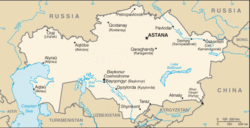
{{Image|CIA Kazakhstan map.gif|right|250px|Kazakhstan, in central Asia}} | {{Image|CIA Kazakhstan map.gif|right|250px|Kazakhstan, in central Asia}} | ||
{{Image|Orthographic projection centred over Astana Kazakhstan.png|right|100px|Directly over Astana, Kazakhstan.}} | {{Image|Orthographic projection centred over Astana Kazakhstan.png|right|100px|Directly over Astana, Kazakhstan.}} | ||
'''Kazakhstan''' ([[Kazakh language|Kazakh]]: ''Қазақстан, Qazaqstan''), officially the ''Republic of Kazakhstan'' (Kazakh: ''Қазақстан Республикасы, Qazaqstan Respublikasy''), is a country in Central [[Asia]] and [[Europe]]. Kazakhstan is the 9th largest country in the world with a territory of 2,727,300 km² and the largest landlocked country. Kazakhstan has the 62nd largest population in the world, with a population density of less than 6 people per square kilometre (15 per sq. mi.). It has borders with [[Russia]], | '''Kazakhstan''' ([[Kazakh language|Kazakh]]: ''Қазақстан, Qazaqstan''), officially the ''Republic of Kazakhstan'' (Kazakh: ''Қазақстан Республикасы, Qazaqstan Respublikasy''), is a country in Central [[Asia]] and [[Europe]]. Kazakhstan is the 9th largest country in the world with a territory of 2,727,300 km² and the largest landlocked country. Kazakhstan has the 62nd largest population in the world, with a population density of less than 6 people per square kilometre (15 per sq. mi.). It has borders with [[Russia]], Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and China. | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
For most of its history the territory of modern-day Kazakhstan has been inhabited by nomadic tribes. By the 16th century the Kazakhs emerged as a distinct group, divided into three hordes. The Russians began advancing into the Kazakh steppe in the 18th century, and by the mid-19th century all of Kazakhstan was part of the Russian Empire. Following the 1917 Russian Revolution and civil war, the territory of Kazakhstan was reorganized several times before becoming the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic in 1936, a part of the USSR. During the 20th century, Kazakhstan was the site of major Soviet projects, including Khrushchev's Virgin Lands campaign, the Baikonur Cosmodrome, and the Semipalatinsk "Polygon", the USSR's primary nuclear weapon testing site. Kazakhstan declared itself an independent country on December 16, 1991, the last Soviet republic to do so. | For most of its history the territory of modern-day Kazakhstan has been inhabited by nomadic tribes. By the 16th century the Kazakhs emerged as a distinct group, divided into three hordes. The Russians began advancing into the Kazakh steppe in the 18th century, and by the mid-19th century all of Kazakhstan was part of the Russian Empire. Following the 1917 Russian Revolution and civil war, the territory of Kazakhstan was reorganized several times before becoming the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic in 1936, a part of the USSR. During the 20th century, Kazakhstan was the site of major Soviet projects, including Khrushchev's Virgin Lands campaign, the Baikonur Cosmodrome, and the Semipalatinsk "Polygon", the USSR's primary nuclear weapon testing site. Kazakhstan declared itself an independent country on December 16, 1991, the last Soviet republic to do so. | ||
Revision as of 07:11, 29 February 2024
Kazakhstan (Kazakh: Қазақстан, Qazaqstan), officially the Republic of Kazakhstan (Kazakh: Қазақстан Республикасы, Qazaqstan Respublikasy), is a country in Central Asia and Europe. Kazakhstan is the 9th largest country in the world with a territory of 2,727,300 km² and the largest landlocked country. Kazakhstan has the 62nd largest population in the world, with a population density of less than 6 people per square kilometre (15 per sq. mi.). It has borders with Russia, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and China.
History
For most of its history the territory of modern-day Kazakhstan has been inhabited by nomadic tribes. By the 16th century the Kazakhs emerged as a distinct group, divided into three hordes. The Russians began advancing into the Kazakh steppe in the 18th century, and by the mid-19th century all of Kazakhstan was part of the Russian Empire. Following the 1917 Russian Revolution and civil war, the territory of Kazakhstan was reorganized several times before becoming the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic in 1936, a part of the USSR. During the 20th century, Kazakhstan was the site of major Soviet projects, including Khrushchev's Virgin Lands campaign, the Baikonur Cosmodrome, and the Semipalatinsk "Polygon", the USSR's primary nuclear weapon testing site. Kazakhstan declared itself an independent country on December 16, 1991, the last Soviet republic to do so.
Culture
Kazakhstan is ethnically and culturally diverse, in part due to mass deportations of many ethnic groups to the country during Stalin's rule. Kazakhs are the largest group, followed by Russians. Kazakhstan allows freedom of religion, and many different beliefs are represented in the country. Islam is the primary religion, followed by Orthodox Christianity. The official language is Kazakh, and Russian is a language of interethnic communication.