Normal weight obesity: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Nancy Sabatier No edit summary |
imported>Gareth Leng No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Appetite.jpg|right|250px}} | |||
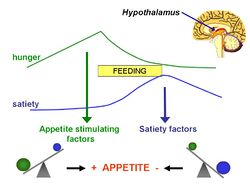
More than half of American adults who have a normal body weight nevertheless have high body fat percentages (>20% for men and >30% for women), as well as heart and metabolic disturbances, giving rise to the concept of '''normal weight obesity'''. <ref>Romero-Corral A ''et al.'' (2010) Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality'' Eur Heart J'' 31:737-46 PMID 19933515</ref> | More than half of American adults who have a normal body weight nevertheless have high body fat percentages (>20% for men and >30% for women), as well as heart and metabolic disturbances, giving rise to the concept of '''normal weight obesity'''. <ref>Romero-Corral A ''et al.'' (2010) Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality'' Eur Heart J'' 31:737-46 PMID 19933515</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 09:08, 13 September 2011
For the course duration, the article is closed to outside editing. Of course you can always leave comments on the discussion page. The anticipated date of course completion is 01 April 2012. One month after that date at the latest, this notice shall be removed. Besides, many other Citizendium articles welcome your collaboration! |
More than half of American adults who have a normal body weight nevertheless have high body fat percentages (>20% for men and >30% for women), as well as heart and metabolic disturbances, giving rise to the concept of normal weight obesity. [1]
References
- ↑ Romero-Corral A et al. (2010) Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality Eur Heart J 31:737-46 PMID 19933515