Malassezia pachydermatis: Difference between revisions
imported>Mellie Tulcan No edit summary |
imported>Meg Taylor (restoring missing subpages) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
| color = violet | | color = violet | ||
Revision as of 21:35, 5 September 2009
 | ||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
Description and significance
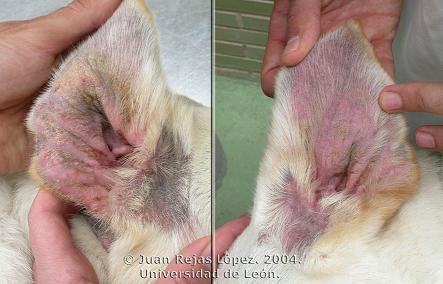
Malassezia pachydermatis is a lipophilic organism (prefer lipid rich areas) whose uncontrolled growth may lead to pruritic (itching) dermatitis. 1,3 It is one of the 10 species that make up the Malassezia genus. It most commonly affects pets that have preexisting allergies that have not properly been treated or are predisposed to excess moisture in certain parts of the body such as the ear canal or nail bed. 3
Signs and Symptoms1
Each case is unique but may exhibit varying degrees of the following symptoms:
- Lesions between the affected pet’s skin folds and varying parts of the body.
- Bruised skin may be red (erythematous), hyperpigmented, scaly, greasy or dry. The fur may also be stained brown due to salivary staining from excessive licking.
- Persistent and painful scratching and/or head shaking.
- The skin folds may have plaques or discharge as a result of a seborrheic infection.
- A strong odor similar to that of rancid milk.
Treatment Methods1
Treatment may vary depending on the doctor and the severity of the case but may include:
- Topical medications that are both antiseborrheic and antifungal that should be used several times a week. They may include formulas that are salicylic acid, benzoyl peroxide, or ketoconazole based along with other active ingredients.
- Systemic (oral) medications can be used in conjunction with topical therapies or for the most severe cases. Medications such as ketoconazole, itraconazole, or fluconazole may be used.
- Oral antibiotics are also helpful to treat secondary bacterial infections that may arise.
In severe cases that do not respond quickly to treatment, the infection can only be controlled when the underlying cause of Malassezia overgrowth is suppressed. It should also be noted that excessive use of corticosteroids may cause the Malassezia pachydermatis to develop a resistance to therapy. Such an event would cause an overgrowth of the yeast that cannot be easily treated.
Cell structure and metabolism
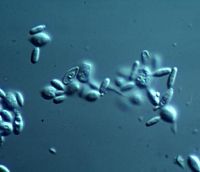
Malassezia pachydermatis is an ovoid peanut shaped yeast that reproduces by unipolar budding (producing two individuals from one organism).3,4 They can be seen with a microscope under high magnification and are between 3 and 8 μm in length. Malassezia pachydermatis is not a lipid dependent organism therefore it can be cultured using Sabouraud’s dextrose agar. 3
Ecology
It is part of the animal’s normal microflora and is commonly found within the ear canals, the mucosa of the anus and oral cavities, as well as the anal sacs and vagina. 1,3 Malassezia pachydermatis is an opportunistic infection in which the organism becomes pathogenic due to an impaired immune system. It can affect any breed if the conditions for overgrowth are ideal, but dogs tend to be more frequently affected then cats. There is no indication that the infection is contagious. 1,3
Pathology
As stated in the pervious section a small amount of Malassezia pachydermatis can normally be found on the skin. When the animal develops certain conditions that allow for excess sebum production or excess moisture, an overgrowth of yeast will result. Excessive licking and an oily coat can allow the yeast to colonize the skin, especially the nail beds. Malassezia dermatitis is more prevalent in animals that live in predominantly humid area or suffer from seasonal allergies. 1,3 Malassezia pachydermatis that has been cultured from affected dogs tend to produce a variety of enzymes that include protease, lipase and glucosidase among others. These enzymes have been known to contribute to the inflammation, and itching associated with Malassezia infections by altering the areas pH levels as well as the degradation of enzymes (proteolysis) and fats (lipolysis). 3 Malassezia infections in dogs are most often a result of allergic hypersensitivity (atopy) to the environment or possibly food. Dogs with preexisting endocrine and keratinization disorders are also prone to Malassezia dermatitis. Malassezia is rare in cats but they do occur as a secondary infection to certain preexisting diseases (feline immunodeficiency virus or diabetes mellitus) or internal malignancy. 4
Current Research
Identification of Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria and Yeast Isolated from Healthy Dogs and Dogs with Otitis Externa5
This study focused on isolating organisms that are commonly found on the external ear canals of both healthy dogs and those suffering from ear infections (otitis externa), and determining their susceptibility to certain antimicrobial. The most commonly found organism was Staphylococcus intermedius followed by Malassezia pachydermatis as well as a variety of different bacteria and yeasts in smaller amounts. While the susceptibility of Staphylococcus intermedius varied based on individual resistance, Malassezia pachydermatis responded well to all the antifungal agents it was exposed to. The yeast, Malassezia pachydermatis, had not yet evolved to the point where it could develop a resistance to treatment allowing it to routinely respond to the medication. Malassezia pachydermatis is commonly found on the skin of most animals; it can become pathogenic when the skin’s normal microflora becomes altered. In healthy ears, Malassezia pachydermatis was isolated 15% to 50% of the time where as in subjects suffering from otitis externa had a higher rate of isolation increased to 83%. Usually, bacteria and yeast will be the causative agents of otitis externa making treatment difficult. Microbial cultures must be performed carefully to ensure that there is proper isolation to determine all the organisms present and their particular susceptibilities.
Comparative in vitro antimicrobial efficacy of commercial ear cleaners6
This study set out to determine which commercial ear cleaner would be the most effective based on its antimicrobial abilities. It was intended to help medical professionals make a decision on which product would be better in individual cases. Isolates of Staphylococcus intermedius, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Malassezia pachydermatis, which are common pathogens of otitis externa, were prepared and incubated with various ear cleaners at 38°C to determine which product would have the most inhibitory effect. Every ear cleaner is unique meaning the active ingredients will vary between the brands altering their effectiveness. Ceruminolytics helps to loosen up earwax within the canal and remove debris from the ear as well. Surfactants will liquefy debris and astringents dry the skin to prevent it from becoming too moist. Ideally the ear cleaners should have limited the growth of yeast and bacteria in order to keep the ear canals healthy and clean. The study revealed the antimicrobial ability of the commercial ear cleaners varied greatly; therefore making it hard to determine which cleaner would be best. The results may have not been reliable because it is difficult to replicate the actual conditions within the ear canal. Also the thirty-minute incubation time may have been an overestimate of how long the cleaner would actually stay within the ear. Usually, dogs with otitis externa have a combination of organisms within the ear not just one; thereby, making it hard to determine which cleaner would be best.
RADP differentiation of Malassezia spp. from cattle, dog and humans7
The molecular makeup of dogs, cattle, and humans has not really been studied. This paper attempted to analyze the DNA profiles of these animals using random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD)-PCR in order to compare the genetic diversity of Malassezia isolates from the external ear canals. The RAPD technique used different primers, which allowed for identification of some intra-species variations indicating that there were differences in the species’ genetic makeup. A total of twenty-seven strains were isolated; fourteen from bovine ears, four from dogs suffering from otitis externa, and seven from human ears. The results of this study indicated that there was a genetic heterogeneity between the profiles of Malassezia pachydermatis, Malassezia slooffiae, and Malassezia furfur. Ideally, identifying the differences and variations between the RAPD profiles from different animals could help in monitoring the possible pathogenicity of Malassezia in animals and humans. There was a study referenced in this paper that showed the normally zoophilic Malassezia pachydermatis was cultured from newborn children in the neonatal intensive care unit. It may be possible to transmit the yeast to others via unwashed exposed hands; as result individuals should consider Malassezia pachydermatis zoonotic. 1 The isolates were shown to be genetically similar showing homogeneity in the RFLP fingerprints.
References
[1] Malassezia Dermatitis. Clinical Veterinary Advisor: Dog and Cats. 2009 http://cote.clinicalvetadvisor.com/content/printpage.cfm?ID=CS141736988 Accessed 8 March 2009
[2] Hnilica, Keith A., DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVD, Medleau, Linda, DVM, MS, Diplomate ACVD (2006) Small Animal Dermatology: A Color Atlas and Therapeutic Guide. Missouri: Saunders El Sevier, 64 p.
[3] Griffin, Craig E., DVM, Miller, William H. JR., VMD, Scoot, Danny W. (2001). Small Animal Dermatology. New York: W.B. Saunders Company. 117, 119, 363-374, 1213-1215 p.
[4] Harvey, Richard G., BVSc, CBiol, MIBiol, DVD, Mckeever, Patrick J., DVM, MS, DACVD (1998). Color Handbook of Skin Diseases of the Dog and Cat. Iowa: Iowa State Press. 34-35
[5] Lyskova, P., Vydrzalova, M., Mazurova, J. (2007) “Identification and Antimicrobial Susceptibility of Bacteria and Yeasts Isolated from Healthy Dogs and Dogs with Otitis Externa” Available: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/118541609/HTMLSTART Accessed 15 April 2009
[6] Swinney, A., Fazakerley, J., McEwan, N., and Nuttall, T. (2008) “Comparative in vitro antimicrobial efficacy of commercial ear cleaners” Available: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/121542126/HTMLSTART Accessed 23 April 2009
[7] Duarte, E., Hamdan, J. (2009) “RADP differentiation of Malassezia spp. from cattle, dog and humans” Available: http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/122239063/HTMLSTART Accessed 23 April 2009