Leptotes (orchid): Difference between revisions
imported>Dalton Holland Baptista No edit summary |
imported>Dalton Holland Baptista |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
{{Image|Leptotes bicolor Edwards.jpg|right|280px|Original illustration published by John Lindley when he described the genus ''Leptotes'', in 1833.}} | {{Image|Leptotes bicolor Edwards.jpg|right|280px|Original illustration published by John Lindley when he described the genus ''Leptotes'', in 1833.}} | ||
In April of 1833, it blossomed in the greenhouse of Mrs. Arnold Harrison, English collector of orchids homaged in diverse descriptions of noted species such as ''[[Bifrenaria harrisoniae]]'' and ''[[Cattleya harrisoniana]]'' an unknown species that she had received from [[Serra dos Órgãos]] mountains, in Brazil. Little time later, Mrs. Harrison sent a drawing and cut of this plant to the botanist [[John Lindley]], who verified to be a new species. In its description, dated of the same year, Lindley suggests the name of ''Leptotes'', of [[Greek language |Greek]], ''mild'', ''delicate'', in reference to the appearance of the flowers of this plant. He affirms that ''Leptotes'' is similar and close to ''[[Tetramicra]]'' from which it is distinguished by the structures of the pollinarium and by the lateral lobes of the lip of its flowers, much smaller; and because they have no calcar attached to the [[ovarium]]. He also explains that from ''Brassavola'' it can be differentiated by the pollinia and trilobed lip. Then Lindley describes its [[type-species]], ''[[Leptotes bicolor]]''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Lindley, John</span>: ''Leptotes bicolor'' in '''Edward's Botanical Register Vol.19''', t.1625. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1833. [http://www.botanicus.org/item/31753002748314 Published on internet.]</ref> | In April of 1833, it blossomed in the greenhouse of Mrs. Arnold Harrison, English collector of orchids homaged in diverse descriptions of noted species such as ''[[Bifrenaria harrisoniae]]'' and ''[[Cattleya harrisoniana]]'' an unknown species that she had received from [[Serra dos Órgãos]] mountains, in Brazil. Little time later, Mrs. Harrison sent a drawing and cut of this plant to the botanist [[John Lindley]], who verified to be a not only a new species but yet new genus. In its description, dated of the same year, Lindley suggests the name of ''Leptotes'', of [[Greek language |Greek]], ''mild'', ''delicate'', in reference to the appearance of the flowers of this plant. He affirms that ''Leptotes'' is similar and close to ''[[Tetramicra]]'' from which it is distinguished by the structures of the pollinarium and by the lateral lobes of the lip of its flowers, much smaller; and because they have no calcar attached to the [[ovarium]]. He also explains that from ''Brassavola'' it can be differentiated by the pollinia and trilobed lip. Then Lindley describes its [[type-species]], ''[[Leptotes bicolor]]''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Lindley, John</span>: ''Leptotes bicolor'' in '''Edward's Botanical Register Vol.19''', t.1625. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1833. [http://www.botanicus.org/item/31753002748314 Published on internet.]</ref> | ||
In 1838, Lindley received two similar but slightly different plants, collected in [[Macaé de Cima]] and [[Ilha Grande]], in [[Rio de Janeiro]]. Considering them different of the previously described species, because the lateral lobes of lip were slightly serrated, because their flowers were bigger, and also because they occasionally had a second leaf by pseudobulb, proposed a new species with the name of ''Leptotes serrulata''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Lindley, John</span>: ''Leptotes serrulata'' in '''Sertum orchidaceum''', t.11. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1838. [http://www.botanicus.org/item/31753002748314 Published on internet.]</ref> Five years later, the German Count [[Johann Centurius von Hoffmannsegg]], considering that the leaves of one plant he cultivated presented a different green-bluish tone, described the plant calling it ''L. glaucophylla''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Hoffmannsegg, Johann Centurius von</span>: ''Leptotes glaucophylla'' in '''Botanische Zeitung Vol.1''', p. 833. Berlin, 1843.</ref> When reviewing all the known species ''Leptotes'' at the time, in 1990, [[Carl Leslie Withner]], opposing diverse previous taxonomists, who already had noticed the great similarity of all the species described so far, goes yet further and, based on the drawings published by Lindley, finds additional differences between ''L. bicolor'' and ''L. serrulata'', affirming that second always bears many more flowers, with up to seven flowers for inflorescence, which is also much longer. <ref name="W"><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Withner, Carl Leslie</span>: '''The Cattleyas and Their Relatives, Vol. 3''', p.96. Timber Press, Oregon. ISBN 0881922692</ref> Today we know that both descriptions are of slight variations of ''L. bicolor'', that, for its ample dispersion and multiplicity of populations, is a much variable plant.<ref name="K"><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Govaerts, Rafaël ''et al''</span>: '''World Checklist of Orchidaceae'''. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. [http://www.kew.org/wcsp Published on Internet] (Access in January 2009).</ref> | In 1838, Lindley received two similar but slightly different plants, collected in [[Macaé de Cima]] and [[Ilha Grande]], in [[Rio de Janeiro]]. Considering them different of the previously described species, because the lateral lobes of lip were slightly serrated, because their flowers were bigger, and also because they occasionally had a second leaf by pseudobulb, proposed a new species with the name of ''Leptotes serrulata''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Lindley, John</span>: ''Leptotes serrulata'' in '''Sertum orchidaceum''', t.11. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1838. [http://www.botanicus.org/item/31753002748314 Published on internet.]</ref> Five years later, the German Count [[Johann Centurius von Hoffmannsegg]], considering that the leaves of one plant he cultivated presented a different green-bluish tone, described the plant calling it ''L. glaucophylla''.<ref><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Hoffmannsegg, Johann Centurius von</span>: ''Leptotes glaucophylla'' in '''Botanische Zeitung Vol.1''', p. 833. Berlin, 1843.</ref> When reviewing all the known species ''Leptotes'' at the time, in 1990, [[Carl Leslie Withner]], opposing diverse previous taxonomists, who already had noticed the great similarity of all the species described so far, goes yet further and, based on the drawings published by Lindley, finds additional differences between ''L. bicolor'' and ''L. serrulata'', affirming that second always bears many more flowers, with up to seven flowers for inflorescence, which is also much longer. <ref name="W"><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Withner, Carl Leslie</span>: '''The Cattleyas and Their Relatives, Vol. 3''', p.96. Timber Press, Oregon. ISBN 0881922692</ref> Today we know that both descriptions are of slight variations of ''L. bicolor'', that, for its ample dispersion and multiplicity of populations, is a much variable plant.<ref name="K"><span style="font-variant:small-caps;">Govaerts, Rafaël ''et al''</span>: '''World Checklist of Orchidaceae'''. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. [http://www.kew.org/wcsp Published on Internet] (Access in January 2009).</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:00, 25 February 2009
| Leptotes | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Leptotes bicolor
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Type species | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Leptotes bicolor Lindl. 1833 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonym | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
None |
Leptotes is a genus of orchids formed by nine small species of Brazil which exist in the dry jungles of South and Southeast, and also in Paraguay or Argentina. They are small epiphytic plants of caespitific growth, that sometimes resemble little Brassavola, as they share same type of thin terete leaves, however, they are more closely related to Loefgrenianthus.
Some species of Leptotes are widely cultivaded and form showy displays when completely in bloom, yet the majority of species are not commonly found under cultivation, some are rare or even almost completely unknown. Five species have only been described after year 2000. They are not included among the orchids easiest to grow. Beside being cultivated for their ornamental value, there are records of eventual uses of the flowers and fruits of Leptotes bicolor as milk, ice cream, tea and candies aromatizers instead of Vanilla.[1]
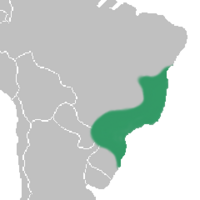
Distribution
The species of Leptotes are originary from Atlantic Forest of Brazil, two species also found in other countries, L. unicolor in Argentina, and L. bicolor in Paraguay, always living epiphyticaly. Three species show high degree of endemism in the South of Bahia State, these do not exist in any other places. The distribution of one species is only an assumption. The states southeastern of Brazil are the ones that present the highest level of species occurrence, however, the extreme limits of distribution range from the Serra da Jibóia chain of mountains, in Bahia, to the North of Rio Grande do Sul State.[2]
The species of the group of wide open flowers, as Leptotes tenuis and L. pauloensis, are more frequent in cloud mountain forests. L. bicolor is the species most spread out and adaptated both to cloud mountanin forests and to the dryer woods of plateaus above of Serra do Mar chain of Mountains. Leptotes unicolor is a plant from coller areas, above 700 meters of altitude, frequently found growing on Araucaria and Podocarpus trees in the Southern areas of Brazil.[2]
Description
The species assigned to the genus Leptotes are plants of short rhizome, of cylindrical section, with very small pseudobulbs that almost imperceptibly prolongate in one, rarely two, short or long, erect or hanging, terete fleishy leaves, of dark green or purple colors, frequently presenting wrinkly surfaces, with a more or less deeper ridge in the face. The inflorescence is apical, generally short, and grows from the apex of the pseudobulb, without a protecting spathe, bearing one to seven flowers, however two or three are more common. The flowers are relatively large when are compared to the plant dimensions, normally partially bent, in some species forming groups of very showy aspect.[2]
Their flowers generally are of different shades of pink, greenish or white, with lip spotted of pale yellow, light purple or lilac, perfumed, which last from ten to twenty days.[3] The petals and sepals are similar, elongated, of the same color, the petals slightly narrower than the sepals. The lip is located along the column, trilobated, with small lateral lobes, raised aside of the column, however never involving it, or flat; the intermediate lobe is much bigger than the lateral ones, showing lanceolated or obovated format, occasionally fleishy, flat or bending backwards; in some species with denticulated edges, in other with smooth ones; rarely calli are present and it has claws wich hold it attached to the sides of the column. This is short, thick and erect, normally greenish, biauriculated, and bears six pollinia of different sizes, two larger in the center and four smaller in two pairs hold by a short caudicle, in an arrangement without similar among the orchids. Their fruits are rounded, succulent and perfumed as the ones of Vanilla.[4]
Leptotes pollination has never been observed and the assumptions about its agents are different, Cássio van den Berg assumes that, because of the colors and morphology of its flowers, they might be pollinated by bees,[2] while other orchidologists indicate the possibility of hummingbird pollination.[3]
Taxonomic notes
In April of 1833, it blossomed in the greenhouse of Mrs. Arnold Harrison, English collector of orchids homaged in diverse descriptions of noted species such as Bifrenaria harrisoniae and Cattleya harrisoniana an unknown species that she had received from Serra dos Órgãos mountains, in Brazil. Little time later, Mrs. Harrison sent a drawing and cut of this plant to the botanist John Lindley, who verified to be a not only a new species but yet new genus. In its description, dated of the same year, Lindley suggests the name of Leptotes, of Greek, mild, delicate, in reference to the appearance of the flowers of this plant. He affirms that Leptotes is similar and close to Tetramicra from which it is distinguished by the structures of the pollinarium and by the lateral lobes of the lip of its flowers, much smaller; and because they have no calcar attached to the ovarium. He also explains that from Brassavola it can be differentiated by the pollinia and trilobed lip. Then Lindley describes its type-species, Leptotes bicolor.[5]
In 1838, Lindley received two similar but slightly different plants, collected in Macaé de Cima and Ilha Grande, in Rio de Janeiro. Considering them different of the previously described species, because the lateral lobes of lip were slightly serrated, because their flowers were bigger, and also because they occasionally had a second leaf by pseudobulb, proposed a new species with the name of Leptotes serrulata.[6] Five years later, the German Count Johann Centurius von Hoffmannsegg, considering that the leaves of one plant he cultivated presented a different green-bluish tone, described the plant calling it L. glaucophylla.[7] When reviewing all the known species Leptotes at the time, in 1990, Carl Leslie Withner, opposing diverse previous taxonomists, who already had noticed the great similarity of all the species described so far, goes yet further and, based on the drawings published by Lindley, finds additional differences between L. bicolor and L. serrulata, affirming that second always bears many more flowers, with up to seven flowers for inflorescence, which is also much longer. [8] Today we know that both descriptions are of slight variations of L. bicolor, that, for its ample dispersion and multiplicity of populations, is a much variable plant.[9]
In 1865, Heinrich Gustav Reichenbach, received, from some unknown locality in Brazil, the second described species to be accepted today, a plant much different from Leptotes bicolor, because of its fewer and smaller rounded flowers, with wide open pale yellowish segments. He published it as L. tenuis.[10] Twelve years later, the third species, Leptotes unicolor, was described by Brazilian Botanist João Barbosa Rodrigues. According to the author, it was a much perfumed little species which he found some colonies with hundreds of plants living epiphyticaly along the banks of rivers Dourado and Sapucai, nearby the city of Alfenas, in Minas Gerais.[11] In 1881, Barbosa Rodrigues found another plant with longer leaves and slight diferences on floral structure, in Joinville, a city that at the time belonged to Paraná State, but today is located in Santa Catarina which didn't exist then, and described it as L. paranaensis.[12] Today this species is considered to be just a variation of L. unicolor he described four years earlier.[13]
Eight years later, Robert Allen Rolfe received form Brazil, also without information of locality, a plant similar to Leptotes tenuis which Reichenbach described in 1865, however, with much thicker and shorter leaves. Rolfe described it as L. minuta.[14] In his revision of Brazilian orchid species, published 1903, Célestin Alfred Cogniaux, ignoring the variability of Leptotes species, both because of populations insolation and because of the variability of lenght and thickness of leaves due to diferent degrees of light exposure on each habitat, accepted this species which we know today is just a variation of L. tenuis. Cogniaux did not have the opportunity to check the types of all other species then described, therefore, he accepted most of them with this remark.[15]
Johan Albert Constantin Loefgren, the Swedish Botanist living in Brazil, received from Itatiaia, Rio de Janeiro, in 1918, one orchid with with pending habit, thin flat leaves, and flowers that rememinded the ones of Leptotes, although its lips formed a pouch. He described it as Leptotes blanche-amesiae.[16] Later Frederico Carlos Hoehne concluded this species, despite closely related, might be better placed in another genus thus, as an hommage to Loefgren, proposed the genus Loefgrenianthus to accomodate it.[17] Hoehne also described a new species, Leptotes pauloensis, naming it so because is was found in São Paulo State, in 1934. This species is close to Leptotes tenuis but has flowers of diferent colors. During decades taxonomists were not sure if this was to be considered a good species indeed. Guido Pabst considered it as a synonym of the later;[13] in 1990 Withner claimed that after being desappeared for many years, finally the doubts about its status were cleared as many had been found and it really should be accepted as good.[8]
Therefore in 2004 four species of Leptotes were known, three sufficiently different to each other and well stablished, L. bicolor, L. unicolor and L. tenuis, and one fourth, L. pauloensis, occasionally considered synonym of the previous one, but more frequently accepted by taxonomists. In this year, the species number doubled as other four were described. However, the history of these descriptions starts much earlier, in 1954, when one of the associates of Círculo Paulista de Orquidófilos, an orchid society in São Paulo, presented a lecture where he talked long and informally about the innumerable varieties of Leptotes that he found and gathered throughout the years and the names he particularly atributed to each. This lecture was printed and distributed in the bulletin of the association.[18] In 2004, Eric A. Christenson, aware of this publication, found in culture in particular collections in the United States two of the several varieties mentioned in the lecture and decided to describe them formally as independent species. One of these plants, Leptotes harryphillipsii, is very similar to L. pauloensis already a problematic species by itself.[19] The other one, L. mogyensis, is an unknown species to Brazilians, both scholar and collectors, except for the plant Christenson found in the US, supposedly originated from Mogi das Cruzes, a city nearby São Paulo.[20]
The other two species described in 2004 belong to the affinity of Leptotes bicolor and have been both found by the same surveyor in the region of Buerarema, south of Bahia. Leptotes bohnkiana , which name is a homage to its finder, can be differentiated because of its smaller size,[21] the other, L. pohlitinocoi, mostly by color.[22] Finally, in 2006 Sidney Marçal de Oliveira discovered the last species to be described, also from Bahia, although inhabitant of Chapada Diamantina, Leptotes vellozicola is much diferent from all the other species.[23]
Phylogeny
According to Cássio van den Berg et al., Leptotes is very closely related to Loefgrenianthus and both situated between Pseudolaelia and the genus which once used to be classified as Schomburgkia, by some now considered part of Laelia.[24]
Species
The three main characteristics that differentiate between the species of Leptotes are the general proportions of the leaves, the shape of the flowers and way the flowers open. Using these differences the species can be classified into two main groups.
One group is formed by the four species with flowers of elongated segments, which generally are not widely open. These species use to present malleable inflorescences that leave the flowers slightly or very overthrown, frequent facing down. Almost all the species of this group have long leaves, of comparatively lighter tones, generally with smooth surfaces, longer than the inflorescences.
- Leptotes unicolor is the exception in this group as it has short, wrinkly and dark leves. Its flowers, of generally uniform pale pink, always face down. The other species of this group have flowers of stronger colors.[25]
- Leptotes bicolor is the species with more flowers per inflorescence and with wider distribution. It is a much variable species, even tho easily recognizeable because of its bicolored flowers, of white sepals and petals and purple lip, occasionally bearing two leaves per pseudobulb. There are some records of this species living as a lithophytic.[3]
- Leptotes bohnkiana is similar to L. bicolor, however, its flowers measure only one third of the dimensions of the second ones, with segments proportionally wider, the plant measures only one half. All the plants found had only one flower per inflorescence. It just exists in Bahia.[21]
- Leptotes pohlitinocoi is even closer to L. bicolor but has slightly smaller flowers with all segments completely pink. It just exists in Bahia.[26]
The other group is formed by five smaller species with more rounded flowers of wide open flatter segments and much shorter wrinkly leaves, generally very dark green or purple colored. The species of this group often have only one or two flowers each inflorescence. Four of them are much similar and sometimes difficult to distinguish.
- Leptotes vellozicola is the only easily recognizeable species in this group as it has a thick central callus next to the lip apex. It is the only species of this group endemic of Bahia, all the other are from Southeast and South Brazil.[23]
- Leptotes tenuis is the only Leptotes species with pale green, yellowish or white flowers and lilac lip. It is a very small and uncommon species from Southeastern States of Brazil.[27]
- Leptotes pauloensis is a species very similar to the previous one and can be separated from it mainly by the color of the floral segments, which are inverted here, that is, pale lilac petals and sepals and white lip with a yellowish cream mark in the middle. Its distribution overlaps L. tenuis but extends much more into South.[28]
- Leptotes harryphillipsii, another similar species to the previous, however with slightly longer lip and discrete pink stripes on the other segments, which shows a little more vibrant colors. It seems this species has been known for long time but has been always confused with the true L. pauloensis.[19]
- Leptotes mogyensis, yet another species closely related to L. tenuis but always bearing white flowers with a deep purple central mark on the lip. There is no record of this plant in the wild. All information comes from a plant found under cultivation in the USA.[20]
Culture
As the roots of Leptotes rot easily with excessive humidity, the best results for their culture are achieved when they are mounted on plaques of vegetal fiber or tree cork. Watering and fertilizer must be more frequent during active growth periods and less during dormant periods. Ideal growth conditions require an intermediate temperature and exposure to filtered sunlight.[29]
References
- ↑ Lawler, L.J.: Ethnobotany of the Orchidaceae in Orchid biology: reviews and perspectives, Vol.3. J. Arditti Ed., Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York, 1984.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Van den Berg, Cássio: Leptotes in Genera Orchidacearum Vol.4, pp. 271-3. Oxford University Press, 2006. ISBN 9780198507123.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Miller, David; Richard Warren; Izabel Moura Miller & Helmut Seehawer: Serra dos Órgãos sua história e suas orquídeas, p. 240. Rio de Janeiro, 2006.
- ↑ Withner, Carl Leslie: The Cattleyas and Their Relatives, Vol. 3, pp.94-95. Timber Press, Oregon. ISBN 0881922692
- ↑ Lindley, John: Leptotes bicolor in Edward's Botanical Register Vol.19, t.1625. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1833. Published on internet.
- ↑ Lindley, John: Leptotes serrulata in Sertum orchidaceum, t.11. James Ridgway & Sons Ed. London, 1838. Published on internet.
- ↑ Hoffmannsegg, Johann Centurius von: Leptotes glaucophylla in Botanische Zeitung Vol.1, p. 833. Berlin, 1843.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Withner, Carl Leslie: The Cattleyas and Their Relatives, Vol. 3, p.96. Timber Press, Oregon. ISBN 0881922692
- ↑ Govaerts, Rafaël et al: World Checklist of Orchidaceae. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Published on Internet (Access in January 2009).
- ↑ Reichenbach, Heinrich Gustav: Leptotes tenuis in Hamburger Garten Blumenzeitung Vol.21, pp. 296. Hamburg, 1865.
- ↑ Barbosa Rodrigues, João: Leptotes unicolor in Genera et species orchidacearum novarum Vol.1, p.74. 1877. Published on Internet, in French and Latin.
- ↑ Barbosa Rodrigues, João: Leptotes paranaensis in Genera et species orchidacearum novarum Vol.2, pp.163. 1881. Published on Internet, in French and Latin.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Pabst, Guido & Dungs, Fritz : Orchidaceae Brasilienses vol. 1 p. 148, Brucke-Verlag Kurt Schmersow, Hildesheim, 1975. ISBN 3871050106
- ↑ Rolfe, Robert Allen: Leptotes minuta in Gardeners' Chronicle Vol.1889-2: p. 323. London, 1889.
- ↑ Cogniaux, Célestin Alfred: Leptotes in Flora Brasiliensis Vol.3 Part.6: pp. 254-259. K.F.P. von Martius Ed., 1903. Published on Internet, in Latin.
- ↑ Loefgren, Johan Albert Constantin: Leptotes blanche-amesiae in Arquivos do Jardim Botânico do Rio de Janeiro Vol.2: p. 58. Rio de Janeiro, 1918.
- ↑ Hoehne, Frederico Carlos: Loefgrenianthus in Arquivos de Botânica do Estado de São Paulo Vol.1: p. 593. São Paulo, Julho de 1927.
- ↑ Krackowizer, F. J.: Monografia do gênero Leptotes in Revista do Círculo Paulista de Orquidófilos Vol.11, pp. 53-63 e 64-72. São Paulo, 1954.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Christenson, Eric A.: Leptotes harryphillipsii in Orchids South Africa Vol.35, pp. 53. Cape Town, 2004.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Christenson, Eric A.: Leptotes mogyensis in Orchids South Africa Vol.35, pp. 54. Cape Town, 2004.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 Campacci, Marcos Antonio: Leptotes bohnkiana in Boletim CAOB Vol.53, p.17. São Paulo, 2004. ISSN 14194590.
- ↑ Vitorino P. Castro Neto & Chiron, Guy: Leptotes pohlitinocoi in Richardiana Vol.4: p.78. Paris, 2004.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Van den Berg, Cássio et al: Leptotes vellozicola em Neodiversity Vol.1, pp. 2, 2006. Publicado na Internet, em inglês.
- ↑ Van den Berg, Cássio et al: A Phylogenetic analysis of Laellinae based on sequence data from internal trancribed spacers of nuclear ribosomal DNA in Lindleyana vol.15-2, pp. 96–114, 2000. Published on Internet.
- ↑ Johnson, Andrés E.: Leptotes unicolor in Las orquídeas del Parque Nacional Iguazú, pp. 110. Fundación Vida Silvestre Argentina, Buenos Aires, 2001. ISBN 9509725412
- ↑ Vitorino P. Castro Neto: Leptotes pohlitinocoi in Icones Orchidacearum Brasilienses Vol.2: pl.163. São Paulo, March 2006. ISBN 8590149447
- ↑ Vitorino P. Castro Neto: Leptotes tenuis in Icones Orchidacearum Brasilienses Vol.2: pl.164. São Paulo, March 2006. ISBN 8590149447
- ↑ Vitorino P. Castro Neto: Leptotes pauloensis in Icones Orchidacearum Brasilienses Vol.2: pl.162. São Paulo, March 2006. ISBN 8590149447
- ↑ Pridgeon, Alex: Leptotes in Genera Orchidacearum Vol.4, p. 274. Oxford Unity Press, 2006. ISBN 9780198507123.