Chief of Naval Operations: Difference between revisions
imported>Hayford Peirce (simplied the Burke business) |
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{TOC-right}} | |||
The '''Chief of Naval Operations''' (CNO) is the senior officer of the [[United States Navy]] unless the [[Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff]] or the [[Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff]] is a naval officer. He is appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate, currently for a four-year term, and usually retires after that single term. Admiral [[Arleigh Burke]], however, served three two-year terms. | The '''Chief of Naval Operations''' (CNO) is the senior officer of the [[United States Navy]] unless the [[Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff]] or the [[Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff]] is a naval officer. He is appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate, currently for a four-year term, and usually retires after that single term. Admiral [[Arleigh Burke]], however, served three two-year terms. | ||
Revision as of 17:41, 17 May 2009
Template:TOC-right The Chief of Naval Operations (CNO) is the senior officer of the United States Navy unless the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff or the Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff is a naval officer. He is appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate, currently for a four-year term, and usually retires after that single term. Admiral Arleigh Burke, however, served three two-year terms.
A member of the Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS), he does not directly command operational forces of the Navy, which are under Unified Combatant Commands that report to the Secretary of Defense and the President of the United States; the latter two constitute the National Command Authority.
The CNO reports to the Secretary of the Navy, especially in matters such as Congressional relations, but has complex relationships with the Joint Chiefs of Staff and Secretary of Defense. While he does not have operational command over naval forces, he has enormous influence.
For the non-JCS activities of the CNO, there is a Shore establishment, an immediate office of the CNO, and the Navy Staff.
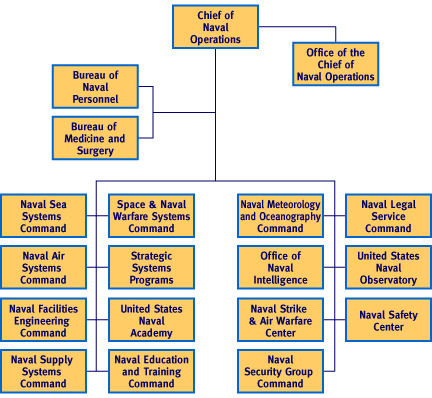
Shore Establishment
In practice, the CNO either directs, or strongly influences, those activities that are not part of Unified Combatant Commands, or are traditionally activities supporting the CNO or staff rather than the field.
There is some overlap among the Shore Establishment, Office of the CNO, and Navy Staff. Remember that the CNO "wears two hats", and the JCS role of the CNO is separate from the pure Navy roles.
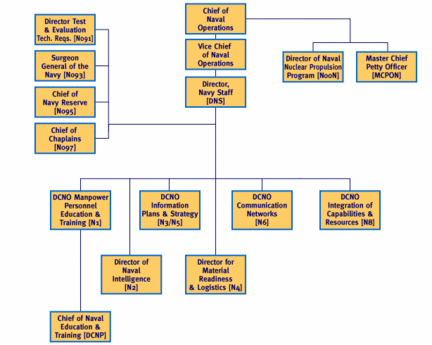
Office of the CNO
The Vice Chief of Naval Operations acts for the CNO in his absence. Each CNO and VCNO work out their particular responsibilities, but the CNO is often more concerned with JCS, White House, and Congressional relations, so the VCNO may be closer to the day-to-day naval structure.
For obscure historical reasons, the immediate staff is also called OpNav. It is a common impression that among the U.S. military services, the organizational designations can be the most obscure, although often tracing to a tradition. At the start of World War II, for example, Admiral Chester Nimitz took over the Pacific Command, coming from heading the "Bureau of Navigation". One might innocently think that the head of that office is the master navigator and shiphandler of the Navy, but, at the time, that Bureau was the Navy personnel office.
There is an overlap between the personal office of the CNO and the Navy Staff.
A large staff organization, headed by the Director of Navy Staff, does report to the CNO, and he has a major role in developing naval doctrine, planning the navy of the future, preparing its budget, etc.
Incumbent
Admiral Gary Roughead became the 29th Chief of Naval Operations on 29 September 2007, the culmination of a career starting with 1973 graduation of the United States Naval Academy. He has commanded six operational units, both ships and larger sea commands.
A surface warfare specialist, he was the first officer to command both types of ships with the AEGIS battle management system, the Arleigh Burke class destroyer USS Barry and the Ticonderoga class cruiser USS Port Royal. He has also commanded the USS George Washington carrier battle group and the U.S. Second Fleet/NATO Striking Fleet Atlantic. He also had the administrative job of commanding the Pacific Fleet.
His Naval shore assignments included Commandant of the United States Naval Academy and Chief of Legislative Affairs.
In joint operational commands, he was Deputy Commander, United States Pacific Command.