Adenosine: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (New page: {{subpages}} {{Chem infobox |align=right |image=center|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Adenosine.jpg/credit|{{Adenosine.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}} |width=200px |molnam...) |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|width=200px | |width=200px | ||
|molname=adenosine | |molname=adenosine | ||
|synonyms= | |synonyms=A, dA, A, Ade, ADE | ||
|molformula= | |molformula= | ||
|molmass= | |molmass= | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|casnumber= | |casnumber= | ||
}} | }} | ||
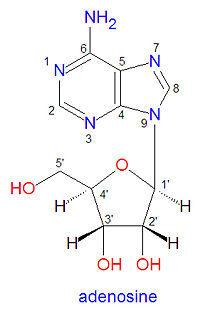
'''Adenosine''', is one of the nucleotides used to build [[RNA]]. It is also incorporated into [[DNA]], but in DNA the ribose ring is a 2'-deoxyribose ring. In both DNA and RNA, adenosine is linked to the other nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds at both the 3'- and 5'- positions. In duplex DNA, the [[adenine]] base present in adenosine is hydrogen bonded with a [[thymidine]] nucleotide on the opposite DNA strand. | |||
Revision as of 11:36, 8 April 2008
|
| |||||||
| adenosine | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | DNA | ||||||
| Properties: | nucleic acid | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Adenosine, is one of the nucleotides used to build RNA. It is also incorporated into DNA, but in DNA the ribose ring is a 2'-deoxyribose ring. In both DNA and RNA, adenosine is linked to the other nucleotides by phosphodiester bonds at both the 3'- and 5'- positions. In duplex DNA, the adenine base present in adenosine is hydrogen bonded with a thymidine nucleotide on the opposite DNA strand.