Deinococcus radiodurans: Difference between revisions
imported>Naisa Thaker |
imported>Naisa Thaker |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Pathology== | ==Pathology== | ||
D. radiodurans is a non-pathogenic, non disease-inducing microbe. | |||
==Application to Biotechnology== | ==Application to Biotechnology== | ||
Revision as of 22:49, 14 April 2008
Articles that lack this notice, including many Eduzendium ones, welcome your collaboration! |
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||
| Binomial name | ||||||||||||||
| Deinococcus radiodurans |
Description and significance
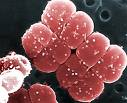
Deinococcus radiodurans, meaning "strange berry that withstands radiation", is a non-pathogenic, Gram-positive aerobic bacteria classified as a member of the family Deinococcaceae. Reddish-pink in color due to the presence of carotenoid pigment, the bacterium has a roughly spherical shape, taking the diplococci form (clusters of two cells) in early growth stages and the tetracocci form (clusters of four cells) in later stages of growth. Nicknamed, "superbug" and "Conan the Bacterium" and was named "the world's strongest (by Guinness World Book or Records), D. radiodurans is the most radiation-resistant vegetative cell, resisting radiation in the megarad range. D. radiodurans was discovered and subsequently isolated in 1956 by Arthur W. Anderson during a laboratory experiment at the Oregon Agriculture Experiment Station (Corvalis, Oregon, US). While seeking new methods for preserving package meat, Anderson noticed bacterial growth after ground meat had been sterilized with radiation.

Biologists consider it a polyextremophile, meaning that it can thrive in a very diverse range of extreme habitats, although no one has been able to identify its natural habitat. D. radiodurans has been located everywhere from cow dung to granite in Antartica’s dry valleys. D. radiodurans' ability to endure environmental conditions far more extreme that those presently found on Earth leads Scientists to believe that it evolved and existed during the planet's primitive stages when it was unshielded by a protective ozone layer and when it was exposed to extreme conditions such as Ionic Radiation (IR) and Ultra Violet (UV) rays from the sun.
In addition to high levels of ionizing and ultraviolet radiation, D. radiodurans can also withstand other extreme stresses such as genotoxic chemicals, oxidative damage, electrophilic mutagens, desiccation, and dehydration. In order to gauge how resistant D. radiodurans is to radiation in comparison to other life forms, consider that, while 5 units of gamma radiation is lethal to humans and 2,000 units of gamma radiation is enough to stop all cell activity for E. Coli, D. radiodurans can be exposed to 10,000 units of gamma radiation without dying or mutating. It can continue to survive despit exposure to small amounts of chronic radiation, for example, 6 kilorads/hr as well as large doses of acute radiation exceeding 1500 kilorads/hr. Although biologists do not yet fully understand why or how, D. radiodurans growing in the tetracocci stage are better able to tolerate radiation than the those growing in the diplococci.
Typically, life forms exposed to extreme stresses such as dehydration, IR or UV, or desiccation experience oxidizing DNA damage in which radiation energizes an atom enough to break a chemical bond (such as in a DNA strand) and then act like an atom of oxygen and bind with another atom, ultimately enabling free radicals to cause genetic mutations or DNA breakage. D. radiodurans, however, demonstrates a unique ability to effectively repair broken DNA. Several factors account for its resistance to radiation and other extreme stresses, including additional genomes, redundancy in genetic code, protiens, and DNA-repair pathways. several different biological mechanisms contribute to resistance. Additional genomes: Allows bacterium to recover at least one complete copy of its genome incase others have been damaged by radiation exposure. If one ring in the stack of lifesavers is damaged due to radiation, the additional genomes allow the bacterium to recover another complete copy of its genome. Compared to other bacteria, the microbe's genome is abundant in repetitive sequences such as IS-like transposons and small intergenic repeats. It is known that subsequent to DNA damage, there are changes in the cellular amount of proteins, with enhanced synthesis of four to nine proteins which encode for repair expression. Researchers were surprised to find that D. radiodurans encodes fewer genes for DNA repair than E. coli. Subsequent studies have shown that D. radiodurans key lies in its effectiveness to full potentiate DNA repair as opposed to the sheer abundance in the number of genes encoded for DNA repair.
Genome Structure
D. radiodurans is the only representative with a completely sequenced genome from a distinct bacterial lineage of extremophiles, the Thermus-Deinococcus group. It's circular genome was completely sequenced in 1999 by M.J. Daly and TIGR, The Institute of Genome Research. It has 3,284,156 base pairs, and over 3246 genes. It carries at least four copies of its genome rather than the usual single chromosome copy, and the copies seem to be stacked on top of each other resembling a lifesaver.
Cell structure and metabolism
D. radiodurans derives energy from aerobic respiration and overall has a complexly charted metabolic pathway, with most reactions leading to the generation of free radicals during irradiation. Researchers discovered that the microbe is unable to use succinate, fumarate, malate, and alpha-ketoglutarate as the only carbon and energy sources and that D. radiodurans is dependent on exogenous nicotinic acid.
Ecology
D. radiodurans major contribution to the environment is in the field of bioremediation (see Biotechnology Applications). Its effectiveness in bioremediation was one of the main incentives for mapping out its genomic sequence.
Pathology
D. radiodurans is a non-pathogenic, non disease-inducing microbe.
Application to Biotechnology
Does this organism produce any useful compounds or enzymes? What are they and how are they used?
Current Research
Enter summaries of the most recent research here--at least three required