Vidarabine: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk m (wikilink fix) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
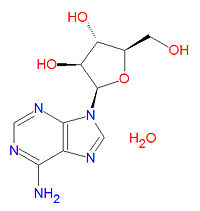
[[Image:Vidarabine structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Vidarabine structure.jpg/credit|{{Vidarabine structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Vidarabine, an antibiotic drug with antiviral properties.]] | [[Image:Vidarabine structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Vidarabine structure.jpg/credit|{{Vidarabine structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Vidarabine, an antibiotic drug with antiviral properties.]] | ||
'''Vidarabine''' is an [[antibiotic | '''Vidarabine''' is an [[antibiotic]] drug with antiviral properties against DNA viruses that is an analog of the nucleoside [[adenosine]]. It can be used to treat some viral infections, including [[herpes virus|herpes]], [[vaccinia virus|vaccinia]] and [[varicella zoster]] viruses. It is isolated from ''[[Streptomyces antibioticus]]''. | ||
== Mechanism of action == | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 18 March 2008
Vidarabine is an antibiotic drug with antiviral properties against DNA viruses that is an analog of the nucleoside adenosine. It can be used to treat some viral infections, including herpes, vaccinia and varicella zoster viruses. It is isolated from Streptomyces antibioticus.
Mechanism of action
Vidarabine is a nucleoside analogue with activity against herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 (HSV), vaccinia virus and varicella zoster virus (VZV). The inhibitory activity of vidarabine is highly selective due to its affinity for the thymidine kinase (TK) enzyme encoded by these viruses. Thymidine kinase converts vidarabine into vidarabine monophosphate. Guanylate kinase then converts it to the diphosphate form and additional steps convert it to the triphosphate form. The triphosphate form competitively inhibits dATP, leading to the formation DNA in which the vidarabine triphosphate is incorporated, replacing the normal dATP. Because no further phoshodiester links can be made, DNA synthesis is halted. Vidarabine stops replication of herpes viral DNA in three ways, by inhibiting viral DNA polymerase, by termination of the growing viral DNA chain, and by inactivation of the viral DNA polymerase.
Chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for vidarabine is (2R,3S,4S,5R)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol hydrate, and it has the chemical formula C10H15N5O5, yielding a molecular mass of 285.2566 g/mol.
Synonyms and brand names
Synonyms
- Adenine Arabinoside
- Arabinofuranosyladenine Triphosphate
- Arabinoside Adenine
- Arabinosyl Adenine
- Arabinosyladenine
- Arabinosyladenine Triphosphate
- Ara Atp
- Ara-A
- Ara-a Triphosphate
- Ara-Atp
- Araadenosine
- Arabinosyl-Atp
- Vidarabine Triphosphate
- 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-adenine
Brand names
- Arasena-A®
- Spongoadenosine®
- Vira-A®
- Vidarabin®
External links
Vidarabine - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine). Template:MedMaster Template:DrugBank