Atorvastatin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (→Drug interactions: typos) |
imported>David E. Volk m (typos on wikilinks) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
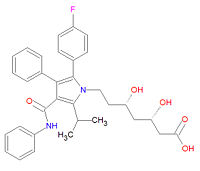
[[Image:Atorvastatin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit|{{Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Atorvastatin, a type II statin.]] | [[Image:Atorvastatin structure.jpg|right|thumb|200px|{{#ifexist:Template:Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit|{{Atorvastatin structure.jpg/credit}}<br/>|}}Atorvastatin, a type II statin.]] | ||
'''Atorvastatin''', commonly called '''Lipitor'''®, is a type II statin used to treat high cholesterol ([[hypercholesterolemia]]), prevent [[ | '''Atorvastatin''', commonly called '''Lipitor'''®, is a type II statin used to treat high cholesterol ([[hypercholesterolemia]]), prevent [[myocardial infarction|heart attacks]] and [[stroke]]s, and to lessen the formation of [[atherosclerosis|artial plaque]]. It is a [[Hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase inhibitor|HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor]] that decreases the synthesis of [[mevalonate]], a key chemical precursor of [[cholesterol]]. Although the structure is based on an indole ring, as are the other type II statins [[fluvastatin]] and [[rosuvastatin]], its longer half-life and specificity for the liver makes atorvastatin a better drug for lowering LDL-cholesterol levels. The metabolites of atorvastatin, ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products, are equivalent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The drug should be taken with a low fat meal and alcohol and grapefruit juice should be avoided. Atorvastatin can be toxic, leading to liver problems, [[rhabdomyolysis]] and eye hemorrhages. | ||
Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>33</sub>H<sub>35</sub>FN<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>. | Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>33</sub>H<sub>35</sub>FN<sub>2</sub>O<sub>5</sub>. | ||
Revision as of 16:08, 28 January 2008
Atorvastatin, commonly called Lipitor®, is a type II statin used to treat high cholesterol (hypercholesterolemia), prevent heart attacks and strokes, and to lessen the formation of artial plaque. It is a HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor that decreases the synthesis of mevalonate, a key chemical precursor of cholesterol. Although the structure is based on an indole ring, as are the other type II statins fluvastatin and rosuvastatin, its longer half-life and specificity for the liver makes atorvastatin a better drug for lowering LDL-cholesterol levels. The metabolites of atorvastatin, ortho- and parahydroxylated derivatives and various beta-oxidation products, are equivalent HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. The drug should be taken with a low fat meal and alcohol and grapefruit juice should be avoided. Atorvastatin can be toxic, leading to liver problems, rhabdomyolysis and eye hemorrhages.
Its official IUPAC chemical name is (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-propan-2-ylpyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid and it has chemical formula C33H35FN2O5.
brand names
- Cardyl®
- Lipitor®
- Sotis®
- Torvast®
- Tozalip®
- Xavator®
- Sortis®
- Torvacard®
- Totalip®
- Tulip®
- Xarator®
- Atorpic®
- Liprimar®
Drug interactions
The effects and/or toxicity of atorvastatin may be increased when taken in combination with amprenavir, ataxanavir, clarithromycin, diltiazem, erythromycin, the NNRT inhibitors delavirdine, eavirenz and nevirapine, fosamprenavir, imatinib, indinavir, josamycin, nefazodone, nelfinavir, quinupristin, ritonavir, saquinavir, tacrolimus, telithromycin and verapamil. The effects of atorvastatin may decrease when used in combination with bosentan, carbamazepine, rifabutin and rifampin. The risks of myopathy and/or rhabdomyolysis increase when atorvastatin is used with bezafibrate, colchicine, cyclosporine, fenofibrate, fluconazole, gemfibrozil, itraconazole and ketoconazole.
External links
- (atorvastatin calcium) 6089 - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Drug Bank at http://redpoll.pharmacy.ualberta.ca/drugbank/cgi-bin/getCard.cgi?CARD=APRD00055