Ester: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
imported>Ro Thorpe |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
In chemistry, an '''ester''' is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality attached to an alkoxide. Esters are widely used in the food industry as artificial flavors. Small esters can be used as solvents. Esters are generally synthesized from in a condensation reaction between a [[carboxylic acid]] and an [[alcohol]]. | In chemistry, an '''ester''' is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality attached to an alkoxide. Esters are widely used in the food industry as artificial flavors. Small esters can be used as solvents. Esters are generally synthesized from in a condensation reaction between a [[carboxylic acid]] and an [[alcohol]]. | ||
== | == Ester synthesis== | ||
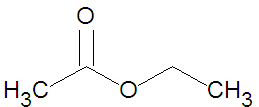
The ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the [[condensation reaction]] between [[acetic acid]] and [[ethanol]]. | The ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the [[condensation reaction]] between [[acetic acid]] and [[ethanol]]. | ||
Revision as of 17:32, 24 January 2008
In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality attached to an alkoxide. Esters are widely used in the food industry as artificial flavors. Small esters can be used as solvents. Esters are generally synthesized from in a condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
Ester synthesis
The ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the condensation reaction between acetic acid and ethanol.