Ester: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
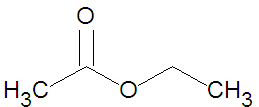
{{Image|Ethyl Acetate stickfigure.jpg|right|350px|Ethyl acetate, a small ester.}} | |||
In chemistry, an '''ester''' is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality (C=O) attached to an alkoxide. This is done by replacing a hydroxyl group (R-OH) of an acid with an alkoxy group (-O-R) from another molecule such as an alcohol. | In chemistry, an '''ester''' is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality (C=O) attached to an alkoxide. This is done by replacing a hydroxyl group (R-OH) of an acid with an alkoxy group (-O-R) from another molecule such as an alcohol. | ||
Revision as of 06:59, 8 June 2009
In chemistry, an ester is a chemical compound that contains a carbonyl functionality (C=O) attached to an alkoxide. This is done by replacing a hydroxyl group (R-OH) of an acid with an alkoxy group (-O-R) from another molecule such as an alcohol.
Applications
Esters are widely used in the food industry as artificial flavors. Small esters can be used as solvents. Another ester, acetylsalicylic acid or aspirin, is used for medicinal purposes[1].
Synthesis
Esters may be formed through a variety of esterification reactions, most typically the condensation reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol[2]. For instance, the ester ethyl acetate (shown in the figure) can be produced from the condensation reaction between acetic acid and ethanol. Another method of ester preparation (alcoholysis) uses an acid chloride instead of a carboxylic acid. Both methods involve nucleophilic acyl substitution, that is, the replacement of one nucleophile attached to a carbonyl group with an alkoxide - a superior nucleophile[2]. In alcoholysis, the leaving nucleophile is a halide rather than a hydroxyl group.
An alternative process, suitable for the addition of a relatively small molecule to an alcohol[2], is the combination of an alcohol and an acid anhydride. Aspirin can be produced by such a reaction, between salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. In these reactions a carboxylate ion substitutes instead of an alkoxide. In all of these reactions an oxygen in the alcohol's hydroxyl group is retained in the ester linkage[1].