Taxon: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Anthony.Sebastian (add content) |
imported>Anthony.Sebastian (rewriting for clarity; needs development) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
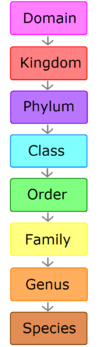
[[Image:Ficheiro.png|thumb|100px|The hierarchy of taxonomic classification]] | [[Image:Ficheiro.png|thumb|100px|The hierarchy of taxonomic classification]] | ||
The figure at the right illustrates the hierarchy of the | Biologists group [[Organism|organisms]] into a hierarchical system of '''taxons''' or '''taxonomic units''', each taxon based on specified criteria of similarity or relationship. | ||
The figure at the right illustrates the hierarchy of taxons. The highest taxon, the 'domain', of which biologists have identified three — [[Archaea]], [[Bacteria]], and [[Eukarya]] — together include all known [[Life|living systems]]. | |||
Revision as of 18:56, 5 May 2009
Biologists group organisms into a hierarchical system of taxons or taxonomic units, each taxon based on specified criteria of similarity or relationship.
The figure at the right illustrates the hierarchy of taxons. The highest taxon, the 'domain', of which biologists have identified three — Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya — together include all known living systems.