Electromagnetic wave: Difference between revisions
imported>Paul Wormer m (→Energy) |
imported>Paul Wormer |
||
| Line 218: | Line 218: | ||
[[Einstein]] postulated in 1905 that an electromagnetic field consists of energy parcels (light quanta, later called [[photon]]s) and in 1927 [[Paul A. M. Dirac]] was able to fit the photon concept into the framework of the new [[quantum mechanics]]. He applied a technique which is now generally called [[second quantization]],<ref>The name derives from the second quantization of quantum mechanical wave functions. Such a wave function is a scalar field: the "Schrödinger field" and can be quantized in the very same way as EM fields. Since a wave function is derived from a "first" quantized Hamiltonian, the quantization of the Schrödinger field is the second time quantization is performed, hence the name.</ref> although this term is somewhat of a misnomer for EM fields, because for these fields, which are, after all, solutions of the classical Maxwell equations, it is the first time that they are quantized. | [[Einstein]] postulated in 1905 that an electromagnetic field consists of energy parcels (light quanta, later called [[photon]]s) and in 1927 [[Paul A. M. Dirac]] was able to fit the photon concept into the framework of the new [[quantum mechanics]]. He applied a technique which is now generally called [[second quantization]],<ref>The name derives from the second quantization of quantum mechanical wave functions. Such a wave function is a scalar field: the "Schrödinger field" and can be quantized in the very same way as EM fields. Since a wave function is derived from a "first" quantized Hamiltonian, the quantization of the Schrödinger field is the second time quantization is performed, hence the name.</ref> although this term is somewhat of a misnomer for EM fields, because for these fields, which are, after all, solutions of the classical Maxwell equations, it is the first time that they are quantized. | ||
Second quantization starts with an expansion of a field in a basis. The coefficients multiplying the basis functions are then interpreted as [[operator]]s | ===Second quantization=== | ||
Second quantization starts with an expansion of a field in a basis consisting of a complete set of functions. The coefficients multiplying the basis functions are then interpreted as [[operator]]s and (anti)commutation relations between these new operators are imposed, [[commutation relation]]s for [[boson]]s and [[anticommutation relations]] for [[fermions]] (nothing happens to the basis functions themselves). By doing this, the expanded field is converted into a fermion or boson operator field. The expansion coefficients have become [[creation operator|creation]] and [[annihilation operator]]s: a creation operator creates a particle in the corresponding basis function and an annihilation operator annihilates a particle in this function. | |||
In the case of EM fields the required expansion is a | ===Fourier series=== | ||
In the case of EM fields the required expansion is a [[Fourier series]], that is, an expansion of the type (for a real vector field '''A'''): | |||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}, t) = \sum_\mathbf{k} \left( \mathbf{a}_k(t) e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} | \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}, t) = \sum_\mathbf{k} \left( \mathbf{a}_k(t) e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} | ||
+ \mathbf{a}_k(t) | + \bar{\mathbf{a}}_k(t) e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \right) | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
where the | where the bar indicates [[complex conjugation]]. Such an expansion, labeled by a discrete (countable) set of vectors '''k''', is always possible when '''A''' satisfies periodic boundary conditions, i.e., '''A'''('''r''' + '''p''',t) = '''A'''('''r''',t) for some finite vector '''p'''. To impose such boundary conditions, it is common to consider EM waves as if they are in a virtual box of finite volume ''V''. Waves on opposite walls of the box are enforced to have the same value (usually zero). Note that the waves are not restricted to the box: the box is replicated an infinite number of times in ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' direction. | ||
===Vector potential=== | |||
It would be possible to quantize the electric and magnetic field separately, however, it is more efficient to quantize the [[vector potential]] in the [[Coulomb gauge]]. The magnetic field '''B''' is a [[Helmholtz decomposition|transverse field]] and hence can be written as | It would be possible to quantize the electric and magnetic field separately, however, it is more efficient to quantize the [[vector potential]] in the [[Coulomb gauge]]. The magnetic field '''B''' is a [[Helmholtz decomposition|transverse field]] and hence can be written as | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\mathbf{B} = \boldsymbol{\nabla}\times \mathbf{A}, | \mathbf{B} = \boldsymbol{\nabla}\times \mathbf{A}, | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
in which appears the vector potential '''A'''. Knowing '''A''', we obtain '''B''' easily. Also the electric field '''E''' is transverse, because we assumed absence of charge distributions. The electric field '''E''' also follows from '''A''', | in which appears the vector potential '''A'''. Knowing '''A''', we obtain '''B''' easily. Also the electric field '''E''' is transverse, because earlier we assumed absence of charge distributions. The electric field '''E''' also follows from '''A''', | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\mathbf{E} = - \frac{\partial \mathbf{A}}{\partial t}. | \mathbf{E} = - \frac{\partial \mathbf{A}}{\partial t}. | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
The fact that '''E''' can be written this way is due to the choice of Coulomb gauge for '''A''': | The fact that '''E''' can be written this way is due to the choice of [[Coulomb gauge]] for '''A''': | ||
:<math> | :<math> | ||
\boldsymbol{\nabla}\cdot\mathbf{A} = 0. | \boldsymbol{\nabla}\cdot\mathbf{A} = 0. | ||
</math> | </math> | ||
By definition a choice of gauge does not affect any measurable properties (the best known example of a choice of gauge is the | By definition a choice of gauge does not affect any measurable properties (the best known example of a choice of gauge is the fixing of the zero of an electric potential, for instance at infinity). | ||
The Coulomb gauge makes '''A''' transverse as well, and clearly '''A''' is anti-parallel to '''E'''. (The time differentiation does not affect direction.) | The Coulomb gauge makes '''A''' transverse as well, and clearly '''A''' is anti-parallel to '''E'''. (The time differentiation does not affect direction.) So, the vectors of the fields '''A''', '''B''', and '''E''' are in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction and can be written in terms of '''e'''<sub>''z''</sub> and '''e'''<sub>''x''</sub> (in the definition of figure 1). It is more convenient to choose complex unit vectors: | ||
:<math> | |||
\mathbf{e}^{(1)} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\mathbf{e}_z + i \mathbf{e}_x)\quad\hbox{and}\quad\mathbf{e}^{(2)} = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\mathbf{e}_z - i \mathbf{e}_x) | |||
</math> | |||
which are orthonormal, | |||
:<math> | |||
\mathbf{e}^{(\lambda)}\cdot\bar{\mathbf{e}}^{(\lambda')} = \delta_{\lambda,\lambda'}\quad\hbox{with}\quad\lambda,\lambda'=1,2. | |||
</math> | |||
The Fourier expansion of the vector potential reads | |||
:<math> | |||
\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}, t) = \sum_\mathbf{k}\sum_{\lambda=1,2} \left( | |||
\mathbf{e}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) a^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t) \, e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} | |||
+ \bar{\mathbf{e}}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) \bar{a}^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t) \, e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} | |||
\right). | |||
</math> | |||
===Classical energy=== | |||
The electromagnetic energy density <math>\scriptstyle \mathcal{E}_\mathrm{Field}</math> can be expressed in terms of the Fourier coefficients. We define the total energy (classical Hamiltonian) by | |||
:<math> | |||
H = \iiint_V \mathcal{E}_\mathrm{Field}(\mathbf{r},t) \mathrm{d}^3\mathbf{r}. | |||
</math> | |||
The classical Hamiltonian takes the form | |||
:<math> | |||
H = V\epsilon_0 \sum_\mathbf{k}\sum_{\lambda=1,2} \omega^2 | |||
\big(\bar{a}^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)a^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)+ a^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)\bar{a}^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)\big) | |||
</math> | |||
with | |||
:<math> | |||
\omega \equiv |\mathbf{k}|c = 2\pi \nu = 2\pi \frac{c}{\lambda} | |||
</math> | |||
and ε<sub>0</sub> is the [[electric constant]]. The two terms in the summand of ''H'' are classically identical (factors commute) and may be summed. However, after quantization (interpretation of the expansion coefficients as operators) the factors do no longer commute and according to quantum mechanical rules one must depart from the symmetrized classical Hamiltonian. | |||
===Quantization=== | |||
The best known example of quantization is the replacement of the (time-dependent) linear momentum of a particle by the rule <math>\scriptstyle \mathbf{p}(t) \rightarrow -i\hbar\boldsymbol{\nabla}</math>. Note that Planck's constant is introduced and that time disappears (in the so-called [[Schrödinger picture]]). | |||
Here we do something similar and apply the ''quantization rules'': | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
a^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)\, &\rightarrow\, \sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2 \omega V\epsilon_0}}\, a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) \\ | |||
\bar{a}^{(\lambda)}_\mathbf{k}(t)\, &\rightarrow\, \sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2 \omega V\epsilon_0}}\, {a^\dagger}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) \\ | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
subject to the boson commutation relations | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
\big[ a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}),\, a^{(\lambda')}(\mathbf{k}') \big] & = 0 \\ | |||
\big[{a^\dagger}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}),\, {a^\dagger}^{(\lambda')}(\mathbf{k}')\big] &=0 \\ | |||
\big[a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}),\,{a^\dagger}^{(\lambda')}(\mathbf{k}')\big]&= \delta_{\mathbf{k},\mathbf{k}'} \delta_{\lambda,\lambda'}. | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
===Hamiltonian=== | |||
Substitution of the operators into the classical Hamiltonian gives the Hamilton operator of the EM field | |||
:<math> | |||
\begin{align} | |||
H &= \frac{1}{2}\sum_{\mathbf{k},\lambda} \hbar c |\mathbf{k}| | |||
\Big(a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}){a^\dagger}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) + a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}){a^\dagger}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k})\Big) \\ | |||
&= \sum_{\mathbf{k},\lambda} \hbar c |\mathbf{k}| \Big({a^\dagger}^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k})a^{(\lambda)}(\mathbf{k}) + \frac{1}{2}\Big) | |||
\end{align} | |||
</math> | |||
By the use of the commutation relations the second line follows from the first. Note that | |||
<math>\scriptstyle \hbar c |\mathbf{k}| = \hbar\omega = h\nu</math>, which is the well-known Einstein expression for photon energy. | |||
<!-- | <!-- | ||
Suppose the station broadcasts at ν = 100 MHz, then it is sending out photons with an energy content of ν''h'' = 1·10<sup>8</sup>× 6.6·10<sup>−34</sup> = 6.6·10<sup>−26</sup> J, where ''h'' is [[Planck's constant]]. The wavelength of the station is λ = ''c''/ν = 3 m and λ/(2π) = 48 cm. The classical approximation is good | Suppose the station broadcasts at ν = 100 MHz, then it is sending out photons with an energy content of ν''h'' = 1·10<sup>8</sup>× 6.6·10<sup>−34</sup> = 6.6·10<sup>−26</sup> J, where ''h'' is [[Planck's constant]]. The wavelength of the station is λ = ''c''/ν = 3 m and λ/(2π) = 48 cm. The classical approximation is good | ||
when the number of photons in the volume (λ/(2π))<sup>3</sup> >> 1. The energy content of this volume element is 2.1·10<sup>−10</sup> × 0.111 = 2.3 ·10<sup>−11</sup> J, which amounts to 3.5 ·10<sup>12</sup> photons of 6.6·10<sup>−26</sup> J each, which is much larger than 1. Quantum effects do not play a role, the music played by this station is well into the classical limit, even when it is R&B. | when the number of photons in the volume (λ/(2π))<sup>3</sup> >> 1. The energy content of this volume element is 2.1·10<sup>−10</sup> × 0.111 = 2.3 ·10<sup>−11</sup> J, which amounts to 3.5 ·10<sup>12</sup> photons of 6.6·10<sup>−26</sup> J each, which is much larger than 1. Quantum effects do not play a role, the music played by this station is well into the classical limit, even when it is R&B. | ||
Revision as of 08:09, 4 September 2008
In physics, an electromagnetic wave is a change, periodic in space and time, of an electric field E(r,t) and a magnetic field B(r,t). A stream of electromagnetic waves is referred to as electromagnetic radiation. Because an electric as well as a magnetic field is involved, the term electromagnetic (EM) is used, a contamination of electric and magnetic. Examples of EM waves, in increasing wavelength, are: gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared, microwaves, and radio waves. All these waves propagate in vacuum with the same speed c, the speed of light. With regard to propagation of electromagnetic waves, air at standard temperature and pressure is very close to vacuum (its refractive index n = 1.0002926, meaning that the speed of light in air is c/n ≈ c).
Classically (non-quantum mechanically), EM radiation is produced by accelerating charges, for instance, the oscillating charge in a radio antenna. Quantum mechanically, EM radiation is emitted whenever a system in an energetically high state (of energy E2) makes a transition to a state of lower energy (E1); during this transition a photon (light quantum) of energy proportional to the difference E2 - E1 > 0 is emitted. This is what happens in a fluorescent tube: mercury atoms are brought into an energetically high state by collisions with electrons, and upon subsequent falling down to their lowest energy state they emit photons.
Electromagnetic waves were predicted on theoretical grounds by James Clerk Maxwell in 1861 and first emitted and received in the laboratory by Heinrich Hertz a quarter century later. The first to see the applicability for communication purposes was the inventor of radiotelegraphy Guglielmo Marconi (around 1900). Later applications are radio, television, radar, cellular phones, gps, and all kinds of wireless applications, from remote control of television sets to internet access in public places.
Properties
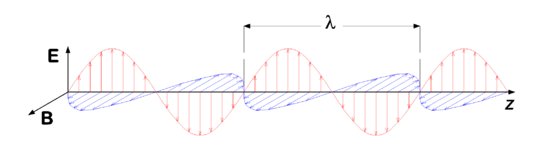
In figure 1 we see a snapshot (i.e., a picture at a certain point in time) of the magnetic and electric fields in adjacent points of space. In each point, the vector E is perpendicular to the vector B. The wave propagates to the right, along an axis which we conveniently refer to as y-axis. Both E and B are perpendicular to the propagation direction, which is expressed by stating that an electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave, in contrast to sound waves, which are longitudinal waves (i.e., air molecules vibrate parallel to the propagation direction of the sound).
Assume that the snapshot in figure 1 is taken at time t, then at a certain point y we see an arrow of certain length representing E(y,t) and also a vector B(y,t). At a point in time Δt later, the same values of E and B (same arrows) are seen at y + c Δt. The arrows seem to have propagated to the right with a speed c.
The time t is fixed and the position y varies in figure 1. Conversely, we can keep the position fixed and imagine what happens if time changes. Focus on a fixed point y, then in progressing time the two vectors E(y,t) and B(y,t) in the point y, grow to a maximum value, then shrink to zero, become negative, go to a minimum value, and grow again, passing through zero on their way to the same maximum value. This cycle is repeated indefinitely. When we now plot E and B in the fixed point y as a function of time t, we see the same type (sine-type) function as in figure 1. The number of times per second that the vectors go through a full cycle is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave.
Periodicity in space means that the EM wave is repeated after a certain distance. This distance, the wavelength is traditionally designated by λ, see figure 1. If we go at a fixed time a distance λ to the right or to the left we encounter the very same fields E and B.
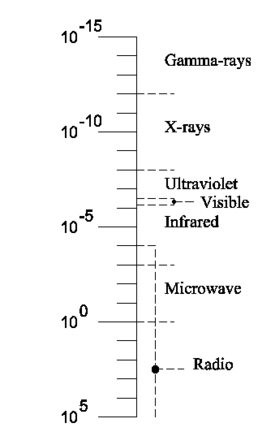
Basically, the only property distinguishing different kinds of EM waves, is their wavelength, see figure 2. Note the enormous span in wavelengths, from one trillionth of a millimeter for gamma-rays (radioactive rays) up to the VLF (very low frequency) radio waves of about 100 kilometer.
Frequency of electromagnetic waves
Often EM waves are characterized by their frequency ν, instead of their wavelength λ. If the EM field goes through ν full cycles in a second, where ν is a positive integral number, the field has a frequency of ν Hz (hertz). The speed of propagation of the EM waves being c, in 1/ν seconds the wave propagates a distance c × (1/ν) meter (according to the formula: distance traveled is speed times traveling time). The distance covered in 1/ν seconds is by definition the wavelength λ:
If we express c in m/s then λ is obtained in m. To convert quickly from wavelength to frequency we can approximate c by 3·108 m/s.
As was pointed out above, the wavelengths of the various parts of the EM spectrum differ many orders of magnitude. Furthermore, the sources of the radiations, the interactions with matter, and the detectors employed differ widely, too. So, it is not surprising that in the past different parts of the spectrum were discovered at different times and that electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths is called by different names. In the table and in figure 2 some illustrative values are given for several kinds of EM waves, together with their names.
| | |||||
|
Some typical values of: wavelength (λ), frequency (ν = c/λ), photon energy (hν), cycle time (T = 1/ν), and inverse wavelength [1/(100⋅λ)]. | |||||
| | |||||
| EM wave | λ (m) | ν (1/s) | hν (J) | T (s) | 1/λ (cm−1) |
| | |||||
| γ-rays | 1.00⋅10−14 | 3.00⋅1022 | 1.98⋅10−11 | 3.33⋅10−23 | 1.00⋅1012 |
| X-rays | 5.00⋅10−10 | 6.00⋅1017 | 3.96⋅10−16 | 1.67⋅10−18 | 2.00⋅107 |
| Ultraviolet | 2.00⋅10−7 | 1.50⋅1015 | 9.90⋅10−19 | 6.67⋅10−16 | 5.00⋅104 |
| Visible | 6.00⋅10−7 | 5.00⋅1014 | 3.30⋅10−19 | 2.00⋅10−15 | 1.67⋅104 |
| Infrared | 5.00⋅10−6 | 6.00⋅1013 | 3.96⋅10−20 | 1.67⋅10−14 | 2.00⋅103 |
| Microwave | 1.00⋅10−2 | 3.00⋅1010 | 1.98⋅10−23 | 3.33⋅10−11 | 1.00 |
| Radio | 1.00⋅102 | 3.00⋅106 | 1.98⋅10−27 | 3.33⋅10−7 | 1.00⋅10−4 |
Monochromatic linearly polarized waves
The wave depicted in figure 1 is monochromatic, i.e., it is characterized by a single wavelength (monochromatic means "of one color". In the visible region, different wavelengths correspond to light of different colors). It is known that EM waves can be linearly superimposed, which is due to the fact that they are solutions of a linear partial differential equation, the wave equation (see next section). A linear superposition of waves is a solution of the same wave equation as the waves themselves. Such a superposition is also an electromagnetic wave (a propagating periodic EM field). If waves of different wavelengths are superimposed, then a non-monochromatic wave is obtained (the term multi-chromatic wave would be apt, but is never used). By means of Fourier analysis a non-monochromatic wave can be decomposed into its monochromatic components.
The electric field vectors in figure 1 are all in one plane, this is the plane of polarization, and a wave with one fixed polarization plane, is called linearly polarized.
The radiation of many lasers is monochromatic and linearly polarized (at least to a very good approximation).
Relation to Maxwell's equations
In this section it will be shown that the electromagnetic wave depicted in figure 1 is a solution of the Maxwell equations in the vacuum.
We assume that at some distance away from the source of EM waves (a radio transmitter, a laser, gamma radiating nuclei, etc.), there is no charge density ρ and no current density J. For that region of space, the microscopic (vacuum) Maxwell equations become (in SI units):
and
Apply to the last Maxwell equation the following relation, known from vector analysis and valid for any (differentiable) vector field,
and use that ∇ · E = 0, then E satisfies the wave equation,
Note that the displacement current (time derivative of E) is essential in this equation, if it were absent (zero), the field E would be a static, time-independent, electric field, and there would be no waves.
In the very same way we derive a wave equation for B,
Observe that E and B are related by the third and fourth Maxwell equation, which express the fact that a displacement current causes a magnetic field, and a changing magnetic field causes an electric field (Faraday's law of induction), respectively. So a time-dependent electric field that is not associated with a time-dependent magnetic field cannot exist, and conversely. Indeed, in special relativity E and c B can be transformed into one another by a Lorentz transformation of the electromagnetic field tensor, which shows their close relationship.
The wave equation is without doubt the most widely studied differential equation in mathematical physics. In figure 1 the electric field depicts a particular solution, with special initial and boundary conditions. The snapshot that is depicted has the analytic form
The snapshot is taken at for some arbitrary integer n. We assumed here that the direction of E defines the direction of the z-axis with unit vector ez along this axis. The quantity E0 is the amplitude of the wave. Insertion of this expression in in the left hand side of the wave equation for E gives
Insertion of this expression in in the right hand side of the wave equation for E gives
so that it follows that the special solution, depicted in figure 1, is indeed a solution of the wave equation for E.
We could now proceed in the very same way and solve the wave equation for B, but then we could easily overlook the relation between the two fields. So we rather substitute the solution for E into the fourth Maxwell equation and use the definition of curl as a determinant,
It is easy to see that
is a solution of this equation. It follows that E and B are perpendicular (along the z-axis and x-axis, respectively) and are in phase. That is, E and B are simultaneously zero and attain simultaneously their maximum and minimum. The fact that (in vacuum) the amplitude of B is a factor c smaller than that of E is due to the use of SI units, in which the amplitudes have different dimensions. In Gaussian units this is not the case and E0 = B0.
Energy
In this section the following balance of power (energy per unit time) densities will be derived:
where
The terms in this equation have dimension W/m3 (power per volume). The quantity represents the rate at which energy is produced per unit volume by ordinary Joulean (resistance) heating. The quantity is the energy density of the EM field and the time derivative is the rate of increase (power density). The vector S, Poynting's vector, is the power flux, the amount of energy crossing unit area perpendicular to the vector, per unit time.
Multiplying the terms by a volume ΔV and a time span Δt, both small enough that the terms in the equation may assumed to be constant over the volume and the time span, the equation represents the conservation of energy: the energy generated in ΔVΔt (the right hand side) is equal to the increase in energy in ΔV plus the net flow of energy leaving ΔV. Hence, when this equation is multiplied by ΔVΔt it is an equation of continuity for energy.
Derivation
Recall from elementary electricity theory the laws of Joule and Ohm . They state that the amount of energy W per unit time, produced by a conduction current I, is equal to
where R is the resistance and V a voltage difference.
Assuming that the current flows along z, we introduce the current density Jz, and using
we obtain
We could continue discussing the system with the small volume . However, because all terms in the equations would be multiplied by the same volume, it is more convenient to consider densities and to divide out the volume. Nevertheless, we still refer to the system. Thus, we define
The negative quantity is the loss of energy of the system per unit time and per unit volume (according to Joule's and Ohm's laws). One may look upon the quantity as the work (per unit time and unit volume) done by the Lorentz force on the moving particles constituting the current density J. Since , this work depends only on the electric field E.
Apply one of Maxwell's equations:
Use a rule known from vector analysis and apply another one of Maxwell's equations,
Define
with
where ε0 is the electric constant and μ0 the magnetic constant of the vacuum. Define also
where S is the Poynting vector called after John Henry Poynting. This vector is perpendicular to the plane of E and B and by the right-hand rule, it points in the direction of propagation of the EM wave. The divergence of the Poynting vector is the energy flow associated with the electromagnetic wave, i.e., with the pair E(r,t) and B(r,t). By definition ∇·S gives the flow leaving the system and − ∇·S gives the flow entering the system. The total energy balance becomes
Here we have found an example of the conservation of energy, known as Poynting's theorem: The energy produced per unit time according to Joule's law is equal to the rate in increase of the electromagnetic energy of the system , plus the flow of EM radiation ∇·S leaving the system.
If there is no current, J = 0, then
which is the continuity equation. The increase of field energy per unit time is the flow of radiation energy into the system.
Example
As an example we give an order-of-magnitude-calculation of an electromagnetic energy density. Consider to that end a radio station with a signal of strength P kW. We compute the energy density at a distance R from the station. First we must assume what the shape is of the waves emitted by the antenna, are they spherical or cylindrical? We choose the latter and call the cylinder height z. Further it is assumed that power density is homogeneous and that all power crosses the cylindrical walls, that is, power crossing the top and bottom of the cylinder is assumed to be zero. Also no absorption by the atmosphere or the Earth will occur. When a steady state is reached (some time after the beginning of the transmission), the time derivative of vanishes. The energy density at a distance R becomes constant in time,
where c is the speed of propagation of the radio signal (is speed of ligth ≈ 3·108 m/s).[1] To give a numerical example: P = 100 kW, R = 5 km (about 3 miles), z = 50 m, then = 2.1·10−10 J/m3.
Field quantization
Einstein postulated in 1905 that an electromagnetic field consists of energy parcels (light quanta, later called photons) and in 1927 Paul A. M. Dirac was able to fit the photon concept into the framework of the new quantum mechanics. He applied a technique which is now generally called second quantization,[2] although this term is somewhat of a misnomer for EM fields, because for these fields, which are, after all, solutions of the classical Maxwell equations, it is the first time that they are quantized.
Second quantization
Second quantization starts with an expansion of a field in a basis consisting of a complete set of functions. The coefficients multiplying the basis functions are then interpreted as operators and (anti)commutation relations between these new operators are imposed, commutation relations for bosons and anticommutation relations for fermions (nothing happens to the basis functions themselves). By doing this, the expanded field is converted into a fermion or boson operator field. The expansion coefficients have become creation and annihilation operators: a creation operator creates a particle in the corresponding basis function and an annihilation operator annihilates a particle in this function.
Fourier series
In the case of EM fields the required expansion is a Fourier series, that is, an expansion of the type (for a real vector field A):
where the bar indicates complex conjugation. Such an expansion, labeled by a discrete (countable) set of vectors k, is always possible when A satisfies periodic boundary conditions, i.e., A(r + p,t) = A(r,t) for some finite vector p. To impose such boundary conditions, it is common to consider EM waves as if they are in a virtual box of finite volume V. Waves on opposite walls of the box are enforced to have the same value (usually zero). Note that the waves are not restricted to the box: the box is replicated an infinite number of times in x, y, and z direction.
Vector potential
It would be possible to quantize the electric and magnetic field separately, however, it is more efficient to quantize the vector potential in the Coulomb gauge. The magnetic field B is a transverse field and hence can be written as
in which appears the vector potential A. Knowing A, we obtain B easily. Also the electric field E is transverse, because earlier we assumed absence of charge distributions. The electric field E also follows from A,
The fact that E can be written this way is due to the choice of Coulomb gauge for A:
By definition a choice of gauge does not affect any measurable properties (the best known example of a choice of gauge is the fixing of the zero of an electric potential, for instance at infinity). The Coulomb gauge makes A transverse as well, and clearly A is anti-parallel to E. (The time differentiation does not affect direction.) So, the vectors of the fields A, B, and E are in a plane perpendicular to the propagation direction and can be written in terms of ez and ex (in the definition of figure 1). It is more convenient to choose complex unit vectors:
which are orthonormal,
The Fourier expansion of the vector potential reads
Classical energy
The electromagnetic energy density can be expressed in terms of the Fourier coefficients. We define the total energy (classical Hamiltonian) by
The classical Hamiltonian takes the form
with
and ε0 is the electric constant. The two terms in the summand of H are classically identical (factors commute) and may be summed. However, after quantization (interpretation of the expansion coefficients as operators) the factors do no longer commute and according to quantum mechanical rules one must depart from the symmetrized classical Hamiltonian.
Quantization
The best known example of quantization is the replacement of the (time-dependent) linear momentum of a particle by the rule . Note that Planck's constant is introduced and that time disappears (in the so-called Schrödinger picture).
Here we do something similar and apply the quantization rules:
subject to the boson commutation relations
Hamiltonian
Substitution of the operators into the classical Hamiltonian gives the Hamilton operator of the EM field
By the use of the commutation relations the second line follows from the first. Note that , which is the well-known Einstein expression for photon energy.
(To be continued)
External link
ISO 21348 Definitions of Solar Irradiance Spectral Categories
- ↑ P is the integral of = −E⋅J over the volume of the cylinder; is the integral of the Poynting vector S over the surface of the cylinder.
- ↑ The name derives from the second quantization of quantum mechanical wave functions. Such a wave function is a scalar field: the "Schrödinger field" and can be quantized in the very same way as EM fields. Since a wave function is derived from a "first" quantized Hamiltonian, the quantization of the Schrödinger field is the second time quantization is performed, hence the name.






![{\displaystyle \mathbf {E} (\mathbf {r} ,t)=\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}\quad {\hbox{with}}\quad k\equiv {\frac {2\pi }{\lambda }}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/83fa7963247f63dd2378b1d9a69120001ee0d3b4)

![{\displaystyle {\boldsymbol {\nabla }}^{2}\mathbf {E} =\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}{\frac {\partial ^{2}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}}{\partial y^{2}}}=-k^{2}\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/8e1141e4a1a8fbc90277182102e69d94c8bcb919)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}}{c^{2}}}{\frac {\partial ^{2}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}}{\partial t^{2}}}=-{\frac {c^{2}\,k^{2}}{c^{2}}}\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}=-k^{2}\mathbf {e} _{z}E_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b1accc0d079be3f3b68293f1ffdc12e300753757)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{vmatrix}\mathbf {e} _{x}&\quad \mathbf {e} _{y}&\mathbf {e} _{z}\\{\frac {\partial }{\partial x}}&\quad {\frac {\partial }{\partial y}}&{\frac {\partial }{\partial z}}\\0&\quad 0&E_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}\\\end{vmatrix}}=k\mathbf {e} _{x}E_{0}\cos {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}=-{\frac {\partial \mathbf {B} }{\partial t}}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/180d5fe6b80023c4a08825f4e6534aafe55afb75)
![{\displaystyle \mathbf {B} (\mathbf {r} ,t)=\mathbf {e} _{x}B_{0}\sin {\big [}k(y-ct){\big ]}\quad {\hbox{with}}\quad B_{0}\equiv {\frac {E_{0}}{c}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0ea80ade49d2f40c90bdf6404ba507910dac139b)


































![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}{\big [}a^{(\lambda )}(\mathbf {k} ),\,a^{(\lambda ')}(\mathbf {k} '){\big ]}&=0\\{\big [}{a^{\dagger }}^{(\lambda )}(\mathbf {k} ),\,{a^{\dagger }}^{(\lambda ')}(\mathbf {k} '){\big ]}&=0\\{\big [}a^{(\lambda )}(\mathbf {k} ),\,{a^{\dagger }}^{(\lambda ')}(\mathbf {k} '){\big ]}&=\delta _{\mathbf {k} ,\mathbf {k} '}\delta _{\lambda ,\lambda '}.\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31be0e3812db887535ea8487f0b2d71f495e9719)


