Carbenicillin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk m (click HIDE MINOR EDITS to not see all of these!) |
imported>Milton Beychok (Undo revision 100471672 by David E. Volk (Talk) Undid inadvertant deletion by David Volk) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Carbenicillin''', or '''carboxybenzylpenicillin''', is a broad-spectrum beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] and is a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including [[E. coli]], [[Enterobacter]] species, [[Enterococci]], [[Morganella morganii]], [[Proteus mirabilis]], [[Proteus vulgaris]], [[Pseudomonas]] and [[{Providencia rettgeri]]. | '''Carbenicillin''', or '''carboxybenzylpenicillin''', is a broad-spectrum beta-[[lactam]]-based [[antibiotic]] and is a derivative of [[penicillin]]. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including [[E. coli]], [[Enterobacter]] species, [[Enterococci]], [[Morganella morganii]], [[Proteus mirabilis]], [[Proteus vulgaris]], [[Pseudomonas]] and [[{Providencia rettgeri]]. | ||
== Mechanism of action== | |||
Like other beta-[[lactam]] penicillin derivatives, carbenicillin interference with final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by acylating the penicillin-sensitive [[transpeptidase]] enzyme's C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands, and leads to [[autolysis]] of the bacterial cells by the [[autolysin]] enzymes. | |||
==Chemistry == | |||
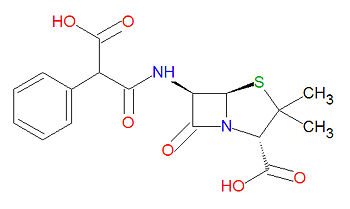
Carbenicillin is a beta-[[lactam]]-based antibiotic, which acylates a transpetidase enyzme through a lactam ring-opening reaction. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(3-hydroxy-3-oxo-2-phenylpropanoyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C<sub>17</sub>H<sub>18</sub>N<sub>2</sub>O<sub>6</sub>S (MW = 378.3996 g/mol). | |||
== External links == | |||
* {{CZMed}} | |||
Revision as of 11:46, 6 April 2009
Carbenicillin, or carboxybenzylpenicillin, is a broad-spectrum beta-lactam-based antibiotic and is a derivative of penicillin. It is used for infections of the urinary tract. The most useful aspect of this drug is its antipseudomonal and antiproteal activity, but is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections in the urinary tract from bacteria including E. coli, Enterobacter species, Enterococci, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Pseudomonas and [[{Providencia rettgeri]].
Mechanism of action
Like other beta-lactam penicillin derivatives, carbenicillin interference with final stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis by acylating the penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase enzyme's C-terminal domain by opening the lactam ring. This prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan strands, and leads to autolysis of the bacterial cells by the autolysin enzymes.
Chemistry
Carbenicillin is a beta-lactam-based antibiotic, which acylates a transpetidase enyzme through a lactam ring-opening reaction. Its IUPAC chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(3-hydroxy-3-oxo-2-phenylpropanoyl)amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid and it has chemical formula C17H18N2O6S (MW = 378.3996 g/mol).
External links
- The most up-to-date information about Carbenicillin and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Carbenicillin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Carbenicillin - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Carbenicillin - Detailed information from DrugBank.