Interspike interval: Difference between revisions
John Leach (talk | contribs) m (Text replacement - "axon" to "axon") |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
b) network interactions, because spike activity in one neuron might have feedback effects on that neuron because of the changes that it produces in reciprocally connected neurons | b) network interactions, because spike activity in one neuron might have feedback effects on that neuron because of the changes that it produces in reciprocally connected neurons | ||
and | and | ||
c) the nature of the inputs to that neuron. | c) the nature of the inputs to that neuron.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:01, 2 September 2024
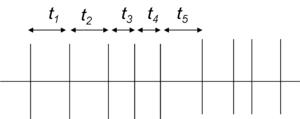
The interspike interval is the time between subsequent action potentials (also known as spikes) of a neuron, or a group average thereof.
Action potentials are propagated along the axons of a neuron, to reach the nerve terminals, where they can trigger the release of chemical messengers to affect other neurons.
Thus spikes are a very important way by which neurons in the brain carry information. The spike itself is an all-or-none phenomenon, so information is coded not in the amplitude of a spike but in the timing of spikes. Accordingly, electrophysiologists, who study the electrical behaviour of neurons, are interested in the patterning of spikes in particular neurons, which they typically analyze by way of an interspike interval histogram.
The patterning of spike activity is influenced by three factors: a) the intrinsic properties of the neuron, especially the properties of its membrane. The neurons in the brain are very diverse; there are very many different subpopulations of neurons that have quite different intrinsic properties b) network interactions, because spike activity in one neuron might have feedback effects on that neuron because of the changes that it produces in reciprocally connected neurons and c) the nature of the inputs to that neuron.