Fourth Party System: Difference between revisions
Pat Palmer (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
* John C. Green and Paul S. Herrnson. "Party Development in the Twentieth Century: Laying the Foundations for Responsible Party Government?" (2000) [http://polisci.wisc.edu/~party/apsa2000green.pdf online version] | * John C. Green and Paul S. Herrnson. "Party Development in the Twentieth Century: Laying the Foundations for Responsible Party Government?" (2000) [http://polisci.wisc.edu/~party/apsa2000green.pdf online version] | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 18 August 2024
The Fourth Party System is a common name for a United States political re-alignment that occurred after 1896. The third party system did not collapse and the Republican and Democratic Parties remained the two dominant political parties although their constituencies and platforms changed.
The Progressive Era is the period in American political history from about 1896 to 1932 that was dominated by the Republican party, except when it split in 1912 and allowed the Democrats in for eight years. The period saw a transformation from the issues and alignments of the Third Party System, which focused on Civil War, Reconstruction, race and the money supply. The era began in the Panic of 1893 and the extraordinarily intense election of 1896. It included the Progressive Era, World War I, and the start of the Great Depression. The failure of the Republicans to deal with the Great Depression caused a realignment that produced the Fifth Party System, which was dominated by the Democratic New Deal Coalition until the 1960s.
The central domestic issues concerned government regulation of railroads and large corporations (called "trusts", hence the Antitrust movement), the protective tariff, the role of labor unions, child labor, the need for a new banking system, corruption in party politics, primary elections, direct election of senators, racial segregation, efficiency in government, woman suffrage, and control of immigration. In foreign policy the main issues involved the War of 1898 with Spain, imperialism in the Philippines, the Mexican Revolution, World War I in Europe, and the creation of the League of Nations. Dominant personalities included presidents William McKinley, Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson, and three-time presidential candidate William Jennings Bryan.
Beginnings
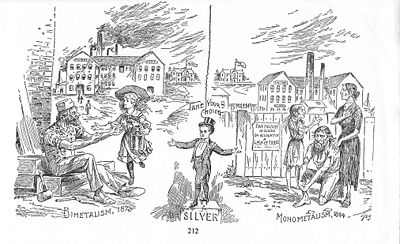
The period began with the realignment of 1894-1896. The overwhelming Republican victory in 1896 over William Jennings Bryan and his Democratic Party, repeated in 1900, restored business confidence, inaugurated a long epoch of prosperity (shown in the table), and swept away most of the issues and personalities of the Third Party System. Most voting blocs continued unchanged, but some realignment took place, giving Republicans dominance in the industrial Northeast and new strength in the border states. Thus the way was clear for the Progressive Movement to impose a new way of thinking and a new agenda for politics.
Economic trends
Table: Real GDP per capita
| 1892 | 1896 | 1900 | 1904 | 1908 | 1912 | 1916 | 1920 | 1924 | 1928 | 1932 |
| 104 | 100 | 114 | 121 | 119 | 139 | 145 | 147 | 164 | 173 | 133 |
source: Susan Carter, ed. Historical Statistics of the U.S. (Millennium Edition) (2006)
Progressive reforms
Alarmed at the new rules of the game for campaign funding, the Progressives launched investigations and exposures (by the "muckraker" journalists) into corrupt links between party bosses and business. New laws and constitutional amendments weakened the party bosses by installing primaries and directly electing senators.[1] Theodore Roosevelt shared the growing concern with business influence on government. When William Howard Taft appeared to be too cozy with pro-business conservatives in terms of tariff and conservation issues, Roosevelt broke with his old friend and his old party. He crusaded for president in 1912 at the head of an ill-fated "Bull Moose" Progressive party. TR's schism helped elect Woodrow Wilson in 1912 and left pro-business conservatives as the dominant force in the GOP. The latter elected Warren G. Harding and Calvin Coolidge. In 1928 the iconic progressive Herbert Hoover became the last president of the Fourth Party System. The Great Depression spoiled the nation's optimism and ruined Republican chances. In long-term perspective Al Smith in 1928 started a voter realignment — a new coalition — based among ethnics and big cities that spelled the end of classless politics of the Fourth Party System and helped usher in the Fifth Party System or New Deal coalition of Franklin D. Roosevelt.[2] As one political scientist explains, "The election of 1896 ushered in the Fourth Party System.... [but] not until 1928, with the nomination of Al Smith, a northeastern reformer, did Democrats make gains among the urban, blue-collar, and Catholic voters who were later to become core components of the New Deal coalition and break the pattern of minimal class polarization that had characterized the Fourth Party System."[3] In 1932 the landslide victory of Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt led to the New Deal coalition that dominated the Fifth Party System, after 1932.
Women's suffrage and feminism
Gustafson (1997) shows that women vigorously define their role in political parties from the 1880s to 1920. Traditionally viewed as nonpartisan, women generally formed auxiliaries to the Republican and Democratic parties. The formation of the Progressive Party in 1912 offered women a chance for equality. Progressive party supporter Jane Addams openly advocated women's partisanship. After the Progressive Party loss in 1912, partisan women continued to form auxiliaries in the major parties. After 1920, inclusion and power in political parties persisted as issues for partisan women. Suffragists shifted from an emphasis on their right to vote to a new emphasis on the need for women to purify politics and guide policy toward education. The suffrage movement gained strength during the World War, and at the end women received the vote, in a major change in the rules of the game.
Prohibition
In most of the country prohibition was of central importance in progressive politics before World War I, with a strong religious and ethnic dimension. Most pietistic Protestants were "dries" who advocated prohibition as a solution to social problems; they were led by aroused ministers and members of the Methodist, Congregationalist, Disciples, Baptist, Presbyterian, Quaker, and Scandinavian Lutheran churches. On the "wet" side, Episcopalians, Catholics, and German Lutherans attacked prohibition as a menace to their social customs and personal liberty. Prohibitionists supported direct democracy to enable voters to bypass the state legislature in lawmaking. In the North, the Republican Party championed the interests of the prohibitionists, while the Democratic Party represented ethnic group interests. In the South, the Baptist and Methodist churches played a major role in forcing the Democratic party to support prohibition. After 1914 the issue shifted to the Germans' opposition to Woodrow Wilson's foreign policy. [4] In the 1920s, however, the sudden, unexpected outburst of big city crime associated with bootlegging undermined support for prohibition, and the Democrats took up the cause for repeal, finally succeeding in 1932.
World War
The United States also appeared on the world scene in the last years of World War I. President Wilson tried to negotiate a peace in Europe, but when Germany began unrestricted submarine warfare against American shipping, especially after the 1915 sinking of the Lusitania, he called on Congress to declare war. Ignoring military affairs, he focused on diplomacy and finance. On the home front he began the first effective draft in 1917, raised billions through Liberty loans, imposed an income tax on the wealthy, set up the War Industries Board, promoted labor union growth, supervised agriculture and food production through the Lever Act, took over control of the railroads, and suppressed left-wing anti-war movements. As the European states, the United States experiment war economy. In 1918, Wilson advocated various international reforms in the Fourteen Points, among them public diplomacy, freedom of navigation, "equality of trade conditions" and removal of economic barriers, an "impartial adjustment of all colonial claims," the "evacuation of all Russian territory" (where the new Bolshevik regime was trying to establish itself firmly during the Russian Civil War, opposed by the White Army supported by Western states), the evacuation of France and Belgium, the creation of a Polish state, and, last but not least of the 14 Points, the creation of an association of nations. The latter would become the League of Nations.
In 1917, the Lansing-Ishii Agreement signed with Japan also pledged to maintain the Open Door policy in China, recognizing Japanese special interests in China. Under the Harding administration, Washington hosted an international naval conference aimed at naval disarmement.
The 1920s were marked, on the international scene, by successful efforts at naval disarmament led by the U.S. at the Washington Confedernce, and by the tangle of economic reparations due by Germany to France. The US acted as mediators in this conflict, first with the Dawes Plan in 1924, then the Young Plan in 1929.
See also
- American election campaigns, 19th century
- Third Party System
- Fifth Party System
- Republican Party (United States), history
- Democratic Party (United States), History
- Progressive Era
Bibliography
- Allen, William H. "The Election of 1900," Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science Vol. 17 (Jan., 1901), pp. 53-73 in JSTOR
- Baker, Jean H. Votes for Women: The Struggle for Suffrage Revisited Oxford University Press, 2002 online edition
- Blum, John Morton. The Progressive Presidents: Roosevelt, Wilson, Roosevelt, Johnson (1980)
- Burner, David. Herbert Hoover: A Public Life. (1979).
- Burnham, Walter Dean, "The System of 1896: An Analysis," in Paul Kleppner, et al., The Evolution of American Electoral Systems , Greenwood. (1983)
- Burnham, Walter Dean. "Periodization Schemes and 'Party Systems': The "System of 1896" as a Case in Point," Social Science History, Vol. 10, No. 3 (Autumn, 1986), pp. 263-314.online at JSTOR
- Campbell, James E., "Party Systems and Realignments in the United States, 1868–2004," Social Science History, 30 (Fall 2006), 359–86.
- Campbell, Tracy. Deliver the Vote: A History of Election Fraud, an American Political Tradition-1742-2004 (2005) excerpt and text search
- Cherny, Robert W. A Righteous Cause: The Life of William Jennings Bryan (1994) excerpt and text search
- Cooper, John Milton The Warrior and the Priest: Woodrow Wilson and Theodore Roosevelt. (1983) a dual biography by leading scholar; excerpt and text search
- Craig, Douglas B. 'After Wilson: The Struggle for the Democratic Party, 1920-1934 (1992) online edition
- Degler, Carl N. "American Political Parties and the Rise of the City: An Interpretation" Journal of American History, 51#1 (1964) pp 41-59 online edition]
- Edwards, Rebecca. Angels in the Machinery: Gender in American Party Politics from the Civil War to the Progressive Era (1997) excerpt and text search
- Folsom, Burton W. "Tinkerers, Tipplers, and Traitors: Ethnicity and Democratic Reform in Nebraska During the Progressive Era." Pacific Historical Review 1981 50(1): 53-75. in JSTOR
- Glad, Paul W. McKinley, Bryan and the People (1991), on 1896 election. excerpt and text search
- Gosnell, Harold F. Boss Platt and His New York Machine: A Study of the Political Leadership of Thomas C. Platt, Theodore Roosevelt, and Others (1924) online edition
- Gould, Lewis L. America in the Progressive Era, 1890 - 1914 (2000) excerpt and text search
- Gould, Lewis L. Four Hats in the Ring: The 1912 Election and the Birth of Modern American Politics (2008) by a leading scholar excerpt and text search
- Gustafson, Melanie. "Partisan Women in the Progressive Era: the Struggle for Inclusion in American Political Parties." Journal of Women's History 1997 9(2): 8-30. Template:ISSN Fulltext online at SwetsWise and Ebsco.
- Harbaugh, William Henry. The Life and Times of Theodore Roosevelt. (1963), standard scholarly biography; also titles Power and Responsibility; excerpt and text search
- Harrison, Robert. Congress, Progressive Reform, and the New American State (2004) excerpt and text search
- Hofstadter, Richard. The Age of Reform: From Bryan to F.D.R. (1955) Pulitzer Prize online at ACLS e-books
- Hofstadter, Richard. The American Political Tradition (1948), chapters on Bryan, Roosevelt, Wilson and Hoover online at ACLS e-books
- Jensen, Richard. The Winning of the Midwest: Social and Political Conflict, 1888-1896 (1971)
- Jensen, Richard. Grass Roots Politics: Parties, Issues, and Voters, 1854-1983 (1983) online edition
- Keller, Morton. Affairs of State: Public Life in Late Nineteenth Century America (1977)
- Keller, Morton. America's Three Regimes: A New Political History (2007) 384pp.
- Kleppner, Paul. Continuity and Change in Electoral Politics, 1893-1928, Greenwood. 1987
- Lawrence, David G. The Collapse of the Democratic Presidential Majority: Realignment, Dealignment, and Electoral Change from Franklin Roosevelt to Bill Clinton (1996) online edition
- Lee, Demetrius Walker, "The Ballot as a Party-System Switch: The Role of the Australian Ballot in Party-System Change and Development in the USA," Party Politics, Vol. 11, No. 2, 217-241 (2005)
- Lichtman, A. J. "Critical elections theory and the reality of American presidential politics, 1916-40." American Historical Review (1976) 81: 317-348. in JSTOR
- Lichtman, Allan J. Prejudice and the Old Politics: The Presidential Election of 1928 (1979).
- Link, Arthur Stanley. Woodrow Wilson and the Progressive Era, 1910-1917 (1972) standard political history of the era
- McSeveney, Samuel T. "The Fourth Party System and Progressive Politics", in. L. Sandy Maisel and William Shade (eds) Parties and Politics in American History (1994)
- Mahan, Russell L. "William Jennings Bryan and the Presidential Campaign of 1896" White House Studies 2003 3(2): 215-227. Template:ISSN
- Morgan, H. Wayne. William McKinley and His America (1963)
- Morris, Edmund. Theodore Rex (2002), detailed biography of Roosevelt as president 1901-1909 excerpt and text search
- Mowry, George. The Era of Theodore Roosevelt and the Birth of Modern America, 1900-1912. (1954) in ACLS e-books
- Sanders, Elizabeth. Roots of Reform: Farmers, Workers, and the American State, 1877-1917 (1999). argues the Democrats were the true progressives and GOP was mostly conservative excerpt and text search
- Sarasohn, David. The Party of Reform: Democrats in the Progressive Era (1989), covers 1910-1930.
- Sundquist, James L. Dynamics of the Party System, Revised Edition, Brookings Institute. 1983 online edition
- Ware, Alan. The American Direct Primary: Party Institutionalization and Transformation in the North (2002) online edition
Primary sources
- Bryan, William Jennings. First Battle (1897), speeches from 1896 campaign.
- Ginger, Ray, ed. William Jennings Bryan; Selections (1967).
- LaFollette, Robert. Autobiography (1913)
- Roosevelt, Theodore. Autobiography (1913)
- Whicher, George F., ed. William Jennings Bryan and the Campaign of 1896 (1953), primary and secondary sources. online edition
External links
- bibliography
- John C. Green and Paul S. Herrnson. "Party Development in the Twentieth Century: Laying the Foundations for Responsible Party Government?" (2000) online version