Oxazolidinone: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (New article generated using Special:MetadataForm) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Chem infobox | |||
|align=right | |||
|image=[[Image:oxazolidinone.png|center|thumb|200px]] | |||
|width=200px | |||
|molname=oxazolidinone | |||
|synonyms= | |||
|molformula= C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>5</sub>O<sub>2</sub>N | |||
|molmass= | |||
|uses=medications & chemistry | |||
|properties= | |||
|hazards= | |||
|iupac= | |||
|casnumber= | |||
}} | |||
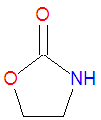
'''Oxazolidinone''' is a cyclopentane-like molecule frequently used in organic chemistry reactions and is a central part of many medications, particularly some cardiac medications and new classes of [[antibiotic]]s. | |||
== Chemistry == | |||
Chemically, oxazolidinones are a subclass of [[azole]]s, which are cyclic molecules containing a [[nitrogen]] atom ("aza"), and [[oxazole]]s, which contain both a nitrogen and an [[oxygen]] atom in the ring system. The [[ketone]] carbon is noted by the suffix "one".[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 30 September 2024
|
| |||||||
| oxazolidinone | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | medications & chemistry | ||||||
| Properties: | |||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Oxazolidinone is a cyclopentane-like molecule frequently used in organic chemistry reactions and is a central part of many medications, particularly some cardiac medications and new classes of antibiotics.
Chemistry
Chemically, oxazolidinones are a subclass of azoles, which are cyclic molecules containing a nitrogen atom ("aza"), and oxazoles, which contain both a nitrogen and an oxygen atom in the ring system. The ketone carbon is noted by the suffix "one".