Erectile dysfunction: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (New page: '''Erectile dysfunction''' is a condition in which a male contain obtain or maintain an erect penis. It can result from several medical conditions, including diabetes, radical prostatecto...) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (25 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Erectile dysfunction''' is a condition in which a male | {{subpages}} | ||
'''Erectile dysfunction''' is a condition in which a male cannot obtain or maintain an erect penis.<ref name="pmid14581493">{{cite journal |author=Corbin JD, Francis SH |title=Molecular biology and pharmacology of PDE-5-inhibitor therapy for erectile dysfunction |journal=J. Androl. |volume=24 |issue=6 Suppl |pages=S38–41 |year=2003 |pmid=14581493 |doi= |url=http://www.andrologyjournal.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14581493 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18077811">{{cite journal |author=McVary KT |title=Clinical practice. Erectile dysfunction |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=357 |issue=24 |pages=2472–81 |year=2007 |month=December |pmid=18077811 |doi=10.1056/NEJMcp067261 |url=http://content.nejm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=short&pmid=18077811 |issn=}}</ref> It can result from a wide range of medical conditions, both physical and psychological. Physical causes include [[diabetes]], radical prostatectomy, vascular insufficiency, nerve damage, or insufficient [[cyclic guanine monophosphate]] (cGMP) levels. Psychological causes include stress, [[post-traumatic stress disorder]] (PTSD), depression, situational anxiety, and relationship problems. | |||
== Diagnosis== | |||
Erectile dysfunction is often diagnosed using the Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) test, a validated questionnaire that is widely used in urology clinics to evaluate and assess treatment efficacy for erectile dysfunction (ED).<ref>{{cite journal |author=Amjad Alwaal, Mohannad Awad, Jake Kuzbel, Brian Snoad |title=Sexual Health Inventory for Men Questionnaire as a Screening Method for Erectile Dysfunction in a General Urology Clinic |journal=Sexual Medicine |volume=8 |issue=4 |pages=660-663 |year=2020 |doi=10.1016/j.esxm.2020.08.002 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7691874/ |issn=}}</ref> | |||
Additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying causes of the condition. | |||
== Treatment == | == Treatment == | ||
[[Clinical practice guideline]]s by the [[American College of Physicians]] address management.<ref name="pmid19884625">{{cite journal| author=Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, Casey DE, Forciea MA, Owens DK et al.| title=Hormonal testing and pharmacologic treatment of erectile dysfunction: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. | journal=Ann Intern Med | year= 2009 | volume= 151 | issue= 9 | pages= 639-49 | pmid=19884625 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19884625 | doi=10.1059/0003-4819-151-9-200911030-00151 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19843532">{{cite journal| author=Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, Casey DE, Forciea MA, Owens DK et al.| title=Hormonal Testing and Pharmacologic Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians. | journal=Ann Intern Med | year= 2009 | volume= | issue= | pages= | pmid=19843532 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19843532 }} </ref><ref name="pmid19884626">{{cite journal| author=Tsertsvadze A, Fink HA, Yazdi F, MacDonald R, Bella AJ, Ansari MT et al.| title=Oral phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and hormonal treatments for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. | journal=Ann Intern Med | year= 2009 | volume= 151 | issue= 9 | pages= 650-61 | pmid=19884626 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19884626 | doi=10.1059/0003-4819-151-9-200911030-00150 }} </ref> | |||
=== Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors === | === Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors === | ||
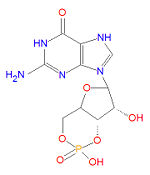
{{Image|CGMP.jpg|left|150px|'''cGMP'''}} | |||
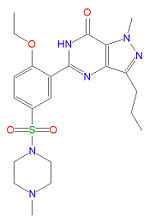
[[Sildenafil]] (Viagra®), [[vardenafil]] (Levitra®) and [[tadalafil] (Cialis®), | {{Image|Sildenafil3.jpg|right|150px|'''sildenafil'''}} | ||
[[Sildenafil]] (Viagra®), [[vardenafil]] (Levitra®) and [[tadalafil]] (Cialis®), may treat erectile dysfunction<ref name="pmid16354303">{{cite journal |author=Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ |title=Indirect comparison of interventions using published randomised trials: systematic review of PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction |journal=BMC Urol |volume=5 |issue= |pages=18 |year=2005 |pmid=16354303 |pmc=1343572 |doi=10.1186/1471-2490-5-18 |url=http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2490/5/18 |issn=}}</ref> and as well as [[pulmonary hypertensive]], are selective [[phosphodiesterase]] type 5 ([[PDE-5]]) inhibitors that bind selectively to PDE-5 and inhibit the binding and subsequent degradation of [[cyclic GMP]] (cGMP). Normally, erection results from increased cGMP levels produced by guanylate cyclase, which in turn is upregulated by [[nitric oxide]] release after stimulation. By decreasing the degradation of cGMP by PDE-5 enzymes increases the levels of cGMP in the [[corpus cavernosum]] and its supply vessels, relaxes the smooth muscle, and enables an erection. Viagra (sildenafil) was the first blockbuster drug for ED treatment in this class, although vardenafil is more potent in vitro. Both sildenafil and vardenafil have structural similarity to cGMP (and the unselective PDE inhibitor [[caffeine]]), with which they compete for binding of PDE-5 enzymes. Tadalafil is significantly different in structure but is thought to act by the same mechanism. | |||
Tadalafil<ref name="pmid18290855">{{cite journal| author=Hatzichristou D, Gambla M, Rubio-Aurioles E, Buvat J, Brock GB, Spera G et al.| title=Efficacy of tadalafil once daily in men with diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction. | journal=Diabet Med | year= 2008 | volume= 25 | issue= 2 | pages= 138-46 | pmid=18290855 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18290855 | doi=10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02338.x }} </ref><ref name="pmid16422874">{{cite journal| author=McMahon C| title=Comparison of efficacy, safety, and tolerability of on-demand tadalafil and daily dosed tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. | journal=J Sex Med | year= 2005 | volume= 2 | issue= 3 | pages= 415-25; discussion 425-7 | pmid=16422874 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=16422874 | doi=10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.20360.x }} </ref> and vardenafil<ref name="pmid18395326">{{cite journal| author=Zumbé J, Porst H, Sommer F, Grohmann W, Beneke M, Ulbrich E| title=Comparable efficacy of once-daily versus on-demand vardenafil in men with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction: findings of the RESTORE study. | journal=Eur Urol | year= 2008 | volume= 54 | issue= 1 | pages= 204-10 | pmid=18395326 | url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=18395326 | doi=10.1016/j.eururo.2008.03.056 }} </ref> can be taken once a day although this schedule is approved by the Food and Drug Administration only for tadalafil. | |||
83% of men who used [[sildenafil]] had at least one episode of intercourse as compared to 45% who received placebo according to a [[systematic review]] of [[randomized controlled trial]]s of using [[sildenafil]].<ref name="pmid12076233">{{cite journal |author=Fink HA, Mac Donald R, Rutks IR, Nelson DB, Wilt TJ |title=Sildenafil for male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis |journal=Arch. Intern. Med. |volume=162 |issue=12 |pages=1349–60 |year=2002 |month=June |pmid=12076233 |doi= |url=http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12076233 |issn=}}</ref> Few randomized controlled trials have compared the different phosphodiesterase inhibitors.<ref name="pmid14693299">{{cite journal |author=Govier F, Potempa AJ, Kaufman J, Denne J, Kovalenko P, Ahuja S |title=A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, crossover study of patient preference for tadalafil 20 mg or sildenafil citrate 50 mg during initiation of treatment for erectile dysfunction |journal=Clin Ther |volume=25 |issue=11 |pages=2709–23 |year=2003 |month=November |pmid=14693299 |doi= |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0149291803803284 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17100937">{{cite journal |author=Rubio-Aurioles E, Porst H, Eardley I, Goldstein I |title=Comparing vardenafil and sildenafil in the treatment of men with erectile dysfunction and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: a randomized, double-blind, pooled crossover study |journal=J Sex Med |volume=3 |issue=6 |pages=1037–49 |year=2006 |month=November |pmid=17100937 |doi=10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00310.x |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00310.x |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid16942534">{{cite journal |author=Tolrà JR, Campaña JM, Ciutat LF, Miranda EF |title=Prospective, randomized, open-label, fixed-dose, crossover study to establish preference of patients with erectile dysfunction after taking the three PDE-5 inhibitors |journal=J Sex Med |volume=3 |issue=5 |pages=901–9 |year=2006 |month=September |pmid=16942534 |doi=10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00297.x |url=http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00297.x |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid17084518">{{cite journal |author=Martin-Morales A, Haro JM, Beardsworth A, Bertsch J, Kontodimas S |title=Therapeutic effectiveness and patient satisfaction after 6 months of treatment with tadalafil, sildenafil, and vardenafil: results from the erectile dysfunction observational study (EDOS) |journal=Eur. Urol. |volume=51 |issue=2 |pages=541–50; discussion 550 |year=2007 |month=February |pmid=17084518 |doi=10.1016/j.eururo.2006.09.027 |url=http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0302-2838(06)01131-6 |issn=}}</ref> | |||
== References == | |||
<references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 13 August 2024
Erectile dysfunction is a condition in which a male cannot obtain or maintain an erect penis.[1][2] It can result from a wide range of medical conditions, both physical and psychological. Physical causes include diabetes, radical prostatectomy, vascular insufficiency, nerve damage, or insufficient cyclic guanine monophosphate (cGMP) levels. Psychological causes include stress, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, situational anxiety, and relationship problems.
Diagnosis
Erectile dysfunction is often diagnosed using the Sexual Health Inventory for Men (SHIM) test, a validated questionnaire that is widely used in urology clinics to evaluate and assess treatment efficacy for erectile dysfunction (ED).[3]
Additional tests may be necessary to determine the underlying causes of the condition.
Treatment
Clinical practice guidelines by the American College of Physicians address management.[4][5][6]
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors
Sildenafil (Viagra®), vardenafil (Levitra®) and tadalafil (Cialis®), may treat erectile dysfunction[7] and as well as pulmonary hypertensive, are selective phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE-5) inhibitors that bind selectively to PDE-5 and inhibit the binding and subsequent degradation of cyclic GMP (cGMP). Normally, erection results from increased cGMP levels produced by guanylate cyclase, which in turn is upregulated by nitric oxide release after stimulation. By decreasing the degradation of cGMP by PDE-5 enzymes increases the levels of cGMP in the corpus cavernosum and its supply vessels, relaxes the smooth muscle, and enables an erection. Viagra (sildenafil) was the first blockbuster drug for ED treatment in this class, although vardenafil is more potent in vitro. Both sildenafil and vardenafil have structural similarity to cGMP (and the unselective PDE inhibitor caffeine), with which they compete for binding of PDE-5 enzymes. Tadalafil is significantly different in structure but is thought to act by the same mechanism.
Tadalafil[8][9] and vardenafil[10] can be taken once a day although this schedule is approved by the Food and Drug Administration only for tadalafil.
83% of men who used sildenafil had at least one episode of intercourse as compared to 45% who received placebo according to a systematic review of randomized controlled trials of using sildenafil.[11] Few randomized controlled trials have compared the different phosphodiesterase inhibitors.[12][13][14][15]
References
- ↑ Corbin JD, Francis SH (2003). "Molecular biology and pharmacology of PDE-5-inhibitor therapy for erectile dysfunction". J. Androl. 24 (6 Suppl): S38–41. PMID 14581493. [e]
- ↑ McVary KT (December 2007). "Clinical practice. Erectile dysfunction". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (24): 2472–81. DOI:10.1056/NEJMcp067261. PMID 18077811. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Amjad Alwaal, Mohannad Awad, Jake Kuzbel, Brian Snoad (2020). "Sexual Health Inventory for Men Questionnaire as a Screening Method for Erectile Dysfunction in a General Urology Clinic". Sexual Medicine 8 (4): 660-663. DOI:10.1016/j.esxm.2020.08.002. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, Casey DE, Forciea MA, Owens DK et al. (2009). "Hormonal testing and pharmacologic treatment of erectile dysfunction: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians.". Ann Intern Med 151 (9): 639-49. DOI:10.1059/0003-4819-151-9-200911030-00151. PMID 19884625. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Qaseem A, Snow V, Denberg TD, Casey DE, Forciea MA, Owens DK et al. (2009). "Hormonal Testing and Pharmacologic Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Physicians.". Ann Intern Med. PMID 19843532.
- ↑ Tsertsvadze A, Fink HA, Yazdi F, MacDonald R, Bella AJ, Ansari MT et al. (2009). "Oral phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors and hormonal treatments for erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis.". Ann Intern Med 151 (9): 650-61. DOI:10.1059/0003-4819-151-9-200911030-00150. PMID 19884626. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Moore RA, Derry S, McQuay HJ (2005). "Indirect comparison of interventions using published randomised trials: systematic review of PDE-5 inhibitors for erectile dysfunction". BMC Urol 5: 18. DOI:10.1186/1471-2490-5-18. PMID 16354303. PMC 1343572. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Hatzichristou D, Gambla M, Rubio-Aurioles E, Buvat J, Brock GB, Spera G et al. (2008). "Efficacy of tadalafil once daily in men with diabetes mellitus and erectile dysfunction.". Diabet Med 25 (2): 138-46. DOI:10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02338.x. PMID 18290855. Research Blogging.
- ↑ McMahon C (2005). "Comparison of efficacy, safety, and tolerability of on-demand tadalafil and daily dosed tadalafil for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.". J Sex Med 2 (3): 415-25; discussion 425-7. DOI:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2005.20360.x. PMID 16422874. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Zumbé J, Porst H, Sommer F, Grohmann W, Beneke M, Ulbrich E (2008). "Comparable efficacy of once-daily versus on-demand vardenafil in men with mild-to-moderate erectile dysfunction: findings of the RESTORE study.". Eur Urol 54 (1): 204-10. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2008.03.056. PMID 18395326. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Fink HA, Mac Donald R, Rutks IR, Nelson DB, Wilt TJ (June 2002). "Sildenafil for male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis". Arch. Intern. Med. 162 (12): 1349–60. PMID 12076233. [e]
- ↑ Govier F, Potempa AJ, Kaufman J, Denne J, Kovalenko P, Ahuja S (November 2003). "A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, crossover study of patient preference for tadalafil 20 mg or sildenafil citrate 50 mg during initiation of treatment for erectile dysfunction". Clin Ther 25 (11): 2709–23. PMID 14693299. [e]
- ↑ Rubio-Aurioles E, Porst H, Eardley I, Goldstein I (November 2006). "Comparing vardenafil and sildenafil in the treatment of men with erectile dysfunction and risk factors for cardiovascular disease: a randomized, double-blind, pooled crossover study". J Sex Med 3 (6): 1037–49. DOI:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00310.x. PMID 17100937. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Tolrà JR, Campaña JM, Ciutat LF, Miranda EF (September 2006). "Prospective, randomized, open-label, fixed-dose, crossover study to establish preference of patients with erectile dysfunction after taking the three PDE-5 inhibitors". J Sex Med 3 (5): 901–9. DOI:10.1111/j.1743-6109.2006.00297.x. PMID 16942534. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Martin-Morales A, Haro JM, Beardsworth A, Bertsch J, Kontodimas S (February 2007). "Therapeutic effectiveness and patient satisfaction after 6 months of treatment with tadalafil, sildenafil, and vardenafil: results from the erectile dysfunction observational study (EDOS)". Eur. Urol. 51 (2): 541–50; discussion 550. DOI:10.1016/j.eururo.2006.09.027. PMID 17084518. Research Blogging.