Burma Road and Ledo Road: Difference between revisions
imported>Richard Jensen (new lede) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''Burma Road''' (1937-45) and the '''Ledo Road''' (1945) were the main | {{subpages}} | ||
The '''Burma Road''' (1937-45) and the '''Ledo Road''' (1945) were the main overland supply routes to China [[CBI|in the CBI Theater during World War II]]. When Japan blockaded the China's coastline in 1937-45, an overland route was needed. The Chinese Army built the Burma Road connecting Kunming, China, to Rangoon, Burma. When Rangoon was captured by the Japanese in March 1942, the U.S. Army began the Ledo Road as a cutoff route from Ledo, India, to the Burma Road; it opened early in 1945. | |||
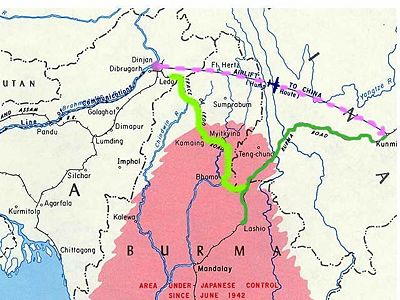
[[Image:Cbi-ledo-road2.jpg|thumb|400px|Burma Road (dark green), Ledo Road (light green) and Hump (dashed)]] | |||
==Burma Road== | ==Burma Road== | ||
In 1937, as Japan attacked China and closed its ports, the need for a new supply route connection to India became urgent. China began an crash project to build a road | In 1937, as Japan attacked China and closed its ports, the need for a new supply route connection to India became urgent. China began an crash project to build a road to bring in supplies from Burma.<ref>The Japanese forced France to end rail traffic from Indochina; and the Soviets as well to stop shipments. </ref> The goal was to link Kunming, China, and Lashio, Burma, which connected by rail to Rangoon. | ||
[[Image:Cbi-roadwork.jpg|thumb|250px]] The two roads were major engineering achievements, but produced minor military results. | |||
The Burma road (unlike the Leo Road) was hand-built, using little machinery; it snaked across the formidable terrain of Yunnan Province and cutting across the grain of the lower Himalayas and the gorges of the Mekong and Salween rivers. The '''Burma Road''' opened in 1938 and by 1940 it was graded, graveled, and bridged to carry ten tons. Bullied by Japan, the British (still neutral) responded to Japanese pressures by closing the 117-mile Burma sector in July -October, 1940. Japanese warplanes attacked traffic on the road. China countered in 1941 with the American Air Volunteers, famed as "[[Flying Tigers]]", a force of Americans with modern fighters controlled by the U.S. but wearing Chinese uniforms. In 1942 Japan's army conquered Burma, in large part to end the traffic. | |||
==Stilwell takes command== | ==Stilwell takes command== | ||
When Lashio fell, a Chinese division fled to India. In June 1942 Gen. [[Joseph Warren Stilwell]], American theater commander in China, Burma, and India, conceived a project to use this Chinese army in India to retake north Burma and build a new 400-mile road to link up with the Burma Road at Wanting. Chinese and British allies showed no enthusiasm for a second Burma campaign, urging instead an all-American air transport route "over the Hump" to aid China. The U.S, compromised by undertaking both strategies, at incredible cost. Stilwell was fiercely determined to build the road despite monsoons, jungle, disease and Japanese attacks. | When Lashio, Burma, fell to Japan, a Chinese division fled to India. In June 1942 Gen. [[Joseph Warren Stilwell]], American theater commander in [[CBI Theater|China, Burma, and India]], conceived a project to use this Chinese army in India to retake north Burma and build a new 400-mile road to link up with the Burma Road at Wanting. Chinese and British allies showed no enthusiasm for a second Burma campaign, urging instead an all-American air transport route "over the Hump" to aid China. The U.S, compromised by undertaking both strategies, at incredible cost. Stilwell was fiercely determined to build the road despite monsoons, jungle, disease and Japanese attacks. | ||
==Ledo Road== | ==Ledo Road== | ||
The '''Ledo Road''' was a 400 mile dirt road through jungle and mountains designed as the major supply route to China | The '''Ledo Road''' was a 400 mile dirt road through jungle and mountains designed as the major supply route to China once Rangoon was occupied by the Japanese. In addition supplies were flown to Kunming "over the hump" (that is, over the high Himalayas.) The road, with two 4-inch oil pipelines alongside, was built in extraordinarily difficult conditions to stretch between Ledo, India, to connect with the existing 720-mile stretch of the Burma Road, which linked northern to Burma to Kunming, China. The first convoys in January, 1945, brought supplies to China across 1100 miles in 24 days. | ||
[[Image:Cbi-Ledo-road2.jpg|thumb|350px|Ledo road near Myitkyina, Burma]] | |||
The Ledo Road project started in October 1942, but it made little progress during 1943. Stilwell's Northern Combat Area Command offensive between October 1943 and August 1944 cleared the Japanese from northern Burma and enabled construction to go forward. The capture of Myitkyina, Burma, in August 1944, meant completion was possible. The Ledo Road opened in late January, 1945. The combined highways were officially named the '''Stilwell Road,''' although Stilwell himself had been relieved of command in October, 1944.<ref> See [http://www.amazon.com/gp/reader/0060746386/ref=sib_dp_bod_ex?ie=UTF8&p=S00L#reader-link Webster (2004) p 335]</ref> | |||
The Ledo road was engineered by 17,000 Americans, half of them in all-black units, under Gen. Lewis A. Pick; the fatalities totaled 1,133 men, 625 of whom died in combat. Over 35,000 Chinese soldiers worked in the project as well. "Pick's Pike" cost $150 million. Sixty-four truck companies--far short of the 375 planned to operate convoys--delivered 150,000 tons of heavy artillery, 25,000 trucks, and miles of gasoline pipeline to parallel the road to Kunming. | |||
==Combat== | |||
There were many minor battles along the way; none of great size. In the siege of Nhpum Ga, a thirteen-day ordeal in June 1944, some 800 Japanese marines attacked with mortars the 1100 Americans of the Second Battalion of "Merrill's Marauders." Surrounded atop an exposed hill, short of water and almost everything except courage and disease, the Marauders shot up the Japanese at all ranges under appalling conditions marked by the overwhelming stench of dead mules and humans decomposing in the jungle heat.<ref> In the midst of their ordeal the Raiders received and consumed an airdrop of fried chicken. [http://www.amazon.com/gp/reader/B0009309A4/ref=sib_dp_pt# Webster (2003) pp 192-95 online]</ref> | |||
==Controversy== | ==Controversy== | ||
Controversy over the Ledo Road's worth plagued the effort from its beginning and it was a contributing factor in Stilwell's recall. Nevertheless, the new Ledo Road revived China's interest in modernizing its Burma Road. Hard to evaluate, these military highways had a great impact on China's morale and ability to finish the war. Sufficient lend-lease supplies arrived on them to flesh out thirty Chinese divisions in 1945, and these divisions were able to stop an eleven-division Japanese drive in East China. After the war the road was little used and fell apart. | Controversy over the Ledo Road's worth plagued the effort from its beginning and it was a contributing factor in Stilwell's recall. Nevertheless, the new Ledo Road revived China's interest in modernizing its Burma Road. Hard to evaluate, these military highways had a great impact on China's morale and ability to finish the war. Sufficient lend-lease supplies arrived on them to flesh out thirty Chinese divisions in 1945, and these divisions were able to stop an eleven-division Japanese drive in East China. After the war the road was little used and fell apart. | ||
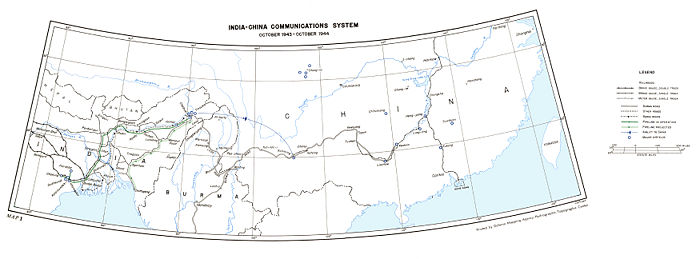
{{Image|Ww2-Ledo-Road.jpg|center|700px|Land and air routes to China}} | |||
== | ==Primary Sources== | ||
* | * Stilwell, Joseph Warren. ''The Stilwell papers'' edited by Theodore H. White, (1958). | ||
* Romanus, Charles F. and Riley Sunderland. '' | * Romanus, Charles F. and Riley Sunderland. ''Stilwell's Mission to China'' (1953), [http://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USA/USA-CBI-Mission/index.html online edition]; ''Stilwell's Command Problems'' (1956) [http://www.ibiblio.net/hyperwar////USA/USA-CBI-Command/index.html online edition]; ''Time runs out in CBI'' (1959) [http://www.ibiblio.net/hyperwar////USA/USA-CBI-Time/index.html online edition]; highly detailed official U.S. Army history | ||
* Tuchman, Barbara. ''Stilwell and the American Experience in China, 1911-45,'' (1972), 624pp; Pulitzer prize (The British edition is ttiled ''Against the Wind: Stilwell and the American Experience in China 1911-45,'') [http://www.amazon.com/Stilwell-American-Experience-China-1911-45/dp/0802138527/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1214005449&sr=8-1 excerpt and text search] | * Tuchman, Barbara. ''Stilwell and the American Experience in China, 1911-45,'' (1972), 624pp; Pulitzer prize (The British edition is ttiled ''Against the Wind: Stilwell and the American Experience in China 1911-45,'') [http://www.amazon.com/Stilwell-American-Experience-China-1911-45/dp/0802138527/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1214005449&sr=8-1 excerpt and text search] | ||
* Webster, Donovan. ''The Burma Road: The Epic Story of the China-Burma-India Theater in World War II'' (2004) 400pp [http://www.amazon.com/Burma-Road-Story-China-Burma-India-Theater/dp/0060746386/ref=sr_1_7?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1214018386&sr=1-7 excerpt and text search] | * Webster, Donovan. ''The Burma Road: The Epic Story of the China-Burma-India Theater in World War II'' (2004) 400pp, the best history. [http://www.amazon.com/Burma-Road-Story-China-Burma-India-Theater/dp/0060746386/ref=sr_1_7?ie=UTF8&s=books&qid=1214018386&sr=1-7 excerpt and text search] | ||
==Notes== | |||
[[Category: | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 22 July 2024
The Burma Road (1937-45) and the Ledo Road (1945) were the main overland supply routes to China in the CBI Theater during World War II. When Japan blockaded the China's coastline in 1937-45, an overland route was needed. The Chinese Army built the Burma Road connecting Kunming, China, to Rangoon, Burma. When Rangoon was captured by the Japanese in March 1942, the U.S. Army began the Ledo Road as a cutoff route from Ledo, India, to the Burma Road; it opened early in 1945.
Burma Road
In 1937, as Japan attacked China and closed its ports, the need for a new supply route connection to India became urgent. China began an crash project to build a road to bring in supplies from Burma.[1] The goal was to link Kunming, China, and Lashio, Burma, which connected by rail to Rangoon.
The two roads were major engineering achievements, but produced minor military results.
The Burma road (unlike the Leo Road) was hand-built, using little machinery; it snaked across the formidable terrain of Yunnan Province and cutting across the grain of the lower Himalayas and the gorges of the Mekong and Salween rivers. The Burma Road opened in 1938 and by 1940 it was graded, graveled, and bridged to carry ten tons. Bullied by Japan, the British (still neutral) responded to Japanese pressures by closing the 117-mile Burma sector in July -October, 1940. Japanese warplanes attacked traffic on the road. China countered in 1941 with the American Air Volunteers, famed as "Flying Tigers", a force of Americans with modern fighters controlled by the U.S. but wearing Chinese uniforms. In 1942 Japan's army conquered Burma, in large part to end the traffic.
Stilwell takes command
When Lashio, Burma, fell to Japan, a Chinese division fled to India. In June 1942 Gen. Joseph Warren Stilwell, American theater commander in China, Burma, and India, conceived a project to use this Chinese army in India to retake north Burma and build a new 400-mile road to link up with the Burma Road at Wanting. Chinese and British allies showed no enthusiasm for a second Burma campaign, urging instead an all-American air transport route "over the Hump" to aid China. The U.S, compromised by undertaking both strategies, at incredible cost. Stilwell was fiercely determined to build the road despite monsoons, jungle, disease and Japanese attacks.
Ledo Road
The Ledo Road was a 400 mile dirt road through jungle and mountains designed as the major supply route to China once Rangoon was occupied by the Japanese. In addition supplies were flown to Kunming "over the hump" (that is, over the high Himalayas.) The road, with two 4-inch oil pipelines alongside, was built in extraordinarily difficult conditions to stretch between Ledo, India, to connect with the existing 720-mile stretch of the Burma Road, which linked northern to Burma to Kunming, China. The first convoys in January, 1945, brought supplies to China across 1100 miles in 24 days.
The Ledo Road project started in October 1942, but it made little progress during 1943. Stilwell's Northern Combat Area Command offensive between October 1943 and August 1944 cleared the Japanese from northern Burma and enabled construction to go forward. The capture of Myitkyina, Burma, in August 1944, meant completion was possible. The Ledo Road opened in late January, 1945. The combined highways were officially named the Stilwell Road, although Stilwell himself had been relieved of command in October, 1944.[2]
The Ledo road was engineered by 17,000 Americans, half of them in all-black units, under Gen. Lewis A. Pick; the fatalities totaled 1,133 men, 625 of whom died in combat. Over 35,000 Chinese soldiers worked in the project as well. "Pick's Pike" cost $150 million. Sixty-four truck companies--far short of the 375 planned to operate convoys--delivered 150,000 tons of heavy artillery, 25,000 trucks, and miles of gasoline pipeline to parallel the road to Kunming.
Combat
There were many minor battles along the way; none of great size. In the siege of Nhpum Ga, a thirteen-day ordeal in June 1944, some 800 Japanese marines attacked with mortars the 1100 Americans of the Second Battalion of "Merrill's Marauders." Surrounded atop an exposed hill, short of water and almost everything except courage and disease, the Marauders shot up the Japanese at all ranges under appalling conditions marked by the overwhelming stench of dead mules and humans decomposing in the jungle heat.[3]
Controversy
Controversy over the Ledo Road's worth plagued the effort from its beginning and it was a contributing factor in Stilwell's recall. Nevertheless, the new Ledo Road revived China's interest in modernizing its Burma Road. Hard to evaluate, these military highways had a great impact on China's morale and ability to finish the war. Sufficient lend-lease supplies arrived on them to flesh out thirty Chinese divisions in 1945, and these divisions were able to stop an eleven-division Japanese drive in East China. After the war the road was little used and fell apart.
Primary Sources
- Stilwell, Joseph Warren. The Stilwell papers edited by Theodore H. White, (1958).
- Romanus, Charles F. and Riley Sunderland. Stilwell's Mission to China (1953), online edition; Stilwell's Command Problems (1956) online edition; Time runs out in CBI (1959) online edition; highly detailed official U.S. Army history
- Tuchman, Barbara. Stilwell and the American Experience in China, 1911-45, (1972), 624pp; Pulitzer prize (The British edition is ttiled Against the Wind: Stilwell and the American Experience in China 1911-45,) excerpt and text search
- Webster, Donovan. The Burma Road: The Epic Story of the China-Burma-India Theater in World War II (2004) 400pp, the best history. excerpt and text search
Notes
- ↑ The Japanese forced France to end rail traffic from Indochina; and the Soviets as well to stop shipments.
- ↑ See Webster (2004) p 335
- ↑ In the midst of their ordeal the Raiders received and consumed an airdrop of fried chicken. Webster (2003) pp 192-95 online