Cholesterol: Difference between revisions
imported>Robert Badgett |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
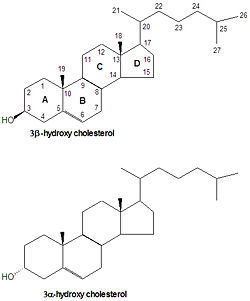
{{Image|Cholesterol structure nomenclature DEVolk.jpg|right|250px|Structure and nomenclature of cholesterol. All steroid nomenclature is based on cholesterol. By convention, substituents pointing up, like C-18 and C-19, are called <math>\beta</math> while those pointing down are called <math>\alpha</math>.}} | |||
'''Cholesterol''' is a [[lipid]] that is the "principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | '''Cholesterol''' is a [[lipid]] that is the "principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils."<ref>{{MeSH}}</ref> | ||
There is much confusion, in the lay press, between cholesterol itself, and the lipoproteins that carry it in the blood. References to "bad cholesterol" are misleading because cholesterol is cholesterol, but low-density lipoproteins (LDL) tend to increase atherosclerosis while high-density lipoproteins (HDL) tend to decrease it. | There is much confusion, in the lay press, between cholesterol itself, and the lipoproteins that carry it in the blood. References to "[[LDL cholesterol|bad cholesterol]]" are misleading because cholesterol is cholesterol, but cholesterol ''carried by'' low-density lipoproteins (LDL) tend to increase atherosclerosis while [[HDL cholesterol|cholesterol carried by high-density lipoproteins]] (HDL) tend to decrease it. | ||
==Disorders of cholesterol== | ==Disorders of cholesterol== | ||
[[Hypercholesterolemia]] may contribute to [[coronary heart disease]], [[stroke]], and other complications. | [[Hypercholesterolemia]] may contribute to [[coronary heart disease]], [[stroke]], and other complications. | ||
[[Hypoalphalipoproteinemia]] is abnormally low levels of alpha-lipoproteins (high-density lipoproteins or HDL) in the blood. Low levels of high-density lipoproteins in the blood is a component of the [[metabolic syndrome]]. | [[Hypoalphalipoproteinemia]] is abnormally low levels of alpha-lipoproteins (high-density lipoproteins or [[HDL]]) in the blood. Low levels of high-density lipoproteins in the blood is a component of the [[metabolic syndrome]]. | ||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
{{main|Hypercholesterolemia}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
* [[Hypercholesterolemia]] | * [[Hypercholesterolemia]] | ||
* [[Lipid]] | * [[Lipid]] | ||
* [[Metabolic syndrome]] | * [[Metabolic syndrome]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:01, 28 July 2024
Cholesterol is a lipid that is the "principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils."[1]
There is much confusion, in the lay press, between cholesterol itself, and the lipoproteins that carry it in the blood. References to "bad cholesterol" are misleading because cholesterol is cholesterol, but cholesterol carried by low-density lipoproteins (LDL) tend to increase atherosclerosis while cholesterol carried by high-density lipoproteins (HDL) tend to decrease it.
Disorders of cholesterol
Hypercholesterolemia may contribute to coronary heart disease, stroke, and other complications.
Hypoalphalipoproteinemia is abnormally low levels of alpha-lipoproteins (high-density lipoproteins or HDL) in the blood. Low levels of high-density lipoproteins in the blood is a component of the metabolic syndrome.
Treatment
References
- ↑ Anonymous (2024), Cholesterol (English). Medical Subject Headings. U.S. National Library of Medicine.