Ritonavir: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
{{Chem infobox | {{Chem infobox | ||
|align=right | |align=right | ||
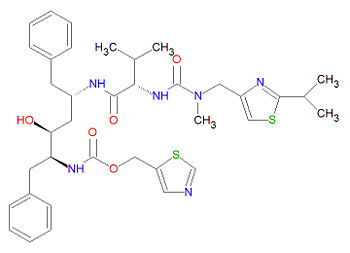
|image=[[Image:Ritonavir structure.jpg| | |image=[[Image:Ritonavir structure.jpg|center|thumb|350px]] | ||
|width=350px | |width=350px | ||
|molname=ritonavir | |molname=ritonavir | ||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
'''Ritonavir''', sold under the brand names '''Norvir®''' and '''Norvir Sec®''', and as a mixture with [[Lopinavir]] called '''Kaletra®''', is a [[protease inhibitor]] used to treat [[HIV]]/[[AIDS]] by disrupting the reproductive cycle of the [[virus]]. Ritonavir binds to and inhibits the HIV-1 viral proteinase enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. Protease inhibitors like ritonavir are almost always used in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs. | '''Ritonavir''', sold under the brand names '''Norvir®''' and '''Norvir Sec®''', and as a mixture with [[Lopinavir]] called '''Kaletra®''', is a [[protease inhibitor]] used to treat [[HIV]]/[[AIDS]] by disrupting the reproductive cycle of the [[virus]]. Ritonavir binds to and inhibits the HIV-1 viral proteinase enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. Protease inhibitors like ritonavir are almost always used in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs. | ||
== Chemistry == | == Chemistry == | ||
| Line 27: | Line 26: | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 12 October 2024
|
| |||||||
| ritonavir | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | HIV | ||||||
| Properties: | protease inhibitor | ||||||
| Hazards: | see drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Ritonavir, sold under the brand names Norvir® and Norvir Sec®, and as a mixture with Lopinavir called Kaletra®, is a protease inhibitor used to treat HIV/AIDS by disrupting the reproductive cycle of the virus. Ritonavir binds to and inhibits the HIV-1 viral proteinase enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. Protease inhibitors like ritonavir are almost always used in combination with at least two other anti-HIV drugs.
Chemistry
Its chemical name is 1,3-thiazol-5-ylmethyl N-[(2S,3S,5S)-3-hydroxy-5-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-[[methyl-[(2-propan- 2-yl-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)methyl]carbamoyl]amino]butanoyl]amino]-1,6-di(phenyl)hexan- 2-yl]carbamate and its chemical formula is C37H48N6O5S2.
External Links
The most up-to-date information about Ritonavir and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Ritonavir - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Ritonavir - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Ritonavir - Detailed information from DrugBank.