Petroleum refining processes: Difference between revisions
imported>Utkarshraj Atmaram m (sp) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (64 intermediate revisions by 11 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Anacortes Refinery.jpg|right|300px|Anacortes Refinery in Anacortes, Washington}} | |||
{{Image|Pascagoula Refinery.jpg|right|300px|Nighttime view of Chevron Oil's refinery in Pascagoula, Mississippi.}} | |||
'''Petroleum refining processes''' are those [[Chemical engineering|chemical engineering]] processes and other facilities used in petroleum refineries (also referred to as oil refineries) to transform [[crude oil]] into useful products such as [[liquefied petroleum gas]] (LPG), [[gasoline|gasoline or petrol]], [[kerosene]], [[jet fuel]], [[diesel oil]] and [[fuel oil]]s.<ref name=Handwerk>{{cite book|author=Gary, J.H. and Handwerk, G.E.|title=Petroleum Refining Technology and Economics|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=Marcel Dekker, Inc|year=1984|id=ISBN 0-8247-7150-8}}</ref><ref name=Leffler>{{cite book|author=Leffler, W.L. |title=Petroleum refining for the nontechnical person|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=PennWell Books|year=1985|id=ISBN 0-87814-280-0}}</ref> | '''Petroleum refining processes''' are those [[Chemical engineering|chemical engineering]] processes and other facilities used in petroleum refineries (also referred to as oil refineries) to transform [[Petroleum crude oil|crude oil]] into useful products such as [[liquefied petroleum gas]] (LPG), [[gasoline|gasoline or petrol]], [[kerosene]], [[jet fuel]], [[diesel oil]] and [[fuel oil]]s.<ref name=Handwerk>{{cite book|author=Gary, J.H. and Handwerk, G.E.|title=Petroleum Refining Technology and Economics|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=Marcel Dekker, Inc|year=1984|id=ISBN 0-8247-7150-8}}</ref><ref name=Leffler>{{cite book|author=Leffler, W.L. |title=Petroleum refining for the nontechnical person|edition=2nd Edition|publisher=PennWell Books|year=1985|id=ISBN 0-87814-280-0}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|author=James G, Speight|title=The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum|edition=Fourth Edition|publisher=CRC Press|year=2006|id=0-8493-9067-2}}</ref> | ||
Petroleum refineries are very large industrial complexes that involve a great many different processing units and auxiliary facilities such as utility units and storage tanks. Each refinery has its own unique arrangement and combination of refining processes largely determined by the refinery location, desired products and economic considerations. There are most probably no two refineries that are identical in every respect. | Petroleum refineries are very large industrial complexes that involve a great many different processing units and auxiliary facilities such as utility units and storage tanks. Each refinery has its own unique arrangement and combination of refining processes largely determined by the refinery location, desired products and economic considerations. There are most probably no two refineries that are identical in every respect. | ||
Some modern petroleum refineries process as much as 800,000 to 900,000 barrels (127,000 to 143,000 cubic meters) per day of crude oil. | |||
==Brief history of the petroleum industry and petroleum refining== | ==Brief history of the petroleum industry and petroleum refining== | ||
Prior to the 19th century, petroleum was known and utilized in various fashions in [[Babylon]], [[Egypt]], China, [[Persia]], [[Rome]] and [[Azerbaijan]]. However, the modern history of the petroleum industry is said to have begun in 1846 when Abraham Gessner of [[Nova Scotia]], [[Canada]] discovered how to produce kerosene from coal. Shortly thereafter, in 1854, Ignacy Lukasiewicz began producing kerosene from hand-dug oil wells near the town of Krosno, now in [[Poland]]. The first large petroleum refinery was built in Ploesti, [[Romania]] in 1856 using the abundant oil available in Romania.<ref>[http://www.150deanidepetrol.ro/history.html 150 Years of Oil in Romania]</ref><ref>[http://www.pbs.org/eakins/we_1844.htm WORLD EVENTS: 1844-1856] www.pbs.org</ref> | |||
In [[North America]], the first oil well was drilled in 1858 by James Miller Williams in [[Ontario]], Canada. In the [[United States of America]], the petroleum industry began in 1859 when Edwin Drake found oil near Titusville, Pennsylvania. The industry grew slowly in the 1800s, primarily producing kerosene for oil lamps. In the early 1900's, the introduction of the internal combustion engine and its use in automobiles created a market for gasoline that was the impetus for fairly rapid growth of the petroleum industry. The early finds of petroleum like those in Ontario and [[Pennsylvania (U.S. state)|Pennsylvania]] were soon outstripped by large oil "booms" in [[Oklahoma (U.S. state)|Oklahoma]], [[Texas (U.S. state)|Texas]] and [[California (U.S. state)|California]].<ref>{{cite book|author=Brian Black|title=Petrolia: the landscape of America's first oil boom|edition=|publisher=John Hopkins University Press|year=2000|id=ISBN 0801863171}}</ref> | |||
Prior to World War II in the early 1940s, most petroleum refineries in the United States consisted simply of [[Petroleum refining processes#The crude oil distillation unit|crude oil distillation units]] (often referred to as atmospheric crude oil distillation units). Some refineries also had [[vacuum distillation]] units as well as [[thermal cracking]] units such as [[visbreakers]] (viscosity breakers, units to lower the [[viscosity]] of the oil). All of the many other refining processes discussed below were developed during the war or within a few years after the war. They became commercially available within 5 to 10 years after the war ended and the worldwide petroleum industry experienced very rapid growth. The driving force for that growth in technology and in the number and size of refineries worldwide was the growing demand for automotive gasoline and aircraft fuel. | |||
In the United States, for various complex economic reasons, the construction of new refineries came to a virtual stop in about the 1980's. However, many of the existing refineries in the United States have revamped many of their units and/or constructed add-on units in order to: increase their crude oil processing capacity, | |||
increase the [[octane]] rating of their product gasoline, lower the [[sulphur]] content of their diesel fuel and home heating fuels to comply with environmental regulations and comply with environmental air pollution and water pollution requirements. | |||
==Processing units used in refineries== | ==Processing units used in refineries== | ||
*[[Petroleum refining processes#The crude oil distillation unit|Crude Oil Distillation unit]]: Distills the incoming crude oil into various fractions for further processing in other units. | *[[Petroleum refining processes#The crude oil distillation unit|Crude Oil Distillation unit]]: Distills the incoming crude oil into various fractions for further processing in other units. | ||
*[[Vacuum Distillation]] unit: Further distills the residue oil | *[[Vacuum Distillation]] unit: Further distills the residue oil from the bottom of the crude oil distillation unit. The vacuum distillation is performed at a pressure well below atmospheric pressure. | ||
*[[Naphtha Hydrotreater]] unit: Uses [[hydrogen]] to desulfurize the naphtha fraction from the crude oil distillation or other units within the refinery. | *[[Hydrodesulfurization|Naphtha Hydrotreater]] unit: Uses [[hydrogen]] to desulfurize the [[petroleum naphtha|naphtha]] fraction from the crude oil distillation or other units within the refinery. | ||
*[[Catalytic | *[[Catalytic reforming|Catalytic Reforming]] unit: Converts the desulfurized naphtha [[molecule]]s into higher-octane molecules to produce ''reformate'', which is a component of the end-product gasoline or petrol. | ||
*[[Alkylation]] unit: Converts isobutane and butylenes into ''alkylate'', which is a very high-octane component of the end-product gasoline or petrol. | *[[Alkylation]] unit: Converts isobutane and butylenes into ''alkylate'', which is a very high-octane component of the end-product gasoline or petrol. | ||
*[[Isomerization]] unit: Converts linear molecules such as normal pentane into higher-octane branched molecules for blending into the end-product gasoline. Also used to convert linear normal butane into isobutane for use in the alkylation unit. | *[[Isomerization]] unit: Converts linear molecules such as normal pentane into higher-octane branched molecules for blending into the end-product gasoline. Also used to convert linear normal butane into isobutane for use in the alkylation unit. | ||
*[[Distillate Hydrotreater]] unit: | *[[Hydrodesulfurization|Distillate Hydrotreater]] unit: Uses hydrogen to desulfurize some of the other distilled fractions from the crude oil distillation unit (such as diesel oil). | ||
*[[Merox]] or similar units: Desulfurize LPG, kerosene or jet fuel by oxidizing undesired | *[[Merox]] (mercaptan oxidizer) or similar units: Desulfurize LPG, kerosene or jet fuel by oxidizing undesired [[mercaptan]]s to organic [[disulfide]]s. | ||
*[[Amine gas treater]], [[Claus process|Claus unit]], and tail gas treatment for converting [[hydrogen | *[[Amine gas treater]], [[Claus process|Claus unit]], and tail [[gas]] treatment for converting [[hydrogen sulphide]] gas from the hydrotreaters into end-product elemental sulfur. The large majority of the 64,000,000 metric tons of sulfur produced worldwide in 2005 was byproduct sulfur from petroleum refining and [[natural gas processing]] plants.<ref>[http://minerals.usgs.gov/minerals/pubs/commodity/sulfur/sulfumcs06.pdf Sulfur production report] by the [[United States Geological Survey]]</ref><ref>[http://www.agiweb.org/geotimes/july03/resources.html Discussion of recovered byproduct sulfur]</ref> | ||
*[[Fluid Catalytic Cracking]] (FCC) unit: Upgrades the heavier, higher-boiling fractions from | *[[Fluid catalytic cracking|Fluid Catalytic Cracking]] (FCC) unit: Upgrades the heavier, higher-boiling fractions from the crude oil distillation by converting them into lighter and lower boiling, more valuable products. | ||
*[[ | *[[Hydrocracking]] unit: Uses hydrogen to upgrade heavier fractions from the crude oil distillation and the vacuum distillation units into lighter, more valuable products. | ||
*[[Visbreaker]] unit upgrades heavy residual oils from the vacuum distillation unit by thermally cracking them into lighter, more valuable reduced viscosity products. | *[[Visbreaking|Visbreaker]] unit upgrades heavy residual oils from the vacuum distillation unit by thermally cracking them into lighter, more valuable reduced viscosity products. | ||
*[[Delayed coking]] and [[Fluid coker]] units: Convert very heavy residual oils into end-product petroleum coke as well as naphtha and diesel oil by-products. | *[[Delayed coking]] and [[Fluid coker]] units: Convert very heavy residual oils into end-product petroleum coke as well as naphtha and diesel oil by-products. | ||
==Auxiliary facilities required in refineries== | ==Auxiliary facilities required in refineries== | ||
*[[Steam reformer]] unit: Converts natural gas into hydrogen for the hydrotreaters and/or the hydrocracker. | |||
*[[Steam | *[[Sour water stripper]] unit: Uses steam to remove hydrogen sulfide gas from various wastewater streams for subsequent conversion into end-product sulfur in the Claus unit.<ref name=Beychok>{{cite book|author=Beychok, Milton R.|title=[[Aqueous Wastes from Petroleum and Petrochemical Plants]]|edition=1st Edition|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|year=1967|id=Library of Congress Control Number 67019834}}</ref> | ||
*[[Sour water stripper]] unit: Uses steam to remove hydrogen sulfide gas from various wastewater streams for subsequent conversion into end-product sulfur in the Claus unit.<ref name=Beychok>{{cite book|author=Beychok, Milton R.|title=Aqueous Wastes from Petroleum and Petrochemical Plants|edition=1st Edition|publisher=John Wiley & Sons|year=1967|id=Library of Congress Control Number 67019834}}</ref> | *Utility units such as [[Industrial cooling tower|cooling towers]] for furnishing circulating cooling water, [[steam generator]]s, instrument air systems for pneumatically operated [[control valve]]s and an [[electrical substation]]. | ||
*Utility units such as cooling towers for furnishing circulating cooling water, | *Wastewater collection and treating systems consisting of [[API oil-water separator]]s, [[dissolved air flotation]] (DAF) units and some type of further treatment (such as an [[activated sludge]] biotreater) to make the wastewaters suitable for reuse or for disposal.<ref name=Beychok/> | ||
*Wastewater collection and treating systems consisting of [[API separator]]s, [[ | |||
*Liquified gas (LPG) storage vessels for propane and similar gaseous fuels at a pressure sufficient to maintain them in liquid form. These are usually spherical vessels or ''bullets'' (horizontal vessels with rounded ends). | *Liquified gas (LPG) storage vessels for propane and similar gaseous fuels at a pressure sufficient to maintain them in liquid form. These are usually spherical vessels or ''bullets'' (horizontal vessels with rounded ends). | ||
*Storage tanks for crude oil and finished products, usually vertical, cylindrical vessels with some sort of vapor emission control and surrounded by an earthen berm to contain liquid spills. | *Storage tanks for crude oil and finished products, usually vertical, cylindrical vessels with some sort of vapor emission control and surrounded by an earthen berm to contain liquid spills. | ||
==The crude oil distillation unit== | ==The crude oil distillation unit== | ||
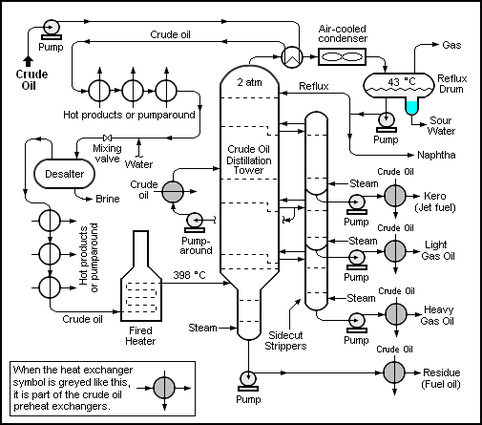
The crude oil distillation unit (CDU) is the first processing unit in virtually all petroleum refineries. The CDU distills the incoming crude oil into various fractions of different boiling ranges, each of which are then processed further in the other refinery processing units. The CDU is often referred to as the ''atmospheric distillation unit'' because it operates at slightly above atmospheric pressure.<ref name=Handwerk/><ref name=Leffler/><ref>{{cite book|author=Kister, Henry Z.|title=[[Distillation Design]]|edition=1st Edition |publisher=McGraw-Hill|year=1992|id=ISBN 0-07-034909-6}}</ref> | |||
Below is a schematic [[process flow diagram]] of a typical crude oil distillation unit. The incoming crude oil is preheated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then desalted to remove inorganic salts (primarily sodium chloride). | |||
Below is a schematic flow diagram of a typical crude oil distillation unit. The incoming crude oil is preheated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then desalted to remove inorganic salts (primarily sodium chloride). | |||
Following the desalter, the crude oil is further heated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then heated in a fuel-fired furnace (fired heater) to a temperature of about 398 °C and routed into the bottom of the distillation unit. | Following the [[Crude oil desalter|desalter]], the crude oil is further heated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then heated in a fuel-fired furnace (fired heater) to a temperature of about 398 °C and routed into the bottom of the distillation unit. | ||
The cooling and condensing of the distillation tower overhead is provided partially by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil and partially by either an air-cooled or water-cooled condenser. Additional heat is removed from the distillation column by a pumparound system as shown in the diagram below. | The cooling and [[Condensation (phase transition)|condensing]] of the distillation tower overhead is provided partially by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil and partially by either an air-cooled or water-cooled [[Condenser (heat transfer)|condenser]]. Additional heat is removed from the distillation column by a pumparound system as shown in the diagram below. | ||
The fractions removed from the side of the distillation column at various points between the column top and bottom are called ''sidecuts''. Each of the sidecuts (i.e., the kerosene, light gas oil and heavy gas oil) is cooled by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil. All of the fractions (i.e., the overhead naphtha, the sidecuts and the bottom residue) are sent to intermediate storage tanks before being processed further. | As shown in the flow diagram, the overhead distillate fraction from the distillation column is naphtha. The fractions removed from the side of the distillation column at various points between the column top and bottom are called ''sidecuts''. Each of the sidecuts (i.e., the kerosene, light gas oil and heavy gas oil) is cooled by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil. All of the fractions (i.e., the overhead naphtha, the sidecuts and the bottom residue) are sent to intermediate storage tanks before being processed further. | ||
{{Image|Crude oil distillation unit.png|center|482px|Schematic flow diagram of a typical crude oil distillation unit.}} | |||
==Flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery== | ==Flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery== | ||
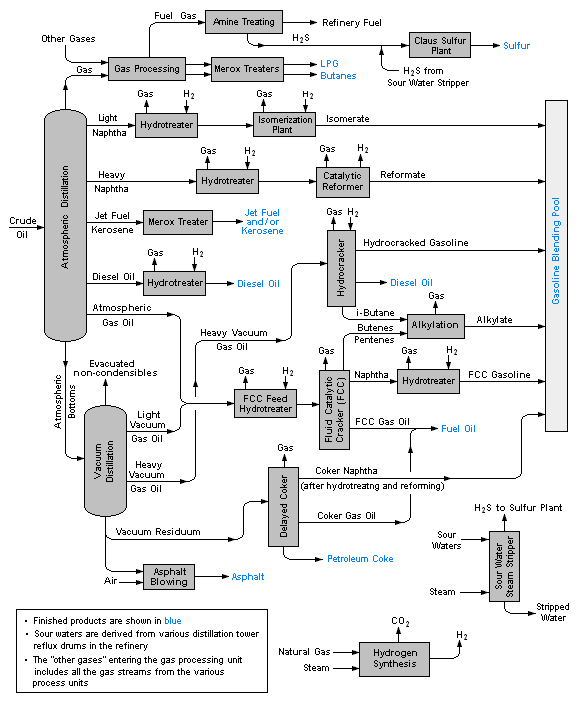
The image below is a schematic flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery that depicts the various refining processes and the flow of intermediate product streams that occurs between the inlet crude oil feedstock and the final end-products. | The image below is a schematic flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery that depicts the various refining processes and the flow of intermediate product streams that occurs between the inlet crude oil feedstock and the final end-products. | ||
The diagram depicts only one of the literally hundreds of different oil refinery configurations. The diagram also does not include any of the usual refinery facilities providing utilities such as steam, cooling water, and electric power as well as storage tanks for crude oil feedstock and for intermediate products and end products.<ref name=Handwerk/><ref name=Leffler/><ref>[http://www.uop.com/refining/1010.html Refinery flowchart] from the website of Universal Oil Products</ref> | The diagram depicts only one of the literally hundreds of different oil refinery configurations. The diagram also does not include any of the usual refinery facilities providing utilities such as steam, cooling water, and electric power as well as storage tanks for crude oil feedstock and for intermediate products and end products.<ref name=Handwerk/><ref name=Leffler/><ref>[http://www.uop.com/refining/1010.html Refinery flowchart] from the website of Universal Oil Products</ref> | ||
{{Image|RefineryFlow.png|center|584px|A schematic flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery.}} | |||
==Refining end-products== | ==Refining end-products== | ||
The primary end-products produced in petroleum refining may be grouped into four categories: light distillates, middle distillates, heavy distillates and others. | The primary end-products produced in petroleum refining may be grouped into four categories: light distillates, middle distillates, heavy distillates and others. | ||
| Line 85: | Line 82: | ||
Many of these are not produced in all petroleum refineries. | Many of these are not produced in all petroleum refineries. | ||
*Specialty | *Specialty [[petroleum naphtha]]s | ||
*Specialty | *Specialty [[solvent]]s | ||
*Elemental sulfur (and sometimes [[sulfuric acid]]) | *Elemental sulfur (and sometimes [[sulfuric acid]]) | ||
*Petrochemical feedstocks | *[[Petrochemical]] feedstocks | ||
*Asphalt | *[[Asphalt (petroleum)|Asphalt]] | ||
*Petroleum | *[[Delayed coking|Petroleum coke]] | ||
*Lubricating | *[[Lubricating oil]]s | ||
*Waxes and greases | *[[Waxes and greases]] | ||
*Transformer and cable oils | *[[Transformer]] and cable oils | ||
*Carbon black | *[[Carbon black]] | ||
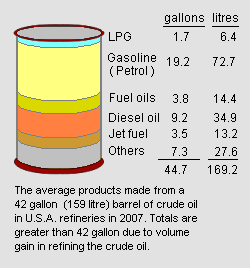
{{Image|Refinery Products Barrel.png|right|250px|Add image caption here.}} | |||
==Average refinery product yields== | |||
Petroleum refinery product yields differ significantly from one refinery to another because the large majority of refineries process their own unique slate of crude oils and, even more significantly, have different refining process configurations. | |||
Many refineries also change their product yields seasonally (i.e., from summer to winter) since typically the winter season demand decreases for gasoline and increases for heating oil. | |||
However, the average of all the product yields from refineries in the United States during 2007 is depicted in the adjacent diagram.<ref>[http://www.eia.doe.gov/bookshelf/brochures/gasoline/index.html Where Does My Gasoline Come from?], [[U.S. Department of Energy]], [[Energy Information Administration]], April 2008.</ref> | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
[[Category: | |||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 3 October 2024
Petroleum refining processes are those chemical engineering processes and other facilities used in petroleum refineries (also referred to as oil refineries) to transform crude oil into useful products such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), gasoline or petrol, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel oil and fuel oils.[1][2][3]
Petroleum refineries are very large industrial complexes that involve a great many different processing units and auxiliary facilities such as utility units and storage tanks. Each refinery has its own unique arrangement and combination of refining processes largely determined by the refinery location, desired products and economic considerations. There are most probably no two refineries that are identical in every respect.
Some modern petroleum refineries process as much as 800,000 to 900,000 barrels (127,000 to 143,000 cubic meters) per day of crude oil.
Brief history of the petroleum industry and petroleum refining
Prior to the 19th century, petroleum was known and utilized in various fashions in Babylon, Egypt, China, Persia, Rome and Azerbaijan. However, the modern history of the petroleum industry is said to have begun in 1846 when Abraham Gessner of Nova Scotia, Canada discovered how to produce kerosene from coal. Shortly thereafter, in 1854, Ignacy Lukasiewicz began producing kerosene from hand-dug oil wells near the town of Krosno, now in Poland. The first large petroleum refinery was built in Ploesti, Romania in 1856 using the abundant oil available in Romania.[4][5]
In North America, the first oil well was drilled in 1858 by James Miller Williams in Ontario, Canada. In the United States of America, the petroleum industry began in 1859 when Edwin Drake found oil near Titusville, Pennsylvania. The industry grew slowly in the 1800s, primarily producing kerosene for oil lamps. In the early 1900's, the introduction of the internal combustion engine and its use in automobiles created a market for gasoline that was the impetus for fairly rapid growth of the petroleum industry. The early finds of petroleum like those in Ontario and Pennsylvania were soon outstripped by large oil "booms" in Oklahoma, Texas and California.[6]
Prior to World War II in the early 1940s, most petroleum refineries in the United States consisted simply of crude oil distillation units (often referred to as atmospheric crude oil distillation units). Some refineries also had vacuum distillation units as well as thermal cracking units such as visbreakers (viscosity breakers, units to lower the viscosity of the oil). All of the many other refining processes discussed below were developed during the war or within a few years after the war. They became commercially available within 5 to 10 years after the war ended and the worldwide petroleum industry experienced very rapid growth. The driving force for that growth in technology and in the number and size of refineries worldwide was the growing demand for automotive gasoline and aircraft fuel.
In the United States, for various complex economic reasons, the construction of new refineries came to a virtual stop in about the 1980's. However, many of the existing refineries in the United States have revamped many of their units and/or constructed add-on units in order to: increase their crude oil processing capacity, increase the octane rating of their product gasoline, lower the sulphur content of their diesel fuel and home heating fuels to comply with environmental regulations and comply with environmental air pollution and water pollution requirements.
Processing units used in refineries
- Crude Oil Distillation unit: Distills the incoming crude oil into various fractions for further processing in other units.
- Vacuum Distillation unit: Further distills the residue oil from the bottom of the crude oil distillation unit. The vacuum distillation is performed at a pressure well below atmospheric pressure.
- Naphtha Hydrotreater unit: Uses hydrogen to desulfurize the naphtha fraction from the crude oil distillation or other units within the refinery.
- Catalytic Reforming unit: Converts the desulfurized naphtha molecules into higher-octane molecules to produce reformate, which is a component of the end-product gasoline or petrol.
- Alkylation unit: Converts isobutane and butylenes into alkylate, which is a very high-octane component of the end-product gasoline or petrol.
- Isomerization unit: Converts linear molecules such as normal pentane into higher-octane branched molecules for blending into the end-product gasoline. Also used to convert linear normal butane into isobutane for use in the alkylation unit.
- Distillate Hydrotreater unit: Uses hydrogen to desulfurize some of the other distilled fractions from the crude oil distillation unit (such as diesel oil).
- Merox (mercaptan oxidizer) or similar units: Desulfurize LPG, kerosene or jet fuel by oxidizing undesired mercaptans to organic disulfides.
- Amine gas treater, Claus unit, and tail gas treatment for converting hydrogen sulphide gas from the hydrotreaters into end-product elemental sulfur. The large majority of the 64,000,000 metric tons of sulfur produced worldwide in 2005 was byproduct sulfur from petroleum refining and natural gas processing plants.[7][8]
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking (FCC) unit: Upgrades the heavier, higher-boiling fractions from the crude oil distillation by converting them into lighter and lower boiling, more valuable products.
- Hydrocracking unit: Uses hydrogen to upgrade heavier fractions from the crude oil distillation and the vacuum distillation units into lighter, more valuable products.
- Visbreaker unit upgrades heavy residual oils from the vacuum distillation unit by thermally cracking them into lighter, more valuable reduced viscosity products.
- Delayed coking and Fluid coker units: Convert very heavy residual oils into end-product petroleum coke as well as naphtha and diesel oil by-products.
Auxiliary facilities required in refineries
- Steam reformer unit: Converts natural gas into hydrogen for the hydrotreaters and/or the hydrocracker.
- Sour water stripper unit: Uses steam to remove hydrogen sulfide gas from various wastewater streams for subsequent conversion into end-product sulfur in the Claus unit.[9]
- Utility units such as cooling towers for furnishing circulating cooling water, steam generators, instrument air systems for pneumatically operated control valves and an electrical substation.
- Wastewater collection and treating systems consisting of API oil-water separators, dissolved air flotation (DAF) units and some type of further treatment (such as an activated sludge biotreater) to make the wastewaters suitable for reuse or for disposal.[9]
- Liquified gas (LPG) storage vessels for propane and similar gaseous fuels at a pressure sufficient to maintain them in liquid form. These are usually spherical vessels or bullets (horizontal vessels with rounded ends).
- Storage tanks for crude oil and finished products, usually vertical, cylindrical vessels with some sort of vapor emission control and surrounded by an earthen berm to contain liquid spills.
The crude oil distillation unit
The crude oil distillation unit (CDU) is the first processing unit in virtually all petroleum refineries. The CDU distills the incoming crude oil into various fractions of different boiling ranges, each of which are then processed further in the other refinery processing units. The CDU is often referred to as the atmospheric distillation unit because it operates at slightly above atmospheric pressure.[1][2][10]
Below is a schematic process flow diagram of a typical crude oil distillation unit. The incoming crude oil is preheated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then desalted to remove inorganic salts (primarily sodium chloride).
Following the desalter, the crude oil is further heated by exchanging heat with some of the hot, distilled fractions and other streams. It is then heated in a fuel-fired furnace (fired heater) to a temperature of about 398 °C and routed into the bottom of the distillation unit.
The cooling and condensing of the distillation tower overhead is provided partially by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil and partially by either an air-cooled or water-cooled condenser. Additional heat is removed from the distillation column by a pumparound system as shown in the diagram below.
As shown in the flow diagram, the overhead distillate fraction from the distillation column is naphtha. The fractions removed from the side of the distillation column at various points between the column top and bottom are called sidecuts. Each of the sidecuts (i.e., the kerosene, light gas oil and heavy gas oil) is cooled by exchanging heat with the incoming crude oil. All of the fractions (i.e., the overhead naphtha, the sidecuts and the bottom residue) are sent to intermediate storage tanks before being processed further.
Flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery
The image below is a schematic flow diagram of a typical petroleum refinery that depicts the various refining processes and the flow of intermediate product streams that occurs between the inlet crude oil feedstock and the final end-products.
The diagram depicts only one of the literally hundreds of different oil refinery configurations. The diagram also does not include any of the usual refinery facilities providing utilities such as steam, cooling water, and electric power as well as storage tanks for crude oil feedstock and for intermediate products and end products.[1][2][11]
Refining end-products
The primary end-products produced in petroleum refining may be grouped into four categories: light distillates, middle distillates, heavy distillates and others.
Light distillates
- Liquid petroleum gas (LPG)
- Gasoline (also known as petrol)
- Kerosene
- Jet fuel and other aircraft fuel
Middle distillates
- Automotive and railroad diesel fuels
- Residential heating fuel
- Other light fuel oils
Heavy distillates
- Heavy fuel oils
- Bunker fuel oil and other residual fuel oils
Others
Many of these are not produced in all petroleum refineries.
- Specialty petroleum naphthas
- Specialty solvents
- Elemental sulfur (and sometimes sulfuric acid)
- Petrochemical feedstocks
- Asphalt
- Petroleum coke
- Lubricating oils
- Waxes and greases
- Transformer and cable oils
- Carbon black
Average refinery product yields
Petroleum refinery product yields differ significantly from one refinery to another because the large majority of refineries process their own unique slate of crude oils and, even more significantly, have different refining process configurations.
Many refineries also change their product yields seasonally (i.e., from summer to winter) since typically the winter season demand decreases for gasoline and increases for heating oil.
However, the average of all the product yields from refineries in the United States during 2007 is depicted in the adjacent diagram.[12]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gary, J.H. and Handwerk, G.E. (1984). Petroleum Refining Technology and Economics, 2nd Edition. Marcel Dekker, Inc. ISBN 0-8247-7150-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Leffler, W.L. (1985). Petroleum refining for the nontechnical person, 2nd Edition. PennWell Books. ISBN 0-87814-280-0.
- ↑ James G, Speight (2006). The Chemistry and Technology of Petroleum, Fourth Edition. CRC Press. 0-8493-9067-2.
- ↑ 150 Years of Oil in Romania
- ↑ WORLD EVENTS: 1844-1856 www.pbs.org
- ↑ Brian Black (2000). Petrolia: the landscape of America's first oil boom. John Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0801863171.
- ↑ Sulfur production report by the United States Geological Survey
- ↑ Discussion of recovered byproduct sulfur
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Beychok, Milton R. (1967). Aqueous Wastes from Petroleum and Petrochemical Plants, 1st Edition. John Wiley & Sons. Library of Congress Control Number 67019834.
- ↑ Kister, Henry Z. (1992). Distillation Design, 1st Edition. McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-034909-6.
- ↑ Refinery flowchart from the website of Universal Oil Products
- ↑ Where Does My Gasoline Come from?, U.S. Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration, April 2008.
- Pages using ISBN magic links
- Editable Main Articles with Citable Versions
- CZ Live
- Engineering Workgroup
- Chemistry Workgroup
- Chemical Engineering Subgroup
- Articles written in American English
- Advanced Articles written in American English
- All Content
- Engineering Content
- Chemistry Content
- Chemical Engineering tag