Parasympathetic nervous system: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Robert Badgett (Adapted from WP) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
The '''parasympathetic nervous system''' is part of the [[autonomic nervous system]] | {{subpages}} | ||
The '''parasympathetic nervous system''' is part of the [[autonomic nervous system]]. | |||
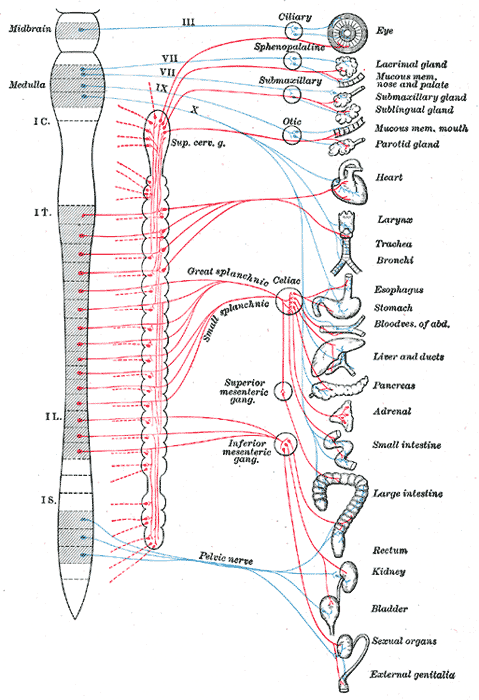
[[Image:Gray839.gif|thumb|479px|The autonomic nervous system<br/>'''Blue = parasympathetic'''<BR>Red = sympathetic]] | |||
==Functions== | |||
* Dilates blood vessels leading to the GI tract, increasing blood flow. This is important following the consumption of food, due to the greater metabolic demands placed on the body by the gut. | * Dilates blood vessels leading to the GI tract, increasing blood flow. This is important following the consumption of food, due to the greater metabolic demands placed on the body by the gut. | ||
*The parasympathetic nervous system can also constrict the bronchiolar diameter when the need for oxygen has diminished. | *The parasympathetic nervous system can also constrict the bronchiolar diameter when the need for oxygen has diminished. | ||
* During accommodation, the parasympathetic nervous system causes constriction of the pupil and lens. | |||
* The parasympathetic nervous system stimulates salivary gland secretion, and accelerates [[peristalsis]], so, in keeping with the rest and digest functions, appropriate parasympathetic nervous system activity mediates digestion of food and indirectly, the absorption of nutrients. | |||
* Is also involved in erection of genitals, via the [[pelvic splanchnic nerves]] 2–4. | |||
==Anatomy== | |||
===Ganglia=== | |||
Ganglia include the "ciliary, [[pterygopalatine ganglion|pterygopalatine]], submandibular, and otic ganglia in the cranial region and intrinsic (terminal) ganglia associated with target organs in the thorax and abdomen."<ref name="MeSH-Ganglia,+Parasympathetic">{{cite web |url=http://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2008/MB_cgi?term=Ganglia,+Parasympathetic |title=Ganglia, Parasympathetic |accessdate=2008-01-22 |author=Anonymous |authorlink= |coauthors= |date= |format= |work= |publisher=National Library of Medicine |pages= |language= |archiveurl= |archivedate= |quote=}}</ref> | |||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
* | == See also == | ||
* [[Acetylcholine receptor]][[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 1 October 2024
The parasympathetic nervous system is part of the autonomic nervous system.
Functions
- Dilates blood vessels leading to the GI tract, increasing blood flow. This is important following the consumption of food, due to the greater metabolic demands placed on the body by the gut.
- The parasympathetic nervous system can also constrict the bronchiolar diameter when the need for oxygen has diminished.
- During accommodation, the parasympathetic nervous system causes constriction of the pupil and lens.
- The parasympathetic nervous system stimulates salivary gland secretion, and accelerates peristalsis, so, in keeping with the rest and digest functions, appropriate parasympathetic nervous system activity mediates digestion of food and indirectly, the absorption of nutrients.
- Is also involved in erection of genitals, via the pelvic splanchnic nerves 2–4.
Anatomy
Ganglia
Ganglia include the "ciliary, pterygopalatine, submandibular, and otic ganglia in the cranial region and intrinsic (terminal) ganglia associated with target organs in the thorax and abdomen."[1]
References
- ↑ Anonymous. Ganglia, Parasympathetic. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved on 2008-01-22.