Amphiboly: Difference between revisions
imported>Subpagination Bot m (Add {{subpages}} and remove any categories (details)) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
'''Amphiboly''' is the phenomenon wherein one sentence (or, more generally, one string of symbols) in a [[language]] obtains two or more constituent structures (see [[syntax]]) according to one grammar. This leads to [[ambiguity]]. In [[natural language]]s, each constituent structure typically corresponds to a different meaning. For example, in [[English language|English]], the sentence | '''Amphiboly''' is the phenomenon wherein one sentence (or, more generally, one string of symbols) in a [[language]] obtains two or more constituent structures (see [[syntax]]) according to one grammar. This leads to [[ambiguity]]. In [[natural language]]s, each constituent structure typically corresponds to a different meaning. For example, in [[English language|English]], the sentence | ||
| Line 8: | Line 7: | ||
obtains two possible constituent structures: | obtains two possible constituent structures: | ||
[[Image: Amphiboly1.jpg|240px|Figure 1]] and [[Image: Amphiboly2.jpg|240px|Figure 2]] | |||
In Figure 1, "with a telescope" describes how the sailor is being seen, whereas in Figure 2, "with a telescope" identifies which sailor is being seen. | |||
[[Parsing]] with any remotely realistic natural language grammar either devised by hand or extracted from [[Corpus linguistics|corpora]] usually yields several constituent structures for each sentence, and so one of the chief occupations of [[computational linguistics]] is determining which of the constituent structures found corresponds to the intended reading. Moreover, as humans usually agree on which of the constituent structures is correct with very little effort, [[psycholinguistics|psycholinguists]] investigate which factors prompt the selection of one constituent structure over another.[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
[[Parsing]] with any remotely realistic natural language grammar either devised by hand or extracted from [[Corpus linguistics|corpora]] usually yields several constituent structures for each sentence, and so one of the chief occupations of [[computational linguistics]] is determining which of the constituent structures found corresponds to the intended reading. Moreover, as humans usually agree on which of the constituent structures is correct with very little effort, [[psycholinguistics|psycholinguists]] investigate which factors prompt the selection of one constituent structure over another. | |||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 10 July 2024
Amphiboly is the phenomenon wherein one sentence (or, more generally, one string of symbols) in a language obtains two or more constituent structures (see syntax) according to one grammar. This leads to ambiguity. In natural languages, each constituent structure typically corresponds to a different meaning. For example, in English, the sentence
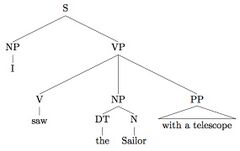
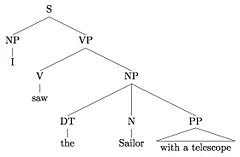
"I saw the sailor with a telescope"
obtains two possible constituent structures:
In Figure 1, "with a telescope" describes how the sailor is being seen, whereas in Figure 2, "with a telescope" identifies which sailor is being seen.
Parsing with any remotely realistic natural language grammar either devised by hand or extracted from corpora usually yields several constituent structures for each sentence, and so one of the chief occupations of computational linguistics is determining which of the constituent structures found corresponds to the intended reading. Moreover, as humans usually agree on which of the constituent structures is correct with very little effort, psycholinguists investigate which factors prompt the selection of one constituent structure over another.