New York, New York: Difference between revisions
imported>Kjetil Ree (→Boroughs: Map by Julius Schorzman) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (112 intermediate revisions by 15 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{dambigbox|the U.S. city|New York}} | |||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
[[Image:Statue of Liberty.jpg|thumb|left|220px|The [[Statue of Liberty]] symbolizes freedom throughout the world, and is one of the best known symbols of New York City]] | |||
'''New York City''' is the largest city in the [[United States of America]]. It is located in [[New York (U.S. state)|New York state]] east of the [[Hudson River]]'s mouth. The wider metropolitan area (including portions in [[New Jersey (U.S. state)|New Jersey]]) has about 20 million people and is the largest urban area in the United States and one of the | |||
larger ones in the world<ref name=Population />. However, [[Albany, New York]], is the state capital. | |||
New York City is home to one of the twelve district [[Federal Reserve System]] banks and is a world center of commerce, business, and culture, as well as one of the world's financial hubs. The [[New York Stock Exchange]] (Wall Street) and the [[NASDAQ]] are the world's first and second largest stock exchanges. | |||
New York saw 12 million immigrants entering the U.S. through [[Ellis Island]]; making the city a cosmopolitan metropolis. New York has always been a melting pot, and it has large groups of Americans with Jewish, Irish, German, Italian or Hispanic descent. In 2005, nearly 170 languages were spoken in the city and 36 percent of its population was foreign born.<ref name="languages in NYC">{{cite web |publisher=New York State Comptroller|New York State Office of the State Comptroller |title=Queens: Economic Development and the State of the Borough Economy |date=June 2006 |url=http://www.osc.state.ny.us/osdc/rpt3-2007queens.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-21}}</ref> | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
The region was inhabited by the | The region was inhabited by the Lenape people at the time of the arrival of the Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano in 1524. Verrazzano called the settlement "Nouvelle Angoulême".<ref name="rodgers">{{cite book |title=New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress | author=Rankin, Rebecca B., and Cleveland Rodgers |publisher=Harper |year=1948}}</ref> The Dutch founded the first European settlement in 1614, called "New Amsterdam," on the southern tip of [[Manhattan (borough)|Manhattan]]. Dutch colonial Director-General Peter Minuit purchased the island of Manhattan from the Canarsie in 1626.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Miller, Christopher L., George R. Hamell |date=September 1986 |title=A New Perspective on Indian-White Contact: Cultural Symbols and Colonial Trade |journal=The Journal of American History |volume=73 |issue=2 |url=http://links.jstor.org/sici?sici=0021-8723%28198609%2973%3A2%3C311%3AANPOIC%3E2.0.CO%3B2-A |accessdate=2007-03-21}}</ref> In 1664, the British conquered the city and renamed it "New York" after James II of [[England]], Duke of York and Albany.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Historical Atlas of New York City: A Visual Celebration of 400 Years of New York City's History |author=Homberger, Eric |year=2005 |pages=p. 34 |publisher=Owl Books |isbn=0805078428}}</ref> | ||
[[Image:Federal Hall.jpg|thumb|The first President of the United States, [[George Washington]], was inaugurated at | [[Image:Federal Hall.jpg|thumb|The first President of the United States, [[George Washington]], was inaugurated at Federal Hall on Wall Street. The Federal Hall is now dwarfed by surrounding skyscrapers]] | ||
New York City grew in importance as a trading port while under [[ | New York City grew in importance as a trading port while under [[United Kingdom|British]] rule. In 1754, [[Columbia University|King's College (later Columbia University)]] was founded under charter by King George II. It was located in Lower Manhattan.<ref>{{cite book |title=An Historical Sketch of Columbia College, in the City of New York, 1754-1876 |author=Moore, Nathaniel Fish |year=1876 |pages=p. 8 |publisher=Columbia College}}</ref> The city emerged as the theater for a series of major battles known as the New York Campaign during the [[American Revolution, military history|American Revolutionary War]]. The [[Continental Congress]] met in New York City, and in 1789 the first President of the United States, [[George Washington]], was inaugurated at [[Federal Hall]] on Wall Street.<ref>[https://www.archives.gov/milestone-documents/president-george-washingtons-first-inaugural-speech President George Washington's First Inaugural Speech], on ''www.archives.gov'', last access 11/27/2022</ref> New York City was the capital of the United States until 1790. | ||
During the 19th century, the city was transformed by immigration | During the 19th century, the city was transformed by immigration. A visionary development proposal, called the Commissioners' Plan of 1811, expanded the city street grid to encompass all of Manhattan. With the opening in 1825 of the [[Erie Canal]], New York was connected to the vast agricultural markets of the North American interior.<ref>{{cite book | ||
|author = Bridges, William | title = Map | |author = Bridges, William | title = Map of the City of New York and Island of Manhattan with Explanatory Remarks and References | date = 1811}}</ref><ref name="lankevich-p67">Lankevich (1998), pp. 67–68.</ref> By 1835, New York City had surpassed [[Philadelphia, Pennsylvania|Philadelphia]] as the largest city in the United States. Local politics fell under the domination of Tammany Hall, a political machine supported by Irish immigrants.<ref>{{cite book |title=Fernando Wood: A Political Biography |author=Mushkat, Jerome Mushkat |publisher=Kent State University Press |year=1990 |pages=p. 36 |isbn=087338413X}}</ref> Public-minded members of the old merchant aristocracy pressed for Central Park, which became the first landscaped park in an American city in 1857. | ||
Anger at military conscription during the [[ | Anger at military conscription during the [[American Civil War]] led to [[New York City draft riots|draft riots in 1863]], one of the worst incidents of civil unrest in American history.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Armies of the Streets: The New York City Draft Riots of 1863 |author=Cook, Adrian |year=1974 |pages=pp. 193-195}}</ref> In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of [[Brooklyn]] (until then an independent city), Manhattan, Queens, Richmond, and the Bronx.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/nyc100/html/classroom/hist_info/100aniv.html The 100 Year Anniversary of the Consolidation of the 5 Boroughs into New York City], New York City. Accessed June 29, 2007.</ref> The opening of the [[New York City Subway]] in 1904 connected the different neighborhoods of the city and spurred development in uptown Manhattan. Throughout the first half of the 20th century, the city became a world center for art, industry, commerce, and communication. In 1911, the [[Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire]], the city's worst industrial disaster, took the lives of 146 garment workers and spurred the growth of the [[International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union]] and major improvements in factory safety standards.<ref name="cornell1">{{cite web |url=http://www.ilr.cornell.edu/trianglefire/ |title=Cornell University Library: Triangle Factory Fire |publisher=Cornell University |accessdate=2007-03-12}}</ref> | ||
[[Image:Bohemian Cigarmakers.jpg|thumb|Bohemian cigarmakers at work in their crowded tenement. Large amounts of European immigrants moved to New York in the second half of the nineteenth century, and living conditions were often poor | [[Image:Bohemian Cigarmakers.jpg|thumb|220px|Bohemian cigarmakers at work in their crowded tenement. Large amounts of European immigrants moved to New York in the second half of the nineteenth century, and living conditions were often poor.]] | ||
In the 1920s, New York City was a major destination for [[African Americans]] during the [[Great Migration]] from the American South. By 1916, New York City was home to the largest urban African diaspora in North America. The [[Harlem Renaissance]] flourished during the era of [[Prohibition in the United States|Prohibition]], coincident with a larger economic boom that saw the skyline develop with the construction of competing [[skyscrapers]]. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking [[London, United Kingdom|London]], which had reigned for a century. The difficult years of the [[Great Depression, U.S.|Great Depression]] saw the election of reformer [[Fiorello LaGuardia]] as mayor and the fall of Tammany Hall after eighty years of political dominance.<ref>{{cite book|title=The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall |author=Allen, Oliver E. |publisher=Addison-Wesley Publishing Company |accessdate=2007-05-25 |chapter=Chapter 9: The Decline |date=1993}}</ref> | |||
After [[World War II]], returning veterans and immigrants from Europe created a postwar economic boom and the development of huge housing tracts in eastern Queens. New York emerged from the war unscathed and the leading city of the world, with Wall Street leading America's ascendance as the world's dominant economic power, the [[United Nations]] headquarters (built in 1952) emphasizing New York's political influence, and the rise of Abstract Expressionism in the city precipitating New York's displacement of Paris as the center of the art world.<ref>{{cite web |title=The Center of the World - New York: A Documentary Film (Transcript) |author=Burns, Ric |publisher=PBS |url=http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/newyork/filmmore/pt.html| accessdate=2006-07-20 |date=2003-08-22}}</ref> Yet like many large American cities, New York suffered a decline in manufacturing and rising crime rates, race riots, and white flight in the 1960s. By the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a crime-ridden relic of history. | |||
The city was one of the sites of the | In the 1980s, a resurgence in the financial industry improved the city's fiscal health. By the 1990s, racial tensions had calmed, crime rates dropped dramatically, and waves of new immigrants arrived from Asia and Latin America. New York's economy was revitalized, and New York's population reached an all-time high in the 2000 census. | ||
The city was one of the sites of the 9/11 terrorist attack in 2001. Nearly 3,000 people died in the destruction of the [[World Trade Center]]. The [[Freedom Tower]] was later built on the site.<ref>{{cite web | title = World Trade Center: Frequently Asked Questions | url=http://www.wtc.com/inner_page.aspx?id=14 | publisher = Silverstein Properties | accessdate = 2007-05-25 }}</ref> | |||
==Geography== | ==Geography== | ||
[[Image:East River.jpg|thumb|The | [[Image:East River.jpg|thumb|220px|The East River separates the Bronx and Manhattan from Long Island. Downtown Manhattan to the left, Brooklyn to the right.]] | ||
New York City is located in the Northeastern United States, in southeastern [[New York]] State, approximately half way between [[Washington, D.C.]] and [[Boston]].<ref>Washington, D.C. is 228 miles driving distance from New York City, and Boston is 217 miles driving distance from New York.</ref> The location at the mouth of the [[Hudson River]], which feeds into a naturally sheltered harbor and then into the [[Atlantic Ocean]], has helped the city grow in significance as a trading city. Most of New York is built on the three islands of Manhattan, Staten Island, and western Long Island, making land scarce and encouraging a high population density. | New York City is located in the Northeastern United States, in southeastern [[New York (disambiguation)|New York]] State, approximately half way between [[Washington, D.C.]] and [[Boston, Massachusetts]].<ref>Washington, D.C. is 228 miles driving distance from New York City, and Boston is 217 miles driving distance from New York.</ref> The location at the mouth of the [[Hudson River]], which feeds into a naturally sheltered harbor and then into the [[Atlantic Ocean]], has helped the city grow in significance as a trading city. Most of New York is built on the three islands of Manhattan, Staten Island, and western Long Island, making land scarce and encouraging a high population density. | ||
The Hudson River flows through the | The Hudson River flows through the Hudson Valley into New York Bay. Between New York City and [[Troy, New York]], the river is a [[tidal estuary]].<ref>[http://life.bio.sunysb.edu/marinebio/fc.1.estuaries.html Information about the Hudson River estuary]</ref> The Hudson separates the city from [[New Jersey (U.S. state)|New Jersey]]. The [[East River]], actually a tidal strait, flows from [[Long Island Sound]] and separates the Bronx and Manhattan from Long Island. The [[Harlem River]], another tidal strait between the East and Hudson Rivers, separates Manhattan from the Bronx. | ||
The city's land has been altered considerably by human intervention, with substantial [[land reclamation]] along the waterfronts since Dutch colonial times. Reclamation is most notable in [[Lower Manhattan]], with developments such as [[Battery Park City]] in the 1970s and 1980s.<ref name="gillespie-p71">{{cite book |author=Gillespie, Angus K. |year=1999 |title=Twin Towers: The Life of New York City's World Trade Center |publisher=Rutgers University Press |pages=p. 71}}</ref> Some of the natural variations in topography have been evened out, particularly in Manhattan.<ref>{{cite book |author=Lopate , Phillip |title=Waterfront: A Walk Around Manhattan |publisher=Anchor Press |year=2004 |isbn=0385497148}}</ref> | The city's land has been altered considerably by human intervention, with substantial [[land reclamation]] along the waterfronts since Dutch colonial times. Reclamation is most notable in [[Lower Manhattan]], with developments such as [[Battery Park City]] in the 1970s and 1980s.<ref name="gillespie-p71">{{cite book |author=Gillespie, Angus K. |year=1999 |title=Twin Towers: The Life of New York City's World Trade Center |publisher=Rutgers University Press |pages=p. 71}}</ref> Some of the natural variations in topography have been evened out, particularly in Manhattan.<ref>{{cite book |author=Lopate , Phillip |title=Waterfront: A Walk Around Manhattan |publisher=Anchor Press |year=2004 |isbn=0385497148}}</ref> | ||
The city's land area is 321 mi² (831.4 km²).<ref name="NYC land area">{{cite web| title=Land Use Facts |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/html/dcp/html/landusefacts/landusefactshome.shtml|publisher=New York City Department of City Planning| accessdate=2007-03-13}} New York City's total area is 468.9 mi². 159.88 mi² of this is water and 321 mi² is land.</ref> The highest point in the city is [[Todt Hill]] on Staten Island, which at 409.8 ft (124.9 m) above sea level is the highest point on the Eastern Seaboard south of [[Maine]].<ref>{{cite book |title=Staten Island: Isle of the Bay, NY |author=Lundrigan, Margaret |publisher=Arcadia Publishing |year=2004 |ID=ISBN 0738524433 |pages=p. 10}}</ref> The summit of the ridge is largely covered in woodlands as part of the [[Staten Island Greenbelt]].<ref>{{cite book |title=Outside Magazine's Urban Adventure New York City |author=Howard, David |publisher=W. W. Norton & Company |year=2002 |isbn= 0393322122 |pages=p. 35}}</ref> | The city's land area is 321 mi² (831.4 km²).<ref name="NYC land area">{{cite web| title=Land Use Facts |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/html/dcp/html/landusefacts/landusefactshome.shtml|publisher=New York City Department of City Planning| accessdate=2007-03-13}} New York City's total area is 468.9 mi². 159.88 mi² of this is water and 321 mi² is land.</ref> The highest point in the city is [[Todt Hill]] on Staten Island, which at 409.8 ft (124.9 m) above sea level is the highest point on the Eastern Seaboard south of [[Maine (U.S. state)|Maine]].<ref>{{cite book |title=Staten Island: Isle of the Bay, NY |author=Lundrigan, Margaret |publisher=Arcadia Publishing |year=2004 |ID=ISBN 0738524433 |pages=p. 10}}</ref> The summit of the ridge is largely covered in woodlands as part of the [[Staten Island Greenbelt]].<ref>{{cite book |title=Outside Magazine's Urban Adventure New York City |author=Howard, David |publisher=W. W. Norton & Company |year=2002 |isbn= 0393322122 |pages=p. 35}}</ref> | ||
=== Climate === | === Climate === | ||
[[Image:Skiing central park.jpg|thumb|Skiing in [[Central Park]]. A record snowfall buried New York City in February 2006. | [[Image:Skiing central park.jpg|thumb|Skiing in [[Central Park]]. A record snowfall buried New York City in February 2006.]] | ||
Although located at about the same latitude as the much warmer European cities of [[Naples]] and [[Madrid]], New York has a humid continental climate resulting from prevailing wind patterns that bring cool air from the interior of the North American continent.<ref name="NYC climate">{{cite web|title=The Climate of New York|publisher=New York State Climate Office|url=http://nysc.eas.cornell.edu/climate_of_ny.html|accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> The city's coastal position keeps temperatures relatively warmer than inland regions during winter, helping to moderate the amount of snow which averages 25 to 35 inches (63.5 to 88.9 cm) each year.<ref name="NYC climate"/> New York City has a frost-free period lasting an average of 199 days between seasonal freezes.<ref name="NYC climate" /> Spring and Fall in New York City are erratic, and can range from cold and snowy to hot and humid, although they can also be cold or cool and rainy. Summer in New York City is very warm and humid, with temperatures of 90°F (32°C) or higher recorded on average 18 to 25 days each summer.<ref name="NYC climate" /> The city's longterm climate patterns have been affected by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, a 70-year-long warming and cooling cycle in the Atlantic that influences the frequency and severity of hurricanes and coastal storms in the region.<ref>{{cite web|author=Riley, Mary Elizabeth|title=Assessing the Impact of Interannual Climate Variability on New York City's Reservoir System|year=2006|publisher=Cornell University Graduate School for Atmospheric Science |url=http://dspace.library.cornell.edu/bitstream/1813/2623/1/MER+Thesis-new.pdf|format=PDF|accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> Many scientists believe, however, that [[global warming]] will change this pattern.<ref>Romm, Joseph J., ''Hell and High Water: Global Warming — the Solution and the Politics'', pp. 44, 47 (2006) William Morrow & Co. ISBN 0-06117-212-X citing MIT's and Kerry Emanuel's research as showing that the AMO has now been supplanted by global warming as the "dominant force" in the Atlantic climate.</ref> | Although located at about the same latitude as the much warmer European cities of [[Naples, Italy]] and [[Madrid]], New York has a humid continental climate resulting from prevailing wind patterns that bring cool air from the interior of the North American continent.<ref name="NYC climate">{{cite web|title=The Climate of New York|publisher=New York State Climate Office|url=http://nysc.eas.cornell.edu/climate_of_ny.html|accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> The city's coastal position keeps temperatures relatively warmer than inland regions during winter, helping to moderate the amount of snow which averages 25 to 35 inches (63.5 to 88.9 cm) each year.<ref name="NYC climate"/> New York City has a frost-free period lasting an average of 199 days between seasonal freezes.<ref name="NYC climate" /> Spring and Fall in New York City are erratic, and can range from cold and snowy to hot and humid, although they can also be cold or cool and rainy. Summer in New York City is very warm and humid, with temperatures of 90°F (32°C) or higher recorded on average 18 to 25 days each summer.<ref name="NYC climate" /> The city's longterm climate patterns have been affected by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, a 70-year-long warming and cooling cycle in the Atlantic that influences the frequency and severity of hurricanes and coastal storms in the region.<ref>{{cite web|author=Riley, Mary Elizabeth|title=Assessing the Impact of Interannual Climate Variability on New York City's Reservoir System|year=2006|publisher=Cornell University Graduate School for Atmospheric Science |url=http://dspace.library.cornell.edu/bitstream/1813/2623/1/MER+Thesis-new.pdf|format=PDF|accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> Many scientists believe, however, that [[global warming]] will change this pattern.<ref>Romm, Joseph J., ''Hell and High Water: Global Warming — the Solution and the Politics'', pp. 44, 47 (2006) William Morrow & Co. ISBN 0-06117-212-X citing MIT's and Kerry Emanuel's research as showing that the AMO has now been supplanted by global warming as the "dominant force" in the Atlantic climate.</ref> | ||
=== Environment === | === Environment === | ||
[[Image:Hearst Tower.jpg|thumb|The Hearst Tower is the first [[green building]] completed in New York City. | [[Image:Hearst Tower.jpg|thumb|The Hearst Tower is the first [[green building]] completed in New York City.]] | ||
Environmental concerns in the city involve managing its extraordinary population density. Mass transit use is the highest in the nation and gasoline consumption in the city is at the rate the national average was in the 1920s.<ref name="NYC energy consumption">{{cite book|first=Ben|last=Jervey|title=The Big Green Apple: Your Guide to Eco-Friendly Living in New York City|isbn=0762738359|publisher=Globe Pequot Press|year=2006}}</ref> New York City's dense population and low automobile dependence help make New York among the most energy efficient in the United States.<ref>{{cite news |author=Owen, David |title=Green Manhattan |publisher=The New Yorker |date= | Environmental concerns in the city involve managing its extraordinary population density. Mass transit use is the highest in the nation and gasoline consumption in the city is at the rate the national average was in the 1920s.<ref name="NYC energy consumption">{{cite book|first=Ben|last=Jervey|title=The Big Green Apple: Your Guide to Eco-Friendly Living in New York City|isbn=0762738359|publisher=Globe Pequot Press|year=2006}}</ref> New York City's dense population and low automobile dependence help make New York among the most energy efficient in the United States.<ref>{{cite news |author=Owen, David |title=Green Manhattan |publisher=The New Yorker |date=October 18, 2004}}</ref> | ||
The city's greenhouse gas emission levels are relatively low when measured per capita, at 7.1 metric tons per person, below San Francisco, at 11.2 metric tons, and the national average, at 24.5.<ref name="NYC emissions"/> New Yorkers are collectively responsible for one percent of the nation's total [[greenhouse gas]] emissions,<ref name="NYC emissions">{{cite web |title=Inventory of New York City Greenhouse Gas Emissions |publisher=New York City Office of Long-term Planning and Sustainability |date=April 2007 |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/om/pdf/ccp_report041007.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-04-11}}</ref> though comprise 2.7% of the nation's population. The average New Yorker consumes less than half the electricity used by a resident of San Francisco and nearly one-quarter the electricity consumed by a resident of [[Dallas]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/planyc2030/html/challenge/faq.shtml |title=Global Warming and Greenhouse Gases |publisher=PlaNYC / The City of New York |date=2006-12-06 |accessdate=2006-12-13}}</ref> | The city's greenhouse gas emission levels are relatively low when measured per capita, at 7.1 metric tons per person, below San Francisco, at 11.2 metric tons, and the national average, at 24.5.<ref name="NYC emissions"/> New Yorkers are collectively responsible for one percent of the nation's total [[greenhouse gas]] emissions,<ref name="NYC emissions">{{cite web |title=Inventory of New York City Greenhouse Gas Emissions |publisher=New York City Office of Long-term Planning and Sustainability |date=April 2007 |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/om/pdf/ccp_report041007.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-04-11}}</ref> though comprise 2.7% of the nation's population. The average New Yorker consumes less than half the electricity used by a resident of San Francisco and nearly one-quarter the electricity consumed by a resident of [[Dallas, Texas]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/planyc2030/html/challenge/faq.shtml |title=Global Warming and Greenhouse Gases |publisher=PlaNYC / The City of New York |date=2006-12-06 |accessdate=2006-12-13}}</ref> | ||
Large amounts of concentrated pollution in New York City lead to high incidence of [[asthma]] and other respiratory conditions among the city's residents.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Urban Asthma and the Neighbourhood Environment in New York City |author=Coburn, Jason, Jeffrey Osleeb, Michael Porter |journal=Health & Place |date= June 2006 |volume=12(2) |pages=pp. 167–179 |pmid=16338632}}</ref> In recent years the city has focused on reducing its environmental impact. The city government is required to purchase only the most energy-efficient equipment for use in city offices and public housing.<ref>{{cite news |author=DePalma, Anthony |title=It Never Sleeps, but It's Learned to Douse the Lights |publisher=The New York Times |date=December 11, 2005 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2005/12/11/nyregion/11efficiency.html |accessdate=2006-07-19|}}</ref> New York has the largest clean air diesel-hybrid and compressed natural gas bus fleet in the country, and some of the first hybrid taxis. | Large amounts of concentrated pollution in New York City lead to high incidence of [[asthma]] and other respiratory conditions among the city's residents.<ref>{{cite journal |title=Urban Asthma and the Neighbourhood Environment in New York City |author=Coburn, Jason, Jeffrey Osleeb, Michael Porter |journal=Health & Place |date= June 2006 |volume=12(2) |pages=pp. 167–179 |pmid=16338632}}</ref> In recent years the city has focused on reducing its environmental impact. The city government is required to purchase only the most energy-efficient equipment for use in city offices and public housing.<ref>{{cite news |author=DePalma, Anthony |title=It Never Sleeps, but It's Learned to Douse the Lights |publisher=The New York Times |date=December 11, 2005 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2005/12/11/nyregion/11efficiency.html |accessdate=2006-07-19|}}</ref> New York has the largest clean air diesel-hybrid and compressed natural gas bus fleet in the country, and some of the first hybrid taxis. The city is also a leader in the construction of energy-efficient green office buildings, including the [[Hearst Tower]] among others.<ref name="greenbuilding">{{cite news |title=7 World Trade Center and Hearst Building: New York's Test Cases for Environmentally Aware Office Towers |publisher=The New York Times |date=April 16, 2006 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/04/16/arts/design/16gree.html |accessdate=2006-07-19 |author=Pogrebin, Robin}}</ref> | ||
New York City is supplied with drinking water by the protected [[Catskill Mountains]] watershed.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/maplevels.html |title=Current Reservoir Levels |publisher=New York City Department of Environmental Protection |accessdate=2007-06-04}}</ref> As a result of the watershed's integrity and undisturbed natural water filtration process, New York is one of only five major cities in the United States with drinking water pure enough not to require purification by | New York City is supplied with drinking water by the protected [[Catskill Mountains]] watershed.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/maplevels.html |title=Current Reservoir Levels |publisher=New York City Department of Environmental Protection |accessdate=2007-06-04}}</ref> As a result of the watershed's integrity and undisturbed natural water filtration process, New York is one of only five major cities in the United States with drinking water pure enough not to require purification by water treatment plants.<ref>{{cite conference|last=Miele|first=Joel A., Sr|title=Maintaining Water Quality that Satisfies Customers: New York City Watershed Agricultural Program|booktitle=International Water Supply Symposium Tokyo 1998|publisher=New York City Department of Environmental Protection| date=November 20, 1998| url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/html/news/tokyo2.html| accessdate=2006-11-17}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=New York City 2005 Drinking Water Supply and Quality Report |publisher=New York City Department of Environmental Protection |date=2005 |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dep/pdf/wsstat05.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-07-17}}</ref> | ||
==Cityscape== | ==Cityscape== | ||
===Architecture=== | ===Architecture=== | ||
[[Image:Woolworth Building.jpg|thumb|The [[Woolworth Building]] is one of the most famous skyscrapers in New York City. | [[Image:Woolworth Building.jpg|thumb|220px|The [[Woolworth Building]] is one of the most famous skyscrapers in New York City.]] | ||
The building form most closely associated with New York City is the | The building form most closely associated with New York City is the skyscraper, a pioneering urban form that saw city building shift from the low-scale European tradition to the vertical rise of business districts. Surrounded mostly by water, New York's residential density and high real estate values in commercial districts saw the city amass the largest collection of individual, free-standing office and [[tower block|residential towers]] in the world.<ref>{{cite web|publisher=Emporis|title=About New York City|url=http://www.emporis.com/en/wm/ci/?id=newyorkcity-ny-usa|accessdate=2007-03-21}}</ref> | ||
New York has architecturally significant buildings in a wide range of styles. These include the | New York has architecturally significant buildings in a wide range of styles. These include the Woolworth Building (1913), an early gothic revival skyscraper built with massively scaled gothic detailing able to be read from street level several hundred feet below. The 1916 Zoning Resolution required setback in new buildings, and restricted towers to a percentage of the lot size, to allow sunlight to reach the streets below.<ref>{{cite journal |title=The Metropolitan Dimension of Early Zoning: Revisiting the 1916 New York City Ordinance |author=Fischler, Raphael |journal=Journal of the American Planning Association |volume=64(2) |year=1998}}</ref> The [[Art Deco]] design of the [[Chrysler Building]] (1930), with its tapered top and steel spire, reflected the zoning requirements. The building is considered by many historians and architects to be New York's finest building, with its distinctive ornamentation such as replicas at the corners of the 61st floor of the 1928 Chrysler eagle hood ornaments and V-shaped lighting inserts capped by a steel spire at the tower's crown.<ref>{{cite web |title=Favorites! 100 Experts Pick Their top 10 New York Towers |publisher=The Skyscraper Museum |date=January 22, 2006 |url=http://www.skyscraper.org/EXHIBITIONS/FAVORITES/fav_exhibits.htm# |accessdate=2007-04-11}}</ref> A highly influential example of the international style in the United States is the [[Seagram Building]] (1957), distinctive for its facade using visible bronze-toned I-beams to evoke the building's structure. The [[Condé Nast Building]] (2000) is an important example of [[green design]] in American skyscrapers.<ref name="greenbuilding" /> | ||
[[Image:Garden apartments, Jackson Heights.jpg|thumb|[[Garden city movement|Garden apartment]]s in [[Jackson Heights]], Queens. | [[Image:Garden apartments, Jackson Heights.jpg|thumb|220px|[[Garden city movement|Garden apartment]]s in [[Jackson Heights]], Queens.]] | ||
The character of New York's large residential districts is often defined by the elegant [[brownstone]] [[rowhouse]]s, [[townhouse]]s, and [[tenement]]s that were built during a period of rapid expansion from 1870 to 1930.<ref>{{cite book |title=History of Housing in New York City: Dwelling Type and Change in the American Metropolis |author=Plunz, Richar A. |chapter=Chapters 3 [Rich and Poor] & 4 [Beyond the Tenement] |year=1990 |publisher=Columbia University Press |id=ISBN 0231062974}}</ref> Stone and brick became the city's building materials of choice after the construction of wood-frame houses was limited in the aftermath of the [[Great Fire of New York|Great Fire of 1835]].<ref name="lankevich-p82">Lankevich (1998), pp. 82–83.</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=New York: Old & New: Its Story, Streets, and Landmarks |author=Wilson, Rufus Rockwell |year=1902 |publisher=J.B. Lippincott |pages=p. 354}}</ref> Unlike Paris, which for centuries was built from its own limestone bedrock, New York has always drawn its building stone from a far-flung network of quarries and its stone buildings have a variety of textures and hues.<ref>{{cite book |author=B. Diamonstein–Spielvoegel, Barbaralee|title=The Landmarks of New York |publisher=Monacelli Press |year=2005 |id=ISBN 1580931545}} See also {{cite book |author=Whyte, William H. |title=The WPA Guide to New York City |year=1939 |publisher=New Press |id=ISBN 1565843215}}</ref> A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the presence of wooden roof-mounted [[water tower]]s. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could burst municipal water pipes.<ref>{{cite web |title=Wondering About Water Towers|author=Elliot, Debbie |publisher=National Public Radio |date=2006-12-02 |url=http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=6567297 |accessdate=2007-04-11}}</ref> [[Garden city movement|Garden apartment]]s became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, including [[Jackson Heights]] in Queens, which became more accessible with expansion of the subway.<ref>{{cite book |title=722 Miles: The Building of the Subways and how They Transformed New York |author=Hood, Clifton |publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press |year=2004 ||pages=pp. 175–177}}</ref> | The character of New York's large residential districts is often defined by the elegant [[brownstone]] [[rowhouse]]s, [[townhouse]]s, and [[tenement]]s that were built during a period of rapid expansion from 1870 to 1930.<ref>{{cite book |title=History of Housing in New York City: Dwelling Type and Change in the American Metropolis |author=Plunz, Richar A. |chapter=Chapters 3 [Rich and Poor] & 4 [Beyond the Tenement] |year=1990 |publisher=Columbia University Press |id=ISBN 0231062974}}</ref> Stone and brick became the city's building materials of choice after the construction of wood-frame houses was limited in the aftermath of the [[Great Fire of New York|Great Fire of 1835]].<ref name="lankevich-p82">Lankevich (1998), pp. 82–83.</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=New York: Old & New: Its Story, Streets, and Landmarks |author=Wilson, Rufus Rockwell |year=1902 |publisher=J.B. Lippincott |pages=p. 354}}</ref> Unlike Paris, which for centuries was built from its own limestone bedrock, New York has always drawn its building stone from a far-flung network of quarries and its stone buildings have a variety of textures and hues.<ref>{{cite book |author=B. Diamonstein–Spielvoegel, Barbaralee|title=The Landmarks of New York |publisher=Monacelli Press |year=2005 |id=ISBN 1580931545}} See also {{cite book |author=Whyte, William H. |title=The WPA Guide to New York City |year=1939 |publisher=New Press |id=ISBN 1565843215}}</ref> A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the presence of wooden roof-mounted [[water tower]]s. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could burst municipal water pipes.<ref>{{cite web |title=Wondering About Water Towers|author=Elliot, Debbie |publisher=National Public Radio |date=2006-12-02 |url=http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=6567297 |accessdate=2007-04-11}}</ref> [[Garden city movement|Garden apartment]]s became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, including [[Jackson Heights]] in Queens, which became more accessible with expansion of the subway.<ref>{{cite book |title=722 Miles: The Building of the Subways and how They Transformed New York |author=Hood, Clifton |publisher=Johns Hopkins University Press |year=2004 ||pages=pp. 175–177}}</ref> | ||
=== Boroughs === | === Boroughs === | ||
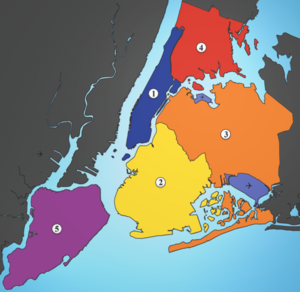
[[Image:5 Boroughs Labels New York City Map Julius Schorzman.png|thumb|300px|The five boroughs: '''<font color="#2a3d94">1: Manhattan</font>''', '''<font color="#f4cc0b">2: Brooklyn</font>''', '''<font color="#ef7b2c">3: Queens</font>''', '''<font color="#dc382c">4: Bronx</font>''', '''<font color="#8a3687">5: Staten Island</font>'''<br/><small>Map by Julius Schorzman</small>]] | [[Image:5 Boroughs Labels New York City Map Julius Schorzman.png|thumb|300px|The five boroughs: '''<font color="#2a3d94">1: Manhattan</font>''', '''<font color="#f4cc0b">2: Brooklyn</font>''', '''<font color="#ef7b2c">3: Queens</font>''', '''<font color="#dc382c">4: Bronx</font>''', '''<font color="#8a3687">5: Staten Island</font>'''<br/><small>Map by Julius Schorzman</small>]] | ||
New York City is | New York City is composed of five boroughs, an unusual form of government used to administer the five constituent counties that make up the city.<ref>{{cite book |title=Regionalism and realism: A Study of Government in the New York Metropolitan Area |author=Benjamin, Gerald, Richard P. Nathan |year=1990 |publisher=Brookings Institute |pages=p. 59}}</ref> Throughout the boroughs there are hundreds of distinct neighborhoods, many with a definable history and character to call their own. If the boroughs were each independent cities, four of the boroughs (Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, and the Bronx) would be among the ten most populous cities in the United States. | ||
*'''[[The Bronx]]''' (pop. 1,364,566)<ref name="census" /> is the northernmost borough of New York City. The site of [[Yankee Stadium]], home of the [[New York Yankees]], and home to the largest cooperatively owned housing complex in the United States, [[Co-op City, Bronx|Co-op City]].<ref>{{cite news |author=Frazier, Ian |title=Utopia, the Bronx |publisher=The New Yorker |date= | *'''[[The Bronx]]''' (Bronx County; pop. 1,364,566)<ref name="census" /> is the northernmost borough of New York City. The site of [[Yankee Stadium]], home of the [[New York Yankees]], and home to the largest cooperatively owned housing complex in the United States, [[Co-op City, Bronx|Co-op City]].<ref>{{cite news |author=Frazier, Ian |title=Utopia, the Bronx |publisher=The New Yorker |date=June 26, 2006 |url=http://www.newyorker.com/archive/2006/06/26/060626fa_fact_frazier |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> Except for a small piece of Manhattan known as [[Marble Hill, Manhattan|Marble Hill]], the Bronx is the only section of the city that is part of the United States mainland. It is home to the [[Bronx Zoo]], the largest metropolitan zoo in the United States, which spans 265 acres (107.2 hectares) and is home to over 6,000 animals.<ref>{{cite book |title=New York City Museum Guide |author=Ward, Candace |publisher=Dover Publications |year=2000 |id=ISBN 0486410005 |pages=p. 72}}</ref> The Bronx is the birthplace of [[rap and hip hop]].<ref>{{cite book|first=David|last=Toop|title=Rap Attack 2: African Rap to Global Hip Hop|publisher=Serpents Tail|year=1992|isbn=1852422432}}</ref> | ||
* '''[[Brooklyn]]''' (pop. 2,511,408)<ref name="census">{{cite web |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |title=The Current Population of NYC (2005) |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/census/detailed_narrative_2005.pdf| format=PDF| accessdate=2007-03-13}} These figures were adopted by the U.S. Census Bureau in September 2006.</ref> is the city's most populous borough and was an independent city until 1898. Brooklyn is known for its cultural, social and ethnic diversity, an independent art scene, distinct neighborhoods and a unique architectural heritage. The borough also features a long beachfront and [[Coney Island]], established in the 1870s as one of the earliest amusement grounds in the country.<ref>{{cite book |title=Coney Island: The People's Playground |author=Immerso, Michael |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2002 |pages=p. 3 |id=ISBN 0813531381}}</ref> | * '''[[Brooklyn]]''' (Kings County; pop. 2,511,408)<ref name="census">{{cite web |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |title=The Current Population of NYC (2005) |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/census/detailed_narrative_2005.pdf| format=PDF| accessdate=2007-03-13}} These figures were adopted by the U.S. Census Bureau in September 2006.</ref> is the city's most populous borough and was an independent city until 1898. Brooklyn is known for its cultural, social and ethnic diversity, an independent art scene, distinct neighborhoods and a unique architectural heritage. The borough also features a long beachfront and [[Coney Island]], established in the 1870s as one of the earliest amusement grounds in the country.<ref>{{cite book |title=Coney Island: The People's Playground |author=Immerso, Michael |publisher=Rutgers University Press |year=2002 |pages=p. 3 |id=ISBN 0813531381}}</ref> | ||
* '''[[Manhattan (borough)|Manhattan]]''' (pop. 1,593,200)<ref name="census" /> is the most densely populated borough and home to most of the city's [[skyscrapers]]. The borough contains the major business and financial centers of the city and many cultural attractions, including numerous museums, the [[Broadway theatre]] district and [[Madison Square Garden]]. Manhattan is loosely divided into [[Downtown Manhattan|Downtown]], [[Midtown Manhattan|Midtown]], and [[Upper Manhattan|Uptown]] regions. Uptown Manhattan is divided by [[Central Park]] into the [[Upper East Side]] and the [[Upper West Side]], and north of it is [[Harlem]]. | * '''[[Manhattan (borough)|Manhattan]]''' (New York County; pop. 1,593,200)<ref name="census" /> is the most densely populated borough and home to most of the city's [[skyscrapers]]. The borough contains the major business and financial centers of the city and many cultural attractions, including numerous museums, the [[Broadway theatre]] district and [[Madison Square Garden]]. Manhattan is loosely divided into [[Downtown Manhattan|Downtown]], [[Midtown Manhattan|Midtown]], and [[Upper Manhattan|Uptown]] regions. Uptown Manhattan is divided by [[Central Park]] into the [[Upper East Side]] and the [[Upper West Side]], and north of it is [[Harlem]]. | ||
* '''[[Queens]]''' (pop. 2,256,576)<ref name="census" /> is geographically the largest borough and the most ethnically diverse county in the United States.<ref name="queensdiverse">{{cite news|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/07/04/nyregion/04fourth.html |author=O'Donnell, Michelle |title=In Queens, It's the Glorious 4th, and 6th, and 16th, and 25th...|publisher=New York Times|date=July 4, 2006 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> Historically a collection of small towns and villages founded by the Dutch colonists, the borough today is mainly residential and middle class. It is the only large county in the United States where the median income among black households, about $52,000 a year, has surpassed that of whites.<ref>{{cite news |title=Black Incomes Surpass Whites in Queens |author=Roberts, Sam |publisher=The New York Times |date=January 10, 2006 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/10/01/nyregion/01census.html?ref=nyregion |accessdate=2007-03-28}}</ref> Queens is the site of [[ | * '''[[Queens]]''' (Queens County; pop. 2,256,576)<ref name="census" /> is geographically the largest borough and the most ethnically diverse county in the United States.<ref name="queensdiverse">{{cite news|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/07/04/nyregion/04fourth.html |author=O'Donnell, Michelle |title=In Queens, It's the Glorious 4th, and 6th, and 16th, and 25th...|publisher=New York Times|date=July 4, 2006 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> Historically a collection of small towns and villages founded by the Dutch colonists, the borough today is mainly residential and middle class. It is the only large county in the United States where the median income among black households, about $52,000 a year, has surpassed that of whites.<ref>{{cite news |title=Black Incomes Surpass Whites in Queens |author=Roberts, Sam |publisher=The New York Times |date=January 10, 2006 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/10/01/nyregion/01census.html?ref=nyregion |accessdate=2007-03-28}}</ref> The borough hosted the New York [[World's Fair]]s of 1939-1940 and 1964-1965. Queens is the site of the [[New York Mets]]' home since 2009, [[Citi Field]], as well as their former home, [[Shea Stadium]], and annually hosts the [[U.S. Open (tennis)|U.S. Open]] tennis tournament. It is also the home to New York City's two major airports, [[LaGuardia Airport]] and [[John F. Kennedy International Airport]]. | ||
* '''[[Staten Island]]''' (pop. 475,014)<ref name="census" /> is the most suburban in character of the five boroughs. It is connected to Brooklyn by the [[Verrazano-Narrows Bridge]] and to Manhattan via the free [[Staten Island Ferry]]. Until 2001, the borough was home to the [[Fresh Kills Landfill]], formerly the largest landfill in the world, which is now being reconstructed as a large urban park.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/fkl/dmp.pdf|format=PDF|title=Fresh Kills Park: Lifescape - Draft Master Plan |date=March 2006 |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |format=pdf |accessdate=2007-06-03}}</ref> | * '''[[Staten Island]]''' (Richmond County; pop. 475,014)<ref name="census" /> is the most suburban in character of the five boroughs. It is connected to Brooklyn by the [[Verrazano-Narrows Bridge]], to [[New Jersey (U.S. state)|New Jersey]] by the [[Goethals Bridge]], the [[Bayonne Bridge]] and the [[Outerbridge Crossing]], and to Manhattan via the free [[Staten Island Ferry]]. Until 2001, the borough was home to the [[Fresh Kills Landfill]], formerly the largest landfill in the world, which is now being reconstructed as a large urban park.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/fkl/dmp.pdf|format=PDF|title=Fresh Kills Park: Lifescape - Draft Master Plan |date=March 2006 |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |format=pdf |accessdate=2007-06-03}}</ref> | ||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
[[Image:Guggenheim museum.jpg|thumb|The [[Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum]], interior view.]] | [[Image:Guggenheim museum.jpg|thumb|The [[Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum]], interior view.]] | ||
The writer [[Tom Wolfe]] once said of New York that "Culture just seems to be in the air, like part of the weather." | The writer [[Tom Wolfe]] once said of New York that "Culture just seems to be in the air, like part of the weather." Numerous major American cultural movements began in the city, such as the [[Harlem Renaissance]], which established the African-American literary canon in the United States. The city was the epicenter of [[jazz]] in the 1940s, [[abstract expressionism]] in the 1950s, and the birthplace of [[rap and hip hop]] in the 1970s. The city's [[punk rock]] scene was influential in the 1970s and 1980s, and the city has long had a flourishing scene for Jewish-American literature. The city is also important in the American film industry. ''[[Manhatta]]'' (1920), the nation's first [[avante-garde]] film, was filmed in the city.<ref>{{cite video | people = Bruce Posner | title = Picturing a Metropolis: New York City Unveiled | medium = DVD | publisher = Unseen Cinema | date = 2005}}</ref> Most of the film industry moved to [[Hollywood]] in the 1910s, but New York City is still the second largest center for the American film industry. | ||
The city has more than 2,000 arts and cultural organizations and more than 500 art galleries of all sizes. The city government funds the arts with a larger annual budget than the National Endowment for the Arts.<ref name="NYC arts">{{cite web |title=Creative New York |publisher=Center for an Urban Future |date=December 2005 |url=http://www.nycfuture.org/images_pdfs/pdfs/CREATIVE_NEW_YORK.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-06-19}}</ref> Wealthy industrialists in the 19th century built a network of major cultural institutions, such as the famed [[Carnegie Hall]] and [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], that would become internationally established. The advent of electric lighting led to elaborate theater productions, and in the 1880s New York City theaters on Broadway and along 42nd Street began showcasing a new stage form that came to be known as the Broadway [[musical]]. | The city has more than 2,000 arts and cultural organizations and more than 500 art galleries of all sizes. The city government funds the arts with a larger annual budget than the National Endowment for the Arts.<ref name="NYC arts">{{cite web |title=Creative New York |publisher=Center for an Urban Future |date=December 2005 |url=http://www.nycfuture.org/images_pdfs/pdfs/CREATIVE_NEW_YORK.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-06-19}}</ref> Wealthy industrialists in the 19th century built a network of major cultural institutions, such as the famed [[Carnegie Hall]] and [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], that would become internationally established. The advent of electric lighting led to elaborate theater productions, and in the 1880s New York City theaters on Broadway and along 42nd Street began showcasing a new stage form that came to be known as the Broadway [[musical]]. | ||
Strongly influenced by the city's immigrants, productions such as those of [[Edward Harrigan|Harrigan and Hart]], [[George M. Cohan]] and others used song in narratives that often reflected themes of hope and ambition. Today these productions are a mainstay of the New York theater scene. The city's 39 largest theaters (with more than 500 seats) are collectively known as "[[Broadway theater|Broadway]]", after the [[Broadway (Manhattan)|major thoroughfare]] that crosses the [[Times Square]] theater district.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.signonsandiego.com/news/features/20040606-9999-1a6tony.html |title=2 plays + 9 nominations = good odds for locals |publisher=San Diego Union-Tribune |author=Welsh, Anne Marie |date=June 6, 2004 | accessdate=2007-06-08}}</ref> | Strongly influenced by the city's immigrants, productions such as those of [[Edward Harrigan|Harrigan and Hart]], [[George M. Cohan]] and others used song in narratives that often reflected themes of hope and ambition. Today these productions are a mainstay of the New York theater scene. The city's 39 largest theaters (with more than 500 seats) are collectively known as "[[Broadway theater|Broadway]]", after the [[Broadway (Manhattan)|major thoroughfare]] that crosses the [[Times Square]] theater district.<ref>{{cite news |url=http://www.signonsandiego.com/news/features/20040606-9999-1a6tony.html |title=2 plays + 9 nominations = good odds for locals |publisher=San Diego Union-Tribune |author=Welsh, Anne Marie |date=June 6, 2004 | accessdate=2007-06-08}}</ref> | ||
[[Image:Times Square.jpg|thumb|left|220px|[[Times Square]] is in the center of New York City's theater district.]] | |||
The [[Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts]], which includes [[Jazz at Lincoln Center]], the [[Metropolitan Opera]], the [[New York City Opera]], the [[New York Philharmonic]], the [[New York City Ballet]], the [[Vivian Beaumont Theatre]], [[The Juilliard School]], and [[Alice Tully Hall]], is the largest performing arts center in the United States. [[Summerstage]] presents performances of free plays and music in Central Park and 1,200 free concerts, dance, and theater events across all five boroughs in the summer months.<ref>{{cite web | title = Summerstage: Our Mission | url=http://www.summerstage.org/index.aspx?lobid=854 | publisher = Summerstage.org | accessdate = 2007-05-31 }}</ref> | The [[Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts]], which includes [[Jazz at Lincoln Center]], the [[Metropolitan Opera]], the [[New York City Opera]], the [[New York Philharmonic]], the [[New York City Ballet]], the [[Vivian Beaumont Theatre]], [[The Juilliard School]], and [[Alice Tully Hall]], is the largest performing arts center in the United States. [[Summerstage]] presents performances of free plays and music in Central Park and 1,200 free concerts, dance, and theater events across all five boroughs in the summer months.<ref>{{cite web | title = Summerstage: Our Mission | url=http://www.summerstage.org/index.aspx?lobid=854 | publisher = Summerstage.org | accessdate = 2007-05-31 }}</ref> | ||
=== Tourism === | === Tourism === | ||
[[Image:Rockefeller Center Christmas tree.jpg|thumb|[[Rockefeller Center]] and its [[Christmas tree]] are popular tourist attractions in New York City]] | [[Image:Rockefeller Center Christmas tree.jpg|thumb|220px|The [[Rockefeller Center]] and its [[Christmas tree]] are popular tourist attractions in New York City.]] | ||
About 40 million foreign and American tourists visit New York City each year.<ref>{{cite web |title=NYC Statistics |publisher=NYC & Company |url=http://www.nycvisit.com/content/index.cfm?pagePkey=57 |accessdate=2006-08-03}}</ref> Major destinations include the [[Empire State Building]], [[Ellis Island]], Broadway theatre productions, museums such as the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], and other tourist attractions including [[Central Park]], [[Washington Square Park]], [[Rockefeller Center]], [[Times Square]], the [[Bronx Zoo]], [[New York Botanical Garden]], luxury shopping along Fifth and Madison Avenues, and events such as the Halloween Parade in [[Greenwich Village]], the [[Tribeca Film Festival]], and free performances in Central Park at Summerstage. The [[Statue of Liberty]] is a major tourist attraction and one of the most recognizable icons of the United States.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://nymag.com/listings/attraction/statue_of_liberty/ |title=Statue of Liberty |publisher=New York Magazine |accessdate=2006-06-20}}</ref> Many of the city's ethnic enclaves, such as [[Jackson Heights, Queens|Jackson Heights]], [[Flushing, Queens|Flushing]], and [[Brighton Beach]] are major shopping destinations for first and second generation Americans up and down the East Coast. | About 40 million foreign and American tourists visit New York City each year.<ref>{{cite web |title=NYC Statistics |publisher=NYC & Company |url=http://www.nycvisit.com/content/index.cfm?pagePkey=57 |accessdate=2006-08-03}}</ref> Major destinations include the [[Empire State Building]], [[Ellis Island]], Broadway theatre productions, museums such as the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]], and other tourist attractions including [[Central Park]], [[Washington Square Park]], [[Rockefeller Center]], [[Times Square]], the [[Bronx Zoo]], [[New York Botanical Garden]], luxury shopping along Fifth and Madison Avenues, and events such as the Halloween Parade in [[Greenwich Village]], the [[Tribeca Film Festival]], and free performances in Central Park at Summerstage. The [[Statue of Liberty]] is a major tourist attraction and one of the most recognizable icons of the United States.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://nymag.com/listings/attraction/statue_of_liberty/ |title=Statue of Liberty |publisher=New York Magazine |accessdate=2006-06-20}}</ref> Many of the city's ethnic enclaves, such as [[Jackson Heights, Queens|Jackson Heights]], [[Flushing, Queens|Flushing]], and [[Brighton Beach]] are major shopping destinations for first and second generation Americans up and down the East Coast. | ||
| Line 98: | Line 103: | ||
New York City has over 28,000 acres (113 km²) of parkland and 14 miles (22 km) of public beaches.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/om/html/99a/pr042-99.html |title=Mayor Giuliani Announces Amount of Parkland in New York City has Passed 28,000 Acre Mark |date=February 3, 1999 |publisher=New York City Mayor's Office |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_things_to_do/facilities/af_beaches.html |title=Beaches |publisher=New York City Department of Parks & Recreation |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> Manhattan's [[Central Park]], designed by [[Frederick Law Olmsted]] and [[Calvert Vaux]], is the most visited city park in the United States.<ref>{{cite web |title=City Park Facts |publisher=The Trust for Public Land, Center for City Park Excellence |date=June 2006 |url=http://www.tpl.org/tier3_cd.cfm?content_item_id=20531&folder_id=3208|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> [[Prospect Park (Brooklyn)|Prospect Park]] in Brooklyn, also designed by Olmsted and Vaux, has a 90 acre (36 Hectare) meadow.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.prospectpark.org/general/main.cfm?target=home |title=General Information |publisher=Prospect Park Alliance |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> [[Flushing Meadows Park]] in Queens, the city's third largest, was the setting for the 1939 [[World's Fair]] and 1964 World's Fair. | New York City has over 28,000 acres (113 km²) of parkland and 14 miles (22 km) of public beaches.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/om/html/99a/pr042-99.html |title=Mayor Giuliani Announces Amount of Parkland in New York City has Passed 28,000 Acre Mark |date=February 3, 1999 |publisher=New York City Mayor's Office |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nycgovparks.org/sub_things_to_do/facilities/af_beaches.html |title=Beaches |publisher=New York City Department of Parks & Recreation |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> Manhattan's [[Central Park]], designed by [[Frederick Law Olmsted]] and [[Calvert Vaux]], is the most visited city park in the United States.<ref>{{cite web |title=City Park Facts |publisher=The Trust for Public Land, Center for City Park Excellence |date=June 2006 |url=http://www.tpl.org/tier3_cd.cfm?content_item_id=20531&folder_id=3208|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> [[Prospect Park (Brooklyn)|Prospect Park]] in Brooklyn, also designed by Olmsted and Vaux, has a 90 acre (36 Hectare) meadow.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.prospectpark.org/general/main.cfm?target=home |title=General Information |publisher=Prospect Park Alliance |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> [[Flushing Meadows Park]] in Queens, the city's third largest, was the setting for the 1939 [[World's Fair]] and 1964 World's Fair. | ||
New York's food culture, influenced by the city's immigrants and large number of dining patrons, is diverse. Jewish and Italian immigrants made the city famous for [[bagel]]s, [[cheesecake]] and New York style [[pizza]]. Some 4,000 mobile food vendors licensed by the city, many immigrant-owned, have made Middle Eastern foods such as [[falafel]]s and [[kebab]]s standbys of contemporary New York street food.<ref>{{cite news|title=Kebabs on the Night Shift|first=Jennifer|last=Bleyer|publisher=The New York Times|date=May 14, 2006 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/05/14/nyregion/thecity/14vend.html|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city is also home to many of the finest [[haute cuisine]] restaurants in the United States.<ref>{{cite news|title=Michelin Takes on the City, Giving Some a Bad Taste|first=Glenn|last=Collins|publisher=The New York Times|date= | New York's food culture, influenced by the city's immigrants and large number of dining patrons, is diverse. Jewish and Italian immigrants made the city famous for [[bagel]]s, [[cheesecake]] and New York style [[pizza]]. Some 4,000 mobile food vendors licensed by the city, many immigrant-owned, have made Middle Eastern foods such as [[falafel]]s and [[kebab]]s standbys of contemporary New York street food.<ref>{{cite news|title=Kebabs on the Night Shift|first=Jennifer|last=Bleyer|publisher=The New York Times|date=May 14, 2006 |url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/05/14/nyregion/thecity/14vend.html|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city is also home to many of the finest [[haute cuisine]] restaurants in the United States.<ref>{{cite news|title=Michelin Takes on the City, Giving Some a Bad Taste|first=Glenn|last=Collins|publisher=The New York Times|date=November 3, 2005 |url=http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=F30911F83D5A0C708CDDA80994DD404482|accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> | ||
=== Media === | === Media === | ||
New York is a global center for the television, advertising, music, newspaper and book publishing industries and is also the largest media market in the United States. | New York is a global center for the television, advertising, music, newspaper and book publishing industries and is also the largest media market in the United States. Some of the city's media conglomerates include [[Time Warner]], the [[News Corporation]], the [[Hearst Corporation]], and [[Viacom]]. Seven of the world's top eight global advertising agency networks are headquartered in New York. Three of the "Big Four" record labels are also based in the city. One-third of all American [[independent film]]s are produced in New York.<ref name="NYC Media">{{cite web |title=Request for Expressions of Interest |publisher=The Governors Island Preservation & Education Corporation |date=2005 |url=http://www.govisland.com/PDFs/RFEI/RFEI.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city<ref name="NYC Media" /> and book-publishing industry employs about 25,000 people.<ref>{{cite web |title=Media and Entertainment |publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation |url=http://www.nycedc.com/Web/NYCBusinessClimate/IndustryOverviews/MediaEntertainment/MediaEntertainment.htm |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> | ||
Two of the three national daily newspapers in the United States are New York papers, ''[[The Wall Street Journal]]'' and ''[[The New York Times]]''. Major tabloid newspapers in the city include ''[[The New York Daily News]]'' and ''[[The New York Post]]'', founded in 1801 by [[Alexander Hamilton]]. The city also has a major ethnic press, with 270 newspapers and magazines published in more than 40 languages.<ref>{{cite news |title=Ethnic Press Booms In New York City |publisher=Editor & Publisher |date= | Two of the three national daily newspapers in the United States are New York papers, ''[[The Wall Street Journal]]'' and ''[[The New York Times]]''. Major tabloid newspapers in the city include ''[[The New York Daily News]]'' and ''[[The New York Post]]'', founded in 1801 by [[Alexander Hamilton]]. The city also has a major ethnic press, with 270 newspapers and magazines published in more than 40 languages.<ref>{{cite news |title=Ethnic Press Booms In New York City |publisher=Editor & Publisher |date=July 10, 2002 |url=http://www.editorandpublisher.com/eandp/news/article_display.jsp?vnu_content_id=1538594 |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> ''[[El Diario La Prensa]]'' is New York's largest Spanish-language daily and the oldest in the nation.<ref>{{cite web | url =http://news.newamericamedia.org/news/view_article.html?article_id=e4526a43cc213775795cc84762fce768 | title = el diario/La Prensa: The Nation’s Oldest Spanish-Language Daily| date = July 27, 2005 | publisher = New America Media | accessdate = 2007-06-09}}</ref> ''[[The New York Amsterdam News]]'', published in Harlem, is a prominent African-American newspaper. | ||
The television industry developed in New York and is a significant employer in the city's economy. The four major American broadcast networks, [[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]], [[CBS]], [[Fox Broadcasting Company|FOX]] and [[NBC]], are all headquartered in New York. Many cable channels are based in the city as well, including [[MTV]], | The television industry developed in New York and is a significant employer in the city's economy. The four major American broadcast networks, [[American Broadcasting Company|ABC]], [[CBS]], [[Fox Broadcasting Company|FOX]] and [[NBC]], are all headquartered in New York. Many cable channels are based in the city as well, including [[MTV]], Fox News, [[HBO]] and [[Comedy Central]]. In 2005 there were more than 100 television shows taped in New York City. | ||
New York is also a major center for non-commercial media. The oldest | New York is also a major center for non-commercial media. The oldest public-access television channel in the United States is the [[Manhattan Neighborhood Network]], founded in 1971.<ref>[http://www.mnn.org/en/community-celebrates-public-access-tvs-35th-annive Community Celebrates Public Access TV's 35th Anniversary], Manhattan Neighborhood Network press release dated August 6, 2006. Accessed April 28, 2007. "Public access TV was created in the 1970s to allow ordinary members of the public to make and air their own TV shows—and thereby exercise their free speech. It was first launched in the U.S. in Manhattan July 1st 1971, on the Teleprompter and Sterling Cable systems, now Time Warner Cable."</ref> [[WNET]] is the city's major public television station and a primary provider of national [[PBS]] programming. [[WNYC]], a public radio station owned by the city until 1997, has the largest public radio audience in the United States.<ref>{{cite web |publisher=Radio Research Consortium |title=Top 30 Public Radio Subscribers: Spring 2006 Arbitron |date=[[August 28]], 2006 |url=http://www.rrconline.org/reports/pdf/Sp06%20eRanks.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-11-17}}</ref> The City of New York operates a public broadcast service, [[NYCTV]], that produces several original Emmy Award-winning shows covering music and culture in city neighborhoods, as well as city government. | ||
===Accent=== | ===Accent=== | ||
The New York City area has a distinctive regional speech pattern called the | The New York City area has a distinctive regional speech pattern called the New York dialect, alternatively known as Brooklynese or New Yorkese. It is often considered to be one of the most recognizable accents within [[American English]].<ref>Newman, Michael (2005) "New York Talk" in ''American Voices'' Walt Wolfram and Ben Ward (eds). p.82-87 Blackwell ISBN 1-4051-2109-2</ref> The classic version of this dialect is centered on middle and working class people of European American descent, and the influx of non-European immigrants in recent decades has led to changes in this distinctive dialect. | ||
One of the more notable features of this dialect is its "r-lessness". The traditional New York–area accent is non-rhotic, so that the sound {{IPA|[ɹ]}} does not appear at the end of a syllable or immediately before a consonant; hence the pronunciation of the city as "New Yawk". There is no {{IPA|[ɹ]}} in words like ''park'' {{IPA|[pɔːk]}} (with vowel raised due to the low-back chain shift), ''butter'' {{IPA|[bʌɾə]}}, or ''here'' {{IPA|[hiə]}}. In another feature called the low back chain shift, the {{IPA|[ɔ]}} vowel sound of words like ''talk'', ''law'', ''cross'', and ''coffee'' and the often homophonous {{IPA|[ɔr]}} in ''core'' and ''more'' are tensed and usually raised more than in [[General American]]. In the most old-fashioned and extreme versions of the New York dialect, the vowel sounds of words like ''girl'' and of words like ''oil'' both become a diphthong {{IPA|[ɜɪ]}}. | |||
=== Sports === | === Sports === | ||
New York City has teams in the four major North American professional sports leagues, each of which also has its headquarters in the city. | New York City has teams in the four major North American professional sports leagues, each of which also has its headquarters in the city. | ||
[[Baseball]] is the city's most closely followed sport. There have been fourteen [[World Series]] championship series between New York City teams, in matchups called | [[Baseball]] is the city's most closely followed sport. There have been fourteen [[World Series]] championship series between New York City teams, in matchups called Subway Series. The city's two current [[Major League Baseball]] teams are the [[New York Yankees]] and the [[New York Mets]], who enjoy a rivalry arguably as fierce as that between the Yankees and the [[Boston Red Sox]]. There are also two [minor league baseball teams in the city, the Staten Island Yankees and Brooklyn Cyclones. | ||
The city is represented in the [[National Football League]] by the [[New York Jets]] and [[New York Giants]] (officially the New York Football Giants), although both teams play their home games in [[Giants Stadium]] in nearby New Jersey. | The city is represented in the [[National Football League]] by the [[New York Jets]] and [[New York Giants]] (officially the New York Football Giants), although both teams play their home games in [[Giants Stadium]] in nearby New Jersey. | ||
The | The New York Rangers represent the city in the [[National Hockey League]], playing in the [[Madison Square Garden]]. | ||
The city's [[National Basketball Association]] team is the [[New York Knicks]]. The first national college-level basketball championship | The city's [[National Basketball Association]] team is the [[New York Knicks]]. The first national college-level basketball championship was held in New York in 1938 and remains in the city.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nit.org/history/nit-postseason.html |title=Postseason Overview |publisher=National Invitation Tournament |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> [[Rucker Park]] in [[Harlem]] is a celebrated court where many professional athletes play in the summer league. | ||
As a global city, New York supports many events outside these sports. These include the | As a global city, New York supports many events outside these sports. These include the U.S. Open in tennis, the New York City Marathon, and the Millrose Games, an annual track and field meet whose featured event is the Wanamaker Mile. Boxing is also a very prominent part of the city's sporting scene, with events like the Amateur Boxing Golden Gloves being held at Madison Square Garden each year. The New York City Marathon is the world's largest, with often about 50,000 finishers in recent years. | ||
Many sports are associated with New York's immigrant communities. | Many sports are associated with New York's immigrant communities. Stickball, a street version of baseball, was popularized by youths in working class Puerto Rican, Italian, and Irish neighborhoods in the 1930s. In recent years several amateur [[Cricket (sport)|cricket]] leagues have emerged with the arrival of immigrants from South Asia and the Caribbean. | ||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
[[Image:New York Stock Exchange.JPG|thumb|The [[New York Stock Exchange]], usually called "Wall Street"]] | [[Image:New York Stock Exchange.JPG|thumb|The [[New York Stock Exchange]], usually called "Wall Street."]] | ||
New York City is a global hub of international business and commerce and is one of three "command centers" for the world economy (along with [[London]] and [[Tokyo]]).<ref>{{cite book|author= | New York City is a global hub of international business and commerce and is one of three "command centers" for the world economy (along with [[London, United Kingdom|London]] and [[Tokyo]]).<ref>{{cite book|author=Saskia Sassen|Sassen, Saskia|title=The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo|year=2001|publisher=Princeton University Press|edition=2nd edition|isbn=0691070636}}</ref> The city is a major center for finance, insurance, real estate, media and the arts in the United States. The New York metropolitan area had an estimated [[gross metropolitan product]] of $952.6 billion in 2005, the largest regional economy in the United States. The city's economy accounts for the majority of the economic activity in the states of New York and New Jersey.<ref name="NYC economy">{{cite web |url=http://www.usmayors.org/74thWinterMeeting/metroeconreport_January2006.pdf |format=PDF |publisher=The United States Conference of Mayors|title=The role of metro areas in the U.S. economy |date=January 13, 2006 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> Many major corporations are headquartered in New York City, including 44 [[Fortune 500]] companies.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nycedc.com/Web/NYCBusinessClimate/FactsFigures/FactsFigures.htm |title=NYC Business Climate - Facts & Figures |publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation|accessdate=2007-06-08}}</ref> New York is also unique among American cities for its large number of foreign corporations. One out of ten private sector jobs in the city is with a foreign company.<ref>{{cite news|title=Keeping the Economy Growing |author=Wylde, Kathryn |publisher=Gotham Gazette |date=January 23, 2006 |url=http://www.gothamgazette.com/article/fea/20060123/202/1727 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> | ||
New York City is home to some of the nation's — and world's — most valuable real estate. 450 [[Park Avenue (Manhattan)|Park Avenue]] was sold on [[July 2]], | New York City is home to some of the nation's — and world's — most valuable real estate. 450 [[Park Avenue (Manhattan)|Park Avenue]] was sold on [[July 2]], 2007 for $510 million, about $1,589 per square foot ($148/m²), breaking the barely month-old record for an American office building of $1,476 per square foot ($137/m²) set in the June 2007 sale of 660 Madison Avenue.<ref>Quirk, James. [http://www.northjersey.com/page.php?qstr=eXJpcnk3ZjczN2Y3dnFlZUVFeXk4NDImZmdiZWw3Zjd2cWVlRUV5eTcxNjI5NzEmeXJpcnk3ZjcxN2Y3dnFlZUVFeXkyMg== "Bergen offices have plenty of space"], ''[[The Record (Bergen County)]]'', [[July 5]], 2007. Accessed [[July 5]], 2007. "On Monday, a 26-year-old, 33-story office building at 450 Park Ave. sold for a stunning $1,589 per square foot, or about $510 million. The price is believed to be the most ever paid for a U.S. office building on a per-square-foot basis. That broke the previous record -- set four weeks earlier -- when 660 Madison Ave. sold for $1,476 a square foot."</ref> | ||
[[Image:Domino Sugar.jpg|thumb|New York City hosts a considerable food-processing industry. The picture shows the former factory of Domino Foods in [[Williamsburg]], Brooklyn]] | [[Image:Domino Sugar.jpg|thumb|New York City hosts a considerable food-processing industry. The picture shows the former factory of Domino Foods in [[Williamsburg]], Brooklyn.]] | ||
The [[New York Stock Exchange]], located on [[Wall Street]], and the [[NASDAQ]] are the world's first and second largest stock exchanges, respectively, when measured by average daily trading volume and overall market capitalization.<ref>{{cite web |authors=Claessens, Stjin |title=Electronic Finance: Reshaping the Financial Landscape Around the World |publisher=The World Bank |date=September 2000 |url=http://www.worldbank.org/research/interest/confs/upcoming/papersjuly11/E-finance.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> Financial services account for more than 35 percent of the city's employment income.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/current_issues/ci12-1.pdf|format=PDF |title=Challenges Facing the New York Metropolitan Area Economy |author=Orr, James and Giorgio Topa |work=Current Issues in Economics and Finance - Second District Highlights |publisher=New York Federal Reserve |date=Volume 12, Number 1, January 2006|accessdate=2007-06-05}}</ref> Real estate is a major force in the city's economy, as the total value of all New York City property was $802.4 billion in 2006.<ref name="NYC real estate">{{cite web |title=Tentative Assessment Roll: Fiscal Year 2008 |publisher=New York City Department of Finance |date= | The [[New York Stock Exchange]], located on [[Wall Street]], and the [[NASDAQ]] are the world's first and second largest stock exchanges, respectively, when measured by average daily trading volume and overall market capitalization.<ref>{{cite web |authors=Claessens, Stjin |title=Electronic Finance: Reshaping the Financial Landscape Around the World |publisher=The World Bank |date=September 2000 |url=http://www.worldbank.org/research/interest/confs/upcoming/papersjuly11/E-finance.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> Financial services account for more than 35 percent of the city's employment income.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/current_issues/ci12-1.pdf|format=PDF |title=Challenges Facing the New York Metropolitan Area Economy |author=Orr, James and Giorgio Topa |work=Current Issues in Economics and Finance - Second District Highlights |publisher=New York Federal Reserve |date=Volume 12, Number 1, January 2006|accessdate=2007-06-05}}</ref> Real estate is a major force in the city's economy, as the total value of all New York City property was $802.4 billion in 2006.<ref name="NYC real estate">{{cite web |title=Tentative Assessment Roll: Fiscal Year 2008 |publisher=New York City Department of Finance |date=January 15, 2007 |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/dof/html/pdf/07pdf/tent-ass-roll-07-08t.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-21}}</ref> The [[Time Warner Center]] is the property with the highest-listed market value in the city, at $1.1 billion in 2006.<ref name="NYC real estate" /> | ||
The city's television and film industry is the second largest in the country after [[Hollywood]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/film/html/news/stats.shtml |title=NYC Film Statistics |publisher=Mayor's Office of Film, Theatre, and Broadcasting |accessdate=2007-06-07}}</ref> Creative industries such as new media, advertising, fashion, design and architecture account for a growing share of employment, with New York City possessing a strong competitive advantage in these industries.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Currid, Elizabeth |title=New York as a Global Creative Hub: A Competitive Analysis of Four Theories on World Cities |journal=Economic Development Quarterly |year=2006 |volume=20(4) |pages=pp. 330–350}}</ref> High-tech industries like bioscience, software development, game design, and Internet services are also growing due to its position at the terminus of the [[transatlantic telephone cable|transatlantic fiber optic trunk line]] in New York City.<ref>{{cite web |title=Telecommunications and Economic Development in New York City: A Plan for Action|publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation |date=March 2005 |url=http://www.nycedc.com/about_us/TelecomPlanMarch2005.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> Other important sectors include medical research and technology, non-profit institutions, and universities. | The city's television and film industry is the second largest in the country after [[Hollywood]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyc.gov/html/film/html/news/stats.shtml |title=NYC Film Statistics |publisher=Mayor's Office of Film, Theatre, and Broadcasting |accessdate=2007-06-07}}</ref> Creative industries such as new media, advertising, fashion, design and architecture account for a growing share of employment, with New York City possessing a strong competitive advantage in these industries.<ref>{{cite journal |author=Currid, Elizabeth |title=New York as a Global Creative Hub: A Competitive Analysis of Four Theories on World Cities |journal=Economic Development Quarterly |year=2006 |volume=20(4) |pages=pp. 330–350}}</ref> High-tech industries like bioscience, software development, game design, and Internet services are also growing due to its position at the terminus of the [[transatlantic telephone cable|transatlantic fiber optic trunk line]] in New York City.<ref>{{cite web |title=Telecommunications and Economic Development in New York City: A Plan for Action|publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation |date=March 2005 |url=http://www.nycedc.com/about_us/TelecomPlanMarch2005.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> Other important sectors include medical research and technology, non-profit institutions, and universities. | ||
| Line 148: | Line 151: | ||
!colspan="3"|'''New York City Compared''' | !colspan="3"|'''New York City Compared''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|''' | |'''2000 Census'''||'''NY City'''||'''NY State'''||'''U.S.''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Total population||8,213,839<ref name="census" />||18,976,457||281,421,906 | |Total population||8,213,839<ref name="census" />||18,976,457||281,421,906 | ||
| Line 170: | Line 173: | ||
|Asian||10%||6%||4% | |Asian||10%||6%||4% | ||
|} | |} | ||
New York is the most populous city in the United States, with an estimated | New York is the most populous city in the United States, with an estimated 2023 population of 8,258,00 (up from 8.214 million in 2005).<ref name="census" /> This amounts to about 40% of New York State's population and a similar percentage of the metropolitan regional population. | ||
New York's two key demographic features are its density and diversity. The city's population density of | New York's two key demographic features are its density and diversity. The city's population density of 27,444 people per square mile in 2023 makes it the densest of any American municipality with a population above 100,000. <ref>Highest Density States, Counties and Cities (2022), United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 30, 2023.</ref> Manhattan's population density is 70,451 people per square mile, highest of any county in the United States. | ||
New York City is exceptionally diverse. Throughout its history the city has been a major point of entry for immigrants; the term "[[melting pot]]" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the [[Lower East Side, Manhattan|Lower East Side]]. 36% of the city's population is foreign-born. | New York City is exceptionally diverse. Throughout its history the city has been a major point of entry for immigrants; the term "[[melting pot]]" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the [[Lower East Side, Manhattan|Lower East Side]]. 36% of the city's population is foreign-born. Among American cities, this proportion is higher only in [[Los Angeles, California|Los Angeles]] and [[Miami]]. While the immigrant communities in those cities are dominated by a few nationalities, in New York no single country or region of origin dominates. The ten largest countries of origin for modern immigration are the [[Dominican Republic]], China, [[Jamaica]], [[Guyana]], Pakistan, [[Ecuador]], [[Haiti]], [[Trinidad and Tobago]], [[Colombia]] and [[Russia]].<ref>{{cite web |title=Appendix Table 5-4: Ten Largest Sources of the Foreign-Born by County New York Metropolitan Region, 2000 |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |date=2005 |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/html/dcp/pdf/census/nny_table_5_4.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> About 170 languages are spoken in the city.<ref name="languages in NYC" /> | ||
The New York City metropolitan area is home to the largest [[ | The New York City metropolitan area is home to the largest [[Judaism|Jewish]] community outside [[Israel]]; [[Tel Aviv]] proper (non-metro/within municipal limits) has a smaller population than the Jewish population of New York City proper, making New York the largest Jewish community in the world. About 12% of New Yorkers are Jewish.<ref>{{cite web |title=Jewish Community Study of New York |publisher=United Jewish Appeal-Federation of New York |date=2002 |url=http://www.ujafedny.org/atf/cf/%7BAD848866-09C4-482C-9277-51A5D9CD6246%7D/JCommStudyIntro.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> It is also home to nearly a quarter of the nation's [[Indian-American|South Asians]],<ref>{{cite web |title=Census Profile:New York City's Indian American Population |publisher=Asian American Federation of New York |date=2004 |url=http://www.aafny.org/cic/briefs/indianamer.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-28}}</ref> and the largest [[African American]] community of any city in the country. | ||
The five largest ethnic groups as of | The five largest ethnic groups as of 2005 are Puerto Ricans, Italians, West Indians, Dominicans, and Chinese.<ref>[http://www.nyc.gov/html/dcp/html/census/popacs.shtml ''Socioeconomic Characteristics by Race/Hispanic Origin and Ancestry Group''], 2005 American Community Survey, New York City Department of City Planning, available at </ref> The Puerto Rican population of New York City is the largest outside of Puerto Rico.<ref>Archive of the Mayor's Press Office, [http://www.nyc.gov/html/om/html/98a/pr256-98.html ''Mayor Giuliani Proclaims Puerto Rican Week in New York City''], Tuesday, June 9, 1998.</ref> Italian Americans emigrated to the city in large numbers in the early twentieth century. The Irish, the sixth largest ethnic group in the city, also have a notable presence; one in 50 New Yorkers of European origin carry a distinctive genetic signature on their Y chromosomes inherited from [[Niall of the Nine Hostages]], an Irish high king of the fifth century A.D.<ref>{{cite journal|author=Moore LT, McEvoy B, Cape E, Simms K, Bradley DG| title=A Y-Chromosome Signature of Hegemony in Gaelic Ireland|journal=The American Journal of Human Genetics|volume=78|issue=2|pages=334–338|date=February 2006|url=http://www.journals.uchicago.edu/AJHG/journal/issues/v78n2/43032/43032.web.pdf|format=PDF|pmid=16358217 | accessdate = 2007-06-07}} See also {{cite news|title=If Irish Claim Nobility, Science May Approve|publisher=The New York Times|date=2006-01-18|url=http://www.nytimes.com/2006/01/18/science/18irish.html?ex=1149652800&en=2336ca46c937614b&ei=5070|first=Nicholas|last=Wade|accessdate=2006-07-16}}</ref> | ||
New York City has a high degree of income disparity. In 2005 the median household income in the wealthiest census tract was $188,697, while in the poorest it was $9,320.<ref>{{cite news|author=Roberts, Sam |title=In Manhattan, Poor Make 2 Cents for Each Dollar to the Rich |publisher=The New York Times |date= | New York City has a high degree of income disparity. In 2005 the median household income in the wealthiest census tract was $188,697, while in the poorest it was $9,320.<ref>{{cite news|author=Roberts, Sam |title=In Manhattan, Poor Make 2 Cents for Each Dollar to the Rich |publisher=The New York Times |date=April 9, 2005 |url=http://www.fiscalpolicy.org/SamRoberts4Sep05.htm |accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> The disparity is driven by wage growth in high income brackets, while wages have stagnated for middle and lower income brackets. In 2006 the average weekly wage in Manhattan was $1,453, the highest and fastest growing among the largest counties in the United States.<ref name=ManhattanLabor>{{cite web |title=Average Weekly Wage in Manhattan at $1,453 in Second Quarter 2006 |publisher=Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor|date=February 20, 2007 |url=http://www.bls.gov/ro2/fax/qcew9310.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-02-21}}</ref> The borough is also experiencing a baby boom that is unique among American cities. Since 2000, the number of children under age 5 living in Manhattan grew by more than 32%.<ref>{{cite news|title=In Surge in Manhattan Toddlers, Rich White Families Lead Way |author=Roberts, Sam |publisher=The New York Times |date=2007-03-27 |url= http://www.nytimes.com/2007/03/23/nyregion/23kid.html|accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> | ||
== Government == | == Government == | ||
[[Image:Mayor Bloomberg.jpg|thumb| | [[Image:Mayor Bloomberg.jpg|thumb|left|Michael Bloomberg was mayor of New York City 2002--2013.]] | ||
Since its consolidation in 1898, New York City has been a [[metropolitan municipality]] with a "strong" [[Mayor-council government|mayor-council form of government]]. The government of New York is more centralized than that of most other U.S. cities. In New York City, the central government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply and welfare services. The mayor and councillors are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 Council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyccouncil.info/tools/about_council.cfm |title=About the Council |publisher=New York City Council |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> The mayor and councilors are limited to two four-year terms. | Since its consolidation in 1898, New York City has been a [[metropolitan municipality]] with a "strong" [[Mayor-council government|mayor-council form of government]]. The government of New York is more centralized than that of most other U.S. cities. In New York City, the central government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply and welfare services. The mayor and councillors are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 Council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nyccouncil.info/tools/about_council.cfm |title=About the Council |publisher=New York City Council |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> The mayor and councilors are limited to two four-year terms. | ||
The mayor is | The mayor since 2022 is Eric Adams, a moderate [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democrat]] and former Borough of Brooklyn President. Adams was an officer in the New York City Transit Police and then the New York City Police Department (NYPD) for more than 20 years, retiring at the rank of captain. He served in the New York State Senate from 2006 to 2013, representing the 20th Senate district in Brooklyn. In November 2013, Adams was elected Brooklyn Borough President, the first African-American to hold the position, and reelected in November 2017. | ||
[[Image:New York County Courthouse.jpg|thumb|220px|The New York County Supreme Court building, located between Worth and Pearl Streets.]] | |||
New York is the most important source of political fundraising in the United States, as four of the top five zip codes in the nation for political contributions are in Manhattan. The top zip code, 10021 on the [[Upper East Side]], generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of both [[George W. Bush]] and [[John Kerry]].<ref>{{cite web|title=2006 Election Overview: Top Zip Codes |publisher=Opensecrets.org |url=http://www.opensecrets.org/overview/topzips.asp?cycle=2004 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. New York City receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). The city also sends an additional $11 billion more each year to the state of New York than it receives back.<ref>{{cite web |title=A Fair Share of State Budget: Does Albany Play Fair with NYC?|publisher=New York City Finance Division |date=[[March 11]], | New York is the most important source of political fundraising in the United States, as four of the top five zip codes in the nation for political contributions are in Manhattan. The top zip code, 10021 on the [[Upper East Side]], generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of both [[George W. Bush]] and [[John Kerry]].<ref>{{cite web|title=2006 Election Overview: Top Zip Codes |publisher=Opensecrets.org |url=http://www.opensecrets.org/overview/topzips.asp?cycle=2004 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. New York City receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). The city also sends an additional $11 billion more each year to the state of New York than it receives back.<ref>{{cite web |title=A Fair Share of State Budget: Does Albany Play Fair with NYC?|publisher=New York City Finance Division |date=[[March 11]], 2005 |url=http://webdocs.nyccouncil.info/attachments/65379.htm?CFID=232457&CFTOKEN=33008944 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> | ||
Located near City Hall are the courthouse for the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, and the Jacob K. Javits Federal Building. Brooklyn hosts the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, and each Borough has a branch of the New York Supreme Court and other New York State courts. As the host of the [[United Nations]], New York City is home to the world's largest international [[Consul|consular]] corps, comprising 122 consulates, consulates general and honorary consulate offices.<ref>{{cite web |title=Foreign Consular Offices in the United States |publisher=U.S. Department of State |date=[[August 4]], | Located near City Hall are the courthouse for the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, and the Jacob K. Javits Federal Building. Brooklyn hosts the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, and each Borough has a branch of the New York Supreme Court and other New York State courts. | ||
As the host of the [[United Nations]], New York City is home to Permanent Missions from 191 of the U.N.'s 192 member nations <ref>{{cite web | title=Permanent Missions to the United Nations | publisher=United Nations | date=[[October 3]],2006 | url=http://www.un.org/members/missions.shtml | accessdate=2007-11-28}}</ref>. It also hosts the world's largest international [[Consul|consular]] corps, comprising 122 consulates, consulates general and honorary consulate offices.<ref>{{cite web |title=Foreign Consular Offices in the United States |publisher=U.S. Department of State |date=[[August 4]], 2006 |url=http://www.state.gov/documents/organization/71117.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-01-21}}</ref> | |||
=== Crime and safety=== | === Crime and safety=== | ||
[[Image:NYC police officers.jpg|thumb|220px|NYPD officers, [[Times Square]]]] | |||
New York City is among the safest cities in the United States; out of 216 U.S. cities with populations of more than 100,000 in 2002, the city ranked 197th in overall crime.<ref>{{cite news|''Law Enforcement News''|title=Don’t tell New York, but crime is going up |url=http://www.lib.jjay.cuny.edu/len/2002/12.31/page5.html}}</ref> The murder rate in 2005 was at its lowest level since 1963.<ref>{{cite paper |title=The Remarkable Drop In Crime In New York City |author=Langan, Patrick A. |date= October 21, 2004 |url=http://samoa.istat.it/Eventi/sicurezza/relazioni/Langan_rel.pdf |publisher=Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (Italy) |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-05-22}}</ref> Crime rates spiked in the 1980s and early 1990s as the crack cocaine epidemic hit the city. During the 1990s the [[New York City Police Department]] (NYPD) adopted CompStat, "[[broken windows]] policing" and other strategies in a major effort to reduce crime. The city's dramatic drop in crime has been attributed by criminologists to these policing tactics, the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes.<ref>{{cite book |title=The Crime Drop in America |chapter=The Rise and Decline of Hard Drugs, Drug Markets, and Violence in Inner-City New York |author=Johnson, Bruce D., Andrew Golub, Eloise Dunlap |editor=Blumstein, Alfred, Joel Wallman |year=2006 |publisher=Cambridge University Press |id=ISBN 0521862795}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |title=New York Murder Mystery: The True Story Behind the Crime Crash of the 1990s |author=Karmen, Andrew |year=2000 |publisher=NYU Press |id=0814747175}}</ref> | |||
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City beginning in the early 19th century. The 20th century saw a rise in the [[Mafia]]. Gangs including the Black Spades also grew in the late 20th century.<ref>{{cite book |title=NYPD: A City and Its Police |author=Lardner, James, and Thomas Reppetto |publisher=Owl Books |year=2000 |pages=pp. 18–21}}</ref> Numerous major riots have occurred in New York City since the mid-1800s, including the Draft Riots in 1863, multiple riots at [[Tompkins Square Park]], and in [[Harlem]].<ref>{{cite book |title=Street Justice: A History of Political Violence in New York City |author=Johnson, Marilynn S. |publisher=Beacon Press |year=2003}}</ref> The serial killings by [[David Berkowitz]] (nicknamed "Son of Sam"), which began on July 29, 1976, terrorized the city for the next year.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.crimelibrary.com/serial_killers/notorious/berkowitz/12.html |title=Son of Sam, David Berkowitz, famous serial killer |publisher=Crime Library / Court TV |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> | |||
== Education == | == Education == | ||
[[Image:Columbia University.jpg|thumb|[[Columbia University]] is an [[Ivy League]] university, located in the Manhattan neighborhood of | [[Image:Columbia University.jpg|thumb|220px|[[Columbia University]] is an [[Ivy League]] university, located in the Manhattan neighborhood of Morningside Heights.]] | ||
The city's public school system | The city's public school system is the largest in the United States. About 1.1 million students are taught in more than 1,200 separate primary and secondary schools.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/html/dcp/download/census/sf3edp302.xls |title=School Enrollment by Level of School and Type of School for Population 3 Years and Over |publisher=New York City Department of City Planning |date=2000 |format=MS Excel |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> There are approximately 900 additional privately run secular and religious schools in the city, including some of the most prestigious private schools in the United States.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://nces.ed.gov/surveys/pss/ |title=Private School Universe Survey |publisher=National Center for Education Statistics |accessdate=2007-06-05}}</ref> | ||
Though it is not often thought of as a " | Though it is not often thought of as a "College Town", there are about 594,000 university students in New York City, the highest number of any city in the United States.<ref>{{cite paper |publisher=Brookings Institution |title=New York in Focus: A Profile from Census 2000 |date=November 2003 |url=http://www.brookings.edu/es/urban/livingcities/newyork2.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-11-17}}</ref> In 2005, three out of five Manhattan residents were college graduates and one out of four had advanced degrees, forming one of the highest concentrations of highly educated people in any American city.<ref>{{cite news |title=New York Area Is a Magnet For Graduates |author=McGeehan, Patrick |publisher=The New York Times |date=[[August 16]], 2006 |url=http://select.nytimes.com/gst/abstract.html?res=FB0E16FF3F5A0C758DDDA10894DE404482 |accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> Public postsecondary education is provided by the [[City University of New York]], the nation's third-largest public university system, and the [[Fashion Institute of Technology]], part of the State University of New York. New York City is also home to such notable private universities as Barnard College, Berkeley College, [[Columbia University]], [[Cooper Union]], Fordham University, Manhattan College, The New School, New York Institute of Technology, New York University, Pace University, Polytechnic University, and St. John's University. The city has dozens of other private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions, such as The Juilliard School of Music. | ||
Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. New York City has the most post-graduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in the United States, 40,000 licensed physicians, and 127 Nobel laureates with roots in local institutions.<ref name="NYC science institutions">{{cite press release |title=Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg and Economic Development Corporation President Andrew M. Alper Unveil Plans to Develop Commercial Bioscience Center in Manhattan|publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/portal/site/nycgov/menuitem.c0935b9a57bb4ef3daf2f1c701c789a0/index.jsp?pageID=mayor_press_release&catID=1194&doc_name=http%3A%2F%2Fhome2.nyc.gov%2Fhtml%2Fom%2Fhtml%2F2004b%2Fpr310-04.html&cc=unused1978&rc=1194&ndi=1 |date=[[November 18]], | Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. New York City has the most post-graduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in the United States, 40,000 licensed physicians, and 127 Nobel laureates with roots in local institutions.<ref name="NYC science institutions">{{cite press release |title=Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg and Economic Development Corporation President Andrew M. Alper Unveil Plans to Develop Commercial Bioscience Center in Manhattan|publisher=New York City Economic Development Corporation |url=http://home2.nyc.gov/portal/site/nycgov/menuitem.c0935b9a57bb4ef3daf2f1c701c789a0/index.jsp?pageID=mayor_press_release&catID=1194&doc_name=http%3A%2F%2Fhome2.nyc.gov%2Fhtml%2Fom%2Fhtml%2F2004b%2Fpr310-04.html&cc=unused1978&rc=1194&ndi=1 |date=[[November 18]], 2004 |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> The city receives the second-highest amount of annual funding from the [[National Institutes of Health]] among all U.S. cities.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://grants.nih.gov/grants/award/trends/top100fy03.htm |title=NIH Domestic Institutions Awards Ranked by City, Fiscal Year 2003 |publisher=National Institutes of Health |date=2003 |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> Major biomedical research institutions include Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Rockefeller University, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, and Weill Cornell Medical College. | ||
The | The New York Public Library, which has the largest collection of any public library system in the country, serves Manhattan, The Bronx, and Staten Island.<ref name="libraryspot">{{cite web |url= http://www.libraryspot.com/lists/listlargestlibs.htm |title=Nation's Largest Libraries |publisher=LibrarySpot |accessdate=2007-06-06}}</ref> Queens is served by the [[Queens Borough Public Library]], which is the nation's second largest public library system, and [[Brooklyn Public Library]] serves Brooklyn.<ref name="libraryspot"/> The New York Public Library has several research libraries, including the Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture. | ||
== Transportation == | == Transportation == | ||
[[Image:NYC subway.jpg|thumb|Public transit is overwhelmingly the dominant form of travel for New Yorkers. The New York City Subway is one of the world's most extensive public transportation systems]] | [[Image:NYC subway.jpg|thumb|Public transit is overwhelmingly the dominant form of travel for New Yorkers. The New York City Subway is one of the world's most extensive public transportation systems.]] | ||
Public transit is overwhelmingly the dominant form of travel for New Yorkers.<ref name=2001summary>{{cite web |title=NHTS 2001 Highlights Report, BTS03-05 |publisher=U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics |date=2001 |url=http://www.bts.gov/publications/highlights_of_the_2001_national_household_travel_survey/pdf/entire.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-05-21}}</ref> About one in every three users of mass transit in the United States and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in New York and its suburbs.<ref name="MTAinfo">{{cite web|title=The MTA Network: Public Transportation for the New York Region| publisher=Metropolitan Transportation Authority |url=http://www.mta.info/mta/network.htm |accessdate=2006-05-17}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Commuting in America III: Commuting Facts |author=Pisarski, Alan |publisher=Transportation Research Board |date= | Public transit is overwhelmingly the dominant form of travel for New Yorkers.<ref name=2001summary>{{cite web |title=NHTS 2001 Highlights Report, BTS03-05 |publisher=U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics |date=2001 |url=http://www.bts.gov/publications/highlights_of_the_2001_national_household_travel_survey/pdf/entire.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2006-05-21}}</ref> About one in every three users of mass transit in the United States and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in New York and its suburbs.<ref name="MTAinfo">{{cite web|title=The MTA Network: Public Transportation for the New York Region| publisher=Metropolitan Transportation Authority |url=http://www.mta.info/mta/network.htm |accessdate=2006-05-17}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Commuting in America III: Commuting Facts |author=Pisarski, Alan |publisher=Transportation Research Board |date=October 16, 2006 |url=http://onlinepubs.trb.org/onlinepubs/nchrp/CIAIIIfacts.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-27}}</ref> This is in contrast to the rest of the country, where about 90% of commuters drive automobiles to their workplace.<ref name=2001summary /> New York is the only city in the United States where more than half of all households do not own a car (in Manhattan, more than 75% of residents do not own a car; nationally, the percentage is 8%).<ref name=2001summary /> | ||
The [[New York City Subway]] is the largest [[rapid transit]] system in the world when measured by track with 660 miles (1,062 km ) of mainline track, and by number of stations in operation, with 468. It is also the fourth-largest when measured by annual ridership (1.4 billion passenger trips in 2005).<ref name=MTAinfo /> The transportation system in New York City is extensive and complex. It includes the [[Verrazano-Narrows Bridge]], the longest suspension bridge in North America,<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nycroads.com/crossings/verrazano-narrows/ |title=Verrazano-Narrows Bridge |publisher=Nycroads.com |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> as well as the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel, the [[Holland Tunnel]], and an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan. | |||
New York City's public bus fleet and commuter rail network are the largest in North America.<ref name="MTAinfo" /> The rail network, which connects the suburbs in the [[tri-state region]] to the city, has more than 250 stations and 20 rail lines.<ref name="MTAinfo" /><ref>{{cite web |publisher=Metropolitan Transportation Authority |title=About the MTA Long Island Rail Road |url=http://www.mta.nyc.ny.us/lirr/pubs/aboutlirr.htm |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |title=Facts at a Glance |publisher=NJ Transit |date=2005 |url=http://www.njtransit.com/pdf/an_factsataGlance_FY.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref> The commuter rail system converges at the two busiest rail stations in the United States, [[Grand Central Terminal]] and [[Pennsylvania Station (New York City)|Pennsylvania (Penn) Station]].<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.grandcentralterminal.com/pages/getpage.aspx?id=B6E37786-897D-4174-83C5-2A7404A9E026 |title=Grand Central Demographics |publisher=Metropolitan Transportation Authority |accessdate=2007-03-26}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=Amtrak Facts |url=http://www.nationalatlas.gov/articles/transportation/a_amtrak.html |publisher=National Atlas |accessdate=2006-07-19}}</ref> | |||
New York City | New York City is the top international air passenger gateway to the United States.<ref name=IntlTravel>{{cite web |url=http://www.bts.gov/publications/us_international_travel_and_transportation_trends/2002/index.html |title=U.S. International Travel and Transportation Trends, BTS02-03 |publisher=U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics |date=2002 |accessdate=2007-02-18}}</ref> The area is served by three major airports, [[JFK International Airport|John F. Kennedy International]], [[Newark Liberty International Airport|Newark Liberty International]] and [[La Guardia Airport|LaGuardia]], with plans for a fourth airport, [[Stewart International Airport]] near Newburgh, NY, to be taken over and enlarged by the [[Port Authority of New York and New Jersey]] (which administers the other three airports), as a "reliever" airport to help cope with increasing passenger volume. 100 million travelers used the three airports in 2005 and the city's airspace is the busiest in the nation.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.panynj.gov/CommutingTravel/airports/pdfs/traffic/Air_Traffic_2005.pdf |title=2005 Annual Airport Traffic Report |publisher=The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey |date=November 2, 2006 |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-02-18}}</ref> Outbound international travel from JFK and Newark accounted for about a quarter of all U.S. travelers who went overseas in 2004.<ref>{{cite press release |url=http://www.panynj.gov/AboutthePortAuthority/PressCenter/PressReleases/PressRelease/index.php?id=724 |title=Port Authority Leads Nation in Record-Setting Year for Travel Abroad |publisher=The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey |date=August 29, 2005 |accessdate=2007-02-18}}</ref> | ||
New York | New York's high rate of public transit use, 120,000 daily cyclists<ref>{{cite news |title=Biking It|author=Schaller, Bruce |publisher=Gotham Gazette |date=June 2006 |url=http://www.gothamgazette.com/article/transportation/20060718/16/1910/|accessdate=2006-07-20}}</ref> and many pedestrian commuters makes it the most energy-efficient major city in the United States.<ref name="NYC energy consumption" /> It is well positioned to endure an oil crisis with an extended gasoline price shock in the range of US$3 to US$8 per gallon.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.sustainlane.com/article/747//U.S.+Cities%92+Preparedness+for+an+Oil+Crisis.html |title=U.S. Cities’ Preparedness for an Oil Crisis |publisher=SustainLane |date=March 2006 |accessdate=2006-07-20}}</ref> Walk and bicycle modes of travel account for 21% of all modes for trips in the city; nationally the rate for metro regions is about 8%.<ref>{{cite web |title=2001 National Household Travel Survey: Summary of Travel Trends |publisher=U.S. Department of Transportation |date=December 2004 |url=http://nhts.ornl.gov/2001/pub/STT.pdf |format=PDF |accessdate=2007-02-18}}</ref> | ||
==References== | |||
<small>> | |||
<references> | |||
<ref name=Population> | |||
< | In the 2020 census, the New York City officially had 8,804,190 people and the metro area population (excluding parts in NJ) was 18,804,000. | ||
</ref> | |||
[[Category: | </references> | ||
</small>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 25 September 2024

New York City is the largest city in the United States of America. It is located in New York state east of the Hudson River's mouth. The wider metropolitan area (including portions in New Jersey) has about 20 million people and is the largest urban area in the United States and one of the larger ones in the world[1]. However, Albany, New York, is the state capital.
New York City is home to one of the twelve district Federal Reserve System banks and is a world center of commerce, business, and culture, as well as one of the world's financial hubs. The New York Stock Exchange (Wall Street) and the NASDAQ are the world's first and second largest stock exchanges.
New York saw 12 million immigrants entering the U.S. through Ellis Island; making the city a cosmopolitan metropolis. New York has always been a melting pot, and it has large groups of Americans with Jewish, Irish, German, Italian or Hispanic descent. In 2005, nearly 170 languages were spoken in the city and 36 percent of its population was foreign born.[2]
History
The region was inhabited by the Lenape people at the time of the arrival of the Italian explorer Giovanni da Verrazzano in 1524. Verrazzano called the settlement "Nouvelle Angoulême".[3] The Dutch founded the first European settlement in 1614, called "New Amsterdam," on the southern tip of Manhattan. Dutch colonial Director-General Peter Minuit purchased the island of Manhattan from the Canarsie in 1626.[4] In 1664, the British conquered the city and renamed it "New York" after James II of England, Duke of York and Albany.[5]

New York City grew in importance as a trading port while under British rule. In 1754, King's College (later Columbia University) was founded under charter by King George II. It was located in Lower Manhattan.[6] The city emerged as the theater for a series of major battles known as the New York Campaign during the American Revolutionary War. The Continental Congress met in New York City, and in 1789 the first President of the United States, George Washington, was inaugurated at Federal Hall on Wall Street.[7] New York City was the capital of the United States until 1790.
During the 19th century, the city was transformed by immigration. A visionary development proposal, called the Commissioners' Plan of 1811, expanded the city street grid to encompass all of Manhattan. With the opening in 1825 of the Erie Canal, New York was connected to the vast agricultural markets of the North American interior.[8][9] By 1835, New York City had surpassed Philadelphia as the largest city in the United States. Local politics fell under the domination of Tammany Hall, a political machine supported by Irish immigrants.[10] Public-minded members of the old merchant aristocracy pressed for Central Park, which became the first landscaped park in an American city in 1857.
Anger at military conscription during the American Civil War led to draft riots in 1863, one of the worst incidents of civil unrest in American history.[11] In 1898, the modern City of New York was formed with the consolidation of Brooklyn (until then an independent city), Manhattan, Queens, Richmond, and the Bronx.[12] The opening of the New York City Subway in 1904 connected the different neighborhoods of the city and spurred development in uptown Manhattan. Throughout the first half of the 20th century, the city became a world center for art, industry, commerce, and communication. In 1911, the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire, the city's worst industrial disaster, took the lives of 146 garment workers and spurred the growth of the International Ladies' Garment Workers' Union and major improvements in factory safety standards.[13]
In the 1920s, New York City was a major destination for African Americans during the Great Migration from the American South. By 1916, New York City was home to the largest urban African diaspora in North America. The Harlem Renaissance flourished during the era of Prohibition, coincident with a larger economic boom that saw the skyline develop with the construction of competing skyscrapers. New York City became the most populous city in the world in 1925, overtaking London, which had reigned for a century. The difficult years of the Great Depression saw the election of reformer Fiorello LaGuardia as mayor and the fall of Tammany Hall after eighty years of political dominance.[14]
After World War II, returning veterans and immigrants from Europe created a postwar economic boom and the development of huge housing tracts in eastern Queens. New York emerged from the war unscathed and the leading city of the world, with Wall Street leading America's ascendance as the world's dominant economic power, the United Nations headquarters (built in 1952) emphasizing New York's political influence, and the rise of Abstract Expressionism in the city precipitating New York's displacement of Paris as the center of the art world.[15] Yet like many large American cities, New York suffered a decline in manufacturing and rising crime rates, race riots, and white flight in the 1960s. By the 1970s, the city had gained a reputation as a crime-ridden relic of history.
In the 1980s, a resurgence in the financial industry improved the city's fiscal health. By the 1990s, racial tensions had calmed, crime rates dropped dramatically, and waves of new immigrants arrived from Asia and Latin America. New York's economy was revitalized, and New York's population reached an all-time high in the 2000 census.
The city was one of the sites of the 9/11 terrorist attack in 2001. Nearly 3,000 people died in the destruction of the World Trade Center. The Freedom Tower was later built on the site.[16]
Geography
New York City is located in the Northeastern United States, in southeastern New York State, approximately half way between Washington, D.C. and Boston, Massachusetts.[17] The location at the mouth of the Hudson River, which feeds into a naturally sheltered harbor and then into the Atlantic Ocean, has helped the city grow in significance as a trading city. Most of New York is built on the three islands of Manhattan, Staten Island, and western Long Island, making land scarce and encouraging a high population density.
The Hudson River flows through the Hudson Valley into New York Bay. Between New York City and Troy, New York, the river is a tidal estuary.[18] The Hudson separates the city from New Jersey. The East River, actually a tidal strait, flows from Long Island Sound and separates the Bronx and Manhattan from Long Island. The Harlem River, another tidal strait between the East and Hudson Rivers, separates Manhattan from the Bronx.
The city's land has been altered considerably by human intervention, with substantial land reclamation along the waterfronts since Dutch colonial times. Reclamation is most notable in Lower Manhattan, with developments such as Battery Park City in the 1970s and 1980s.[19] Some of the natural variations in topography have been evened out, particularly in Manhattan.[20]
The city's land area is 321 mi² (831.4 km²).[21] The highest point in the city is Todt Hill on Staten Island, which at 409.8 ft (124.9 m) above sea level is the highest point on the Eastern Seaboard south of Maine.[22] The summit of the ridge is largely covered in woodlands as part of the Staten Island Greenbelt.[23]
Climate

Although located at about the same latitude as the much warmer European cities of Naples, Italy and Madrid, New York has a humid continental climate resulting from prevailing wind patterns that bring cool air from the interior of the North American continent.[24] The city's coastal position keeps temperatures relatively warmer than inland regions during winter, helping to moderate the amount of snow which averages 25 to 35 inches (63.5 to 88.9 cm) each year.[24] New York City has a frost-free period lasting an average of 199 days between seasonal freezes.[24] Spring and Fall in New York City are erratic, and can range from cold and snowy to hot and humid, although they can also be cold or cool and rainy. Summer in New York City is very warm and humid, with temperatures of 90°F (32°C) or higher recorded on average 18 to 25 days each summer.[24] The city's longterm climate patterns have been affected by the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation, a 70-year-long warming and cooling cycle in the Atlantic that influences the frequency and severity of hurricanes and coastal storms in the region.[25] Many scientists believe, however, that global warming will change this pattern.[26]
Environment

Environmental concerns in the city involve managing its extraordinary population density. Mass transit use is the highest in the nation and gasoline consumption in the city is at the rate the national average was in the 1920s.[27] New York City's dense population and low automobile dependence help make New York among the most energy efficient in the United States.[28]
The city's greenhouse gas emission levels are relatively low when measured per capita, at 7.1 metric tons per person, below San Francisco, at 11.2 metric tons, and the national average, at 24.5.[29] New Yorkers are collectively responsible for one percent of the nation's total greenhouse gas emissions,[29] though comprise 2.7% of the nation's population. The average New Yorker consumes less than half the electricity used by a resident of San Francisco and nearly one-quarter the electricity consumed by a resident of Dallas, Texas.[30]
Large amounts of concentrated pollution in New York City lead to high incidence of asthma and other respiratory conditions among the city's residents.[31] In recent years the city has focused on reducing its environmental impact. The city government is required to purchase only the most energy-efficient equipment for use in city offices and public housing.[32] New York has the largest clean air diesel-hybrid and compressed natural gas bus fleet in the country, and some of the first hybrid taxis. The city is also a leader in the construction of energy-efficient green office buildings, including the Hearst Tower among others.[33]
New York City is supplied with drinking water by the protected Catskill Mountains watershed.[34] As a result of the watershed's integrity and undisturbed natural water filtration process, New York is one of only five major cities in the United States with drinking water pure enough not to require purification by water treatment plants.[35][36]
Cityscape
Architecture

The building form most closely associated with New York City is the skyscraper, a pioneering urban form that saw city building shift from the low-scale European tradition to the vertical rise of business districts. Surrounded mostly by water, New York's residential density and high real estate values in commercial districts saw the city amass the largest collection of individual, free-standing office and residential towers in the world.[37]
New York has architecturally significant buildings in a wide range of styles. These include the Woolworth Building (1913), an early gothic revival skyscraper built with massively scaled gothic detailing able to be read from street level several hundred feet below. The 1916 Zoning Resolution required setback in new buildings, and restricted towers to a percentage of the lot size, to allow sunlight to reach the streets below.[38] The Art Deco design of the Chrysler Building (1930), with its tapered top and steel spire, reflected the zoning requirements. The building is considered by many historians and architects to be New York's finest building, with its distinctive ornamentation such as replicas at the corners of the 61st floor of the 1928 Chrysler eagle hood ornaments and V-shaped lighting inserts capped by a steel spire at the tower's crown.[39] A highly influential example of the international style in the United States is the Seagram Building (1957), distinctive for its facade using visible bronze-toned I-beams to evoke the building's structure. The Condé Nast Building (2000) is an important example of green design in American skyscrapers.[33]
The character of New York's large residential districts is often defined by the elegant brownstone rowhouses, townhouses, and tenements that were built during a period of rapid expansion from 1870 to 1930.[40] Stone and brick became the city's building materials of choice after the construction of wood-frame houses was limited in the aftermath of the Great Fire of 1835.[41][42] Unlike Paris, which for centuries was built from its own limestone bedrock, New York has always drawn its building stone from a far-flung network of quarries and its stone buildings have a variety of textures and hues.[43] A distinctive feature of many of the city's buildings is the presence of wooden roof-mounted water towers. In the 1800s, the city required their installation on buildings higher than six stories to prevent the need for excessively high water pressures at lower elevations, which could burst municipal water pipes.[44] Garden apartments became popular during the 1920s in outlying areas, including Jackson Heights in Queens, which became more accessible with expansion of the subway.[45]
Boroughs
New York City is composed of five boroughs, an unusual form of government used to administer the five constituent counties that make up the city.[46] Throughout the boroughs there are hundreds of distinct neighborhoods, many with a definable history and character to call their own. If the boroughs were each independent cities, four of the boroughs (Brooklyn, Queens, Manhattan, and the Bronx) would be among the ten most populous cities in the United States.
- The Bronx (Bronx County; pop. 1,364,566)[47] is the northernmost borough of New York City. The site of Yankee Stadium, home of the New York Yankees, and home to the largest cooperatively owned housing complex in the United States, Co-op City.[48] Except for a small piece of Manhattan known as Marble Hill, the Bronx is the only section of the city that is part of the United States mainland. It is home to the Bronx Zoo, the largest metropolitan zoo in the United States, which spans 265 acres (107.2 hectares) and is home to over 6,000 animals.[49] The Bronx is the birthplace of rap and hip hop.[50]
- Brooklyn (Kings County; pop. 2,511,408)[47] is the city's most populous borough and was an independent city until 1898. Brooklyn is known for its cultural, social and ethnic diversity, an independent art scene, distinct neighborhoods and a unique architectural heritage. The borough also features a long beachfront and Coney Island, established in the 1870s as one of the earliest amusement grounds in the country.[51]
- Manhattan (New York County; pop. 1,593,200)[47] is the most densely populated borough and home to most of the city's skyscrapers. The borough contains the major business and financial centers of the city and many cultural attractions, including numerous museums, the Broadway theatre district and Madison Square Garden. Manhattan is loosely divided into Downtown, Midtown, and Uptown regions. Uptown Manhattan is divided by Central Park into the Upper East Side and the Upper West Side, and north of it is Harlem.
- Queens (Queens County; pop. 2,256,576)[47] is geographically the largest borough and the most ethnically diverse county in the United States.[52] Historically a collection of small towns and villages founded by the Dutch colonists, the borough today is mainly residential and middle class. It is the only large county in the United States where the median income among black households, about $52,000 a year, has surpassed that of whites.[53] The borough hosted the New York World's Fairs of 1939-1940 and 1964-1965. Queens is the site of the New York Mets' home since 2009, Citi Field, as well as their former home, Shea Stadium, and annually hosts the U.S. Open tennis tournament. It is also the home to New York City's two major airports, LaGuardia Airport and John F. Kennedy International Airport.
- Staten Island (Richmond County; pop. 475,014)[47] is the most suburban in character of the five boroughs. It is connected to Brooklyn by the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge, to New Jersey by the Goethals Bridge, the Bayonne Bridge and the Outerbridge Crossing, and to Manhattan via the free Staten Island Ferry. Until 2001, the borough was home to the Fresh Kills Landfill, formerly the largest landfill in the world, which is now being reconstructed as a large urban park.[54]
Culture

The writer Tom Wolfe once said of New York that "Culture just seems to be in the air, like part of the weather." Numerous major American cultural movements began in the city, such as the Harlem Renaissance, which established the African-American literary canon in the United States. The city was the epicenter of jazz in the 1940s, abstract expressionism in the 1950s, and the birthplace of rap and hip hop in the 1970s. The city's punk rock scene was influential in the 1970s and 1980s, and the city has long had a flourishing scene for Jewish-American literature. The city is also important in the American film industry. Manhatta (1920), the nation's first avante-garde film, was filmed in the city.[55] Most of the film industry moved to Hollywood in the 1910s, but New York City is still the second largest center for the American film industry.
The city has more than 2,000 arts and cultural organizations and more than 500 art galleries of all sizes. The city government funds the arts with a larger annual budget than the National Endowment for the Arts.[56] Wealthy industrialists in the 19th century built a network of major cultural institutions, such as the famed Carnegie Hall and Metropolitan Museum of Art, that would become internationally established. The advent of electric lighting led to elaborate theater productions, and in the 1880s New York City theaters on Broadway and along 42nd Street began showcasing a new stage form that came to be known as the Broadway musical.
Strongly influenced by the city's immigrants, productions such as those of Harrigan and Hart, George M. Cohan and others used song in narratives that often reflected themes of hope and ambition. Today these productions are a mainstay of the New York theater scene. The city's 39 largest theaters (with more than 500 seats) are collectively known as "Broadway", after the major thoroughfare that crosses the Times Square theater district.[57]

The Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts, which includes Jazz at Lincoln Center, the Metropolitan Opera, the New York City Opera, the New York Philharmonic, the New York City Ballet, the Vivian Beaumont Theatre, The Juilliard School, and Alice Tully Hall, is the largest performing arts center in the United States. Summerstage presents performances of free plays and music in Central Park and 1,200 free concerts, dance, and theater events across all five boroughs in the summer months.[58]
Tourism
About 40 million foreign and American tourists visit New York City each year.[59] Major destinations include the Empire State Building, Ellis Island, Broadway theatre productions, museums such as the Metropolitan Museum of Art, and other tourist attractions including Central Park, Washington Square Park, Rockefeller Center, Times Square, the Bronx Zoo, New York Botanical Garden, luxury shopping along Fifth and Madison Avenues, and events such as the Halloween Parade in Greenwich Village, the Tribeca Film Festival, and free performances in Central Park at Summerstage. The Statue of Liberty is a major tourist attraction and one of the most recognizable icons of the United States.[60] Many of the city's ethnic enclaves, such as Jackson Heights, Flushing, and Brighton Beach are major shopping destinations for first and second generation Americans up and down the East Coast.
New York City has over 28,000 acres (113 km²) of parkland and 14 miles (22 km) of public beaches.[61][62] Manhattan's Central Park, designed by Frederick Law Olmsted and Calvert Vaux, is the most visited city park in the United States.[63] Prospect Park in Brooklyn, also designed by Olmsted and Vaux, has a 90 acre (36 Hectare) meadow.[64] Flushing Meadows Park in Queens, the city's third largest, was the setting for the 1939 World's Fair and 1964 World's Fair.
New York's food culture, influenced by the city's immigrants and large number of dining patrons, is diverse. Jewish and Italian immigrants made the city famous for bagels, cheesecake and New York style pizza. Some 4,000 mobile food vendors licensed by the city, many immigrant-owned, have made Middle Eastern foods such as falafels and kebabs standbys of contemporary New York street food.[65] The city is also home to many of the finest haute cuisine restaurants in the United States.[66]
Media
New York is a global center for the television, advertising, music, newspaper and book publishing industries and is also the largest media market in the United States. Some of the city's media conglomerates include Time Warner, the News Corporation, the Hearst Corporation, and Viacom. Seven of the world's top eight global advertising agency networks are headquartered in New York. Three of the "Big Four" record labels are also based in the city. One-third of all American independent films are produced in New York.[67] More than 200 newspapers and 350 consumer magazines have an office in the city[67] and book-publishing industry employs about 25,000 people.[68]
Two of the three national daily newspapers in the United States are New York papers, The Wall Street Journal and The New York Times. Major tabloid newspapers in the city include The New York Daily News and The New York Post, founded in 1801 by Alexander Hamilton. The city also has a major ethnic press, with 270 newspapers and magazines published in more than 40 languages.[69] El Diario La Prensa is New York's largest Spanish-language daily and the oldest in the nation.[70] The New York Amsterdam News, published in Harlem, is a prominent African-American newspaper.
The television industry developed in New York and is a significant employer in the city's economy. The four major American broadcast networks, ABC, CBS, FOX and NBC, are all headquartered in New York. Many cable channels are based in the city as well, including MTV, Fox News, HBO and Comedy Central. In 2005 there were more than 100 television shows taped in New York City.
New York is also a major center for non-commercial media. The oldest public-access television channel in the United States is the Manhattan Neighborhood Network, founded in 1971.[71] WNET is the city's major public television station and a primary provider of national PBS programming. WNYC, a public radio station owned by the city until 1997, has the largest public radio audience in the United States.[72] The City of New York operates a public broadcast service, NYCTV, that produces several original Emmy Award-winning shows covering music and culture in city neighborhoods, as well as city government.
Accent
The New York City area has a distinctive regional speech pattern called the New York dialect, alternatively known as Brooklynese or New Yorkese. It is often considered to be one of the most recognizable accents within American English.[73] The classic version of this dialect is centered on middle and working class people of European American descent, and the influx of non-European immigrants in recent decades has led to changes in this distinctive dialect.
One of the more notable features of this dialect is its "r-lessness". The traditional New York–area accent is non-rhotic, so that the sound [ɹ] does not appear at the end of a syllable or immediately before a consonant; hence the pronunciation of the city as "New Yawk". There is no [ɹ] in words like park [pɔːk] (with vowel raised due to the low-back chain shift), butter [bʌɾə], or here [hiə]. In another feature called the low back chain shift, the [ɔ] vowel sound of words like talk, law, cross, and coffee and the often homophonous [ɔr] in core and more are tensed and usually raised more than in General American. In the most old-fashioned and extreme versions of the New York dialect, the vowel sounds of words like girl and of words like oil both become a diphthong [ɜɪ].
Sports
New York City has teams in the four major North American professional sports leagues, each of which also has its headquarters in the city.
Baseball is the city's most closely followed sport. There have been fourteen World Series championship series between New York City teams, in matchups called Subway Series. The city's two current Major League Baseball teams are the New York Yankees and the New York Mets, who enjoy a rivalry arguably as fierce as that between the Yankees and the Boston Red Sox. There are also two [minor league baseball teams in the city, the Staten Island Yankees and Brooklyn Cyclones.
The city is represented in the National Football League by the New York Jets and New York Giants (officially the New York Football Giants), although both teams play their home games in Giants Stadium in nearby New Jersey.
The New York Rangers represent the city in the National Hockey League, playing in the Madison Square Garden.
The city's National Basketball Association team is the New York Knicks. The first national college-level basketball championship was held in New York in 1938 and remains in the city.[74] Rucker Park in Harlem is a celebrated court where many professional athletes play in the summer league.
As a global city, New York supports many events outside these sports. These include the U.S. Open in tennis, the New York City Marathon, and the Millrose Games, an annual track and field meet whose featured event is the Wanamaker Mile. Boxing is also a very prominent part of the city's sporting scene, with events like the Amateur Boxing Golden Gloves being held at Madison Square Garden each year. The New York City Marathon is the world's largest, with often about 50,000 finishers in recent years.
Many sports are associated with New York's immigrant communities. Stickball, a street version of baseball, was popularized by youths in working class Puerto Rican, Italian, and Irish neighborhoods in the 1930s. In recent years several amateur cricket leagues have emerged with the arrival of immigrants from South Asia and the Caribbean.
Economy

New York City is a global hub of international business and commerce and is one of three "command centers" for the world economy (along with London and Tokyo).[75] The city is a major center for finance, insurance, real estate, media and the arts in the United States. The New York metropolitan area had an estimated gross metropolitan product of $952.6 billion in 2005, the largest regional economy in the United States. The city's economy accounts for the majority of the economic activity in the states of New York and New Jersey.[76] Many major corporations are headquartered in New York City, including 44 Fortune 500 companies.[77] New York is also unique among American cities for its large number of foreign corporations. One out of ten private sector jobs in the city is with a foreign company.[78]
New York City is home to some of the nation's — and world's — most valuable real estate. 450 Park Avenue was sold on July 2, 2007 for $510 million, about $1,589 per square foot ($148/m²), breaking the barely month-old record for an American office building of $1,476 per square foot ($137/m²) set in the June 2007 sale of 660 Madison Avenue.[79]

The New York Stock Exchange, located on Wall Street, and the NASDAQ are the world's first and second largest stock exchanges, respectively, when measured by average daily trading volume and overall market capitalization.[80] Financial services account for more than 35 percent of the city's employment income.[81] Real estate is a major force in the city's economy, as the total value of all New York City property was $802.4 billion in 2006.[82] The Time Warner Center is the property with the highest-listed market value in the city, at $1.1 billion in 2006.[82]
The city's television and film industry is the second largest in the country after Hollywood.[83] Creative industries such as new media, advertising, fashion, design and architecture account for a growing share of employment, with New York City possessing a strong competitive advantage in these industries.[84] High-tech industries like bioscience, software development, game design, and Internet services are also growing due to its position at the terminus of the transatlantic fiber optic trunk line in New York City.[85] Other important sectors include medical research and technology, non-profit institutions, and universities.
Manufacturing accounts for a large but declining share of employment. Garments, chemicals, metal products, processed foods, and furniture are some of the principal products.[86] The food-processing industry is the most stable major manufacturing sector in the city.[87] Food making is a $5 billion industry that employs more than 19,000 residents, many of them immigrants who speak little English. Chocolate is New York City's leading specialty-food export, with $234 million worth of exports each year.[87]
Demographics
| New York City Compared | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 Census | NY City | NY State | U.S. |
| Total population | 8,213,839[47] | 18,976,457 | 281,421,906 |
| Population, percent change, 1990 to 2000 | +9.4% | +5.5% | +13.1% |
| Population density | 26,403/mi² | 402/mi² | 80/mi² |
| Median household income (1999) | $38,293 | $43,393 | $41,994 |
| Bachelor's degree or higher | 27% | 27% | 29% |
| Foreign born | 36% | 20% | 11% |
| White (non-Hispanic) | 37% | 62% | 67% |
| Black | 28% | 16% | 12% |
| Hispanic (any race) | 27% | 15% | 11% |
| Asian | 10% | 6% | 4% |
New York is the most populous city in the United States, with an estimated 2023 population of 8,258,00 (up from 8.214 million in 2005).[47] This amounts to about 40% of New York State's population and a similar percentage of the metropolitan regional population.
New York's two key demographic features are its density and diversity. The city's population density of 27,444 people per square mile in 2023 makes it the densest of any American municipality with a population above 100,000. [88] Manhattan's population density is 70,451 people per square mile, highest of any county in the United States.
New York City is exceptionally diverse. Throughout its history the city has been a major point of entry for immigrants; the term "melting pot" was first coined to describe densely populated immigrant neighborhoods on the Lower East Side. 36% of the city's population is foreign-born. Among American cities, this proportion is higher only in Los Angeles and Miami. While the immigrant communities in those cities are dominated by a few nationalities, in New York no single country or region of origin dominates. The ten largest countries of origin for modern immigration are the Dominican Republic, China, Jamaica, Guyana, Pakistan, Ecuador, Haiti, Trinidad and Tobago, Colombia and Russia.[89] About 170 languages are spoken in the city.[2]
The New York City metropolitan area is home to the largest Jewish community outside Israel; Tel Aviv proper (non-metro/within municipal limits) has a smaller population than the Jewish population of New York City proper, making New York the largest Jewish community in the world. About 12% of New Yorkers are Jewish.[90] It is also home to nearly a quarter of the nation's South Asians,[91] and the largest African American community of any city in the country.
The five largest ethnic groups as of 2005 are Puerto Ricans, Italians, West Indians, Dominicans, and Chinese.[92] The Puerto Rican population of New York City is the largest outside of Puerto Rico.[93] Italian Americans emigrated to the city in large numbers in the early twentieth century. The Irish, the sixth largest ethnic group in the city, also have a notable presence; one in 50 New Yorkers of European origin carry a distinctive genetic signature on their Y chromosomes inherited from Niall of the Nine Hostages, an Irish high king of the fifth century A.D.[94]
New York City has a high degree of income disparity. In 2005 the median household income in the wealthiest census tract was $188,697, while in the poorest it was $9,320.[95] The disparity is driven by wage growth in high income brackets, while wages have stagnated for middle and lower income brackets. In 2006 the average weekly wage in Manhattan was $1,453, the highest and fastest growing among the largest counties in the United States.[96] The borough is also experiencing a baby boom that is unique among American cities. Since 2000, the number of children under age 5 living in Manhattan grew by more than 32%.[97]
Government
Since its consolidation in 1898, New York City has been a metropolitan municipality with a "strong" mayor-council form of government. The government of New York is more centralized than that of most other U.S. cities. In New York City, the central government is responsible for public education, correctional institutions, libraries, public safety, recreational facilities, sanitation, water supply and welfare services. The mayor and councillors are elected to four-year terms. The New York City Council is a unicameral body consisting of 51 Council members whose districts are defined by geographic population boundaries.[98] The mayor and councilors are limited to two four-year terms.
The mayor since 2022 is Eric Adams, a moderate Democrat and former Borough of Brooklyn President. Adams was an officer in the New York City Transit Police and then the New York City Police Department (NYPD) for more than 20 years, retiring at the rank of captain. He served in the New York State Senate from 2006 to 2013, representing the 20th Senate district in Brooklyn. In November 2013, Adams was elected Brooklyn Borough President, the first African-American to hold the position, and reelected in November 2017.
New York is the most important source of political fundraising in the United States, as four of the top five zip codes in the nation for political contributions are in Manhattan. The top zip code, 10021 on the Upper East Side, generated the most money for the 2004 presidential campaigns of both George W. Bush and John Kerry.[99] The city has a strong imbalance of payments with the national and state governments. New York City receives 83 cents in services for every $1 it sends to the federal government in taxes (or annually sends $11.4 billion more than it receives back). The city also sends an additional $11 billion more each year to the state of New York than it receives back.[100]
Located near City Hall are the courthouse for the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York and United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit, and the Jacob K. Javits Federal Building. Brooklyn hosts the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York, and each Borough has a branch of the New York Supreme Court and other New York State courts.
As the host of the United Nations, New York City is home to Permanent Missions from 191 of the U.N.'s 192 member nations [101]. It also hosts the world's largest international consular corps, comprising 122 consulates, consulates general and honorary consulate offices.[102]
Crime and safety

New York City is among the safest cities in the United States; out of 216 U.S. cities with populations of more than 100,000 in 2002, the city ranked 197th in overall crime.[103] The murder rate in 2005 was at its lowest level since 1963.[104] Crime rates spiked in the 1980s and early 1990s as the crack cocaine epidemic hit the city. During the 1990s the New York City Police Department (NYPD) adopted CompStat, "broken windows policing" and other strategies in a major effort to reduce crime. The city's dramatic drop in crime has been attributed by criminologists to these policing tactics, the end of the crack epidemic and demographic changes.[105][106]
Organized crime has long been associated with New York City beginning in the early 19th century. The 20th century saw a rise in the Mafia. Gangs including the Black Spades also grew in the late 20th century.[107] Numerous major riots have occurred in New York City since the mid-1800s, including the Draft Riots in 1863, multiple riots at Tompkins Square Park, and in Harlem.[108] The serial killings by David Berkowitz (nicknamed "Son of Sam"), which began on July 29, 1976, terrorized the city for the next year.[109]
Education

The city's public school system is the largest in the United States. About 1.1 million students are taught in more than 1,200 separate primary and secondary schools.[110] There are approximately 900 additional privately run secular and religious schools in the city, including some of the most prestigious private schools in the United States.[111]
Though it is not often thought of as a "College Town", there are about 594,000 university students in New York City, the highest number of any city in the United States.[112] In 2005, three out of five Manhattan residents were college graduates and one out of four had advanced degrees, forming one of the highest concentrations of highly educated people in any American city.[113] Public postsecondary education is provided by the City University of New York, the nation's third-largest public university system, and the Fashion Institute of Technology, part of the State University of New York. New York City is also home to such notable private universities as Barnard College, Berkeley College, Columbia University, Cooper Union, Fordham University, Manhattan College, The New School, New York Institute of Technology, New York University, Pace University, Polytechnic University, and St. John's University. The city has dozens of other private colleges and universities, including many religious and special-purpose institutions, such as The Juilliard School of Music.
Much of the scientific research in the city is done in medicine and the life sciences. New York City has the most post-graduate life sciences degrees awarded annually in the United States, 40,000 licensed physicians, and 127 Nobel laureates with roots in local institutions.[114] The city receives the second-highest amount of annual funding from the National Institutes of Health among all U.S. cities.[115] Major biomedical research institutions include Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, Rockefeller University, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, and Weill Cornell Medical College.
The New York Public Library, which has the largest collection of any public library system in the country, serves Manhattan, The Bronx, and Staten Island.[116] Queens is served by the Queens Borough Public Library, which is the nation's second largest public library system, and Brooklyn Public Library serves Brooklyn.[116] The New York Public Library has several research libraries, including the Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture.
Transportation
Public transit is overwhelmingly the dominant form of travel for New Yorkers.[117] About one in every three users of mass transit in the United States and two-thirds of the nation's rail riders live in New York and its suburbs.[118][119] This is in contrast to the rest of the country, where about 90% of commuters drive automobiles to their workplace.[117] New York is the only city in the United States where more than half of all households do not own a car (in Manhattan, more than 75% of residents do not own a car; nationally, the percentage is 8%).[117]
The New York City Subway is the largest rapid transit system in the world when measured by track with 660 miles (1,062 km ) of mainline track, and by number of stations in operation, with 468. It is also the fourth-largest when measured by annual ridership (1.4 billion passenger trips in 2005).[118] The transportation system in New York City is extensive and complex. It includes the Verrazano-Narrows Bridge, the longest suspension bridge in North America,[120] as well as the world's first mechanically ventilated vehicular tunnel, the Holland Tunnel, and an aerial tramway that transports commuters between Roosevelt Island and Manhattan.
New York City's public bus fleet and commuter rail network are the largest in North America.[118] The rail network, which connects the suburbs in the tri-state region to the city, has more than 250 stations and 20 rail lines.[118][121][122] The commuter rail system converges at the two busiest rail stations in the United States, Grand Central Terminal and Pennsylvania (Penn) Station.[123][124]
New York City is the top international air passenger gateway to the United States.[125] The area is served by three major airports, John F. Kennedy International, Newark Liberty International and LaGuardia, with plans for a fourth airport, Stewart International Airport near Newburgh, NY, to be taken over and enlarged by the Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (which administers the other three airports), as a "reliever" airport to help cope with increasing passenger volume. 100 million travelers used the three airports in 2005 and the city's airspace is the busiest in the nation.[126] Outbound international travel from JFK and Newark accounted for about a quarter of all U.S. travelers who went overseas in 2004.[127]
New York's high rate of public transit use, 120,000 daily cyclists[128] and many pedestrian commuters makes it the most energy-efficient major city in the United States.[27] It is well positioned to endure an oil crisis with an extended gasoline price shock in the range of US$3 to US$8 per gallon.[129] Walk and bicycle modes of travel account for 21% of all modes for trips in the city; nationally the rate for metro regions is about 8%.[130]
References
>
- ↑ In the 2020 census, the New York City officially had 8,804,190 people and the metro area population (excluding parts in NJ) was 18,804,000.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Queens: Economic Development and the State of the Borough Economy (PDF). New York State Comptroller (June 2006). Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- ↑ Rankin, Rebecca B., and Cleveland Rodgers (1948). New York: the World's Capital City, Its Development and Contributions to Progress. Harper.
- ↑ Miller, Christopher L., George R. Hamell (September 1986). "A New Perspective on Indian-White Contact: Cultural Symbols and Colonial Trade". The Journal of American History 73 (2). Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- ↑ Homberger, Eric (2005). The Historical Atlas of New York City: A Visual Celebration of 400 Years of New York City's History. Owl Books, p. 34. ISBN 0805078428.
- ↑ Moore, Nathaniel Fish (1876). An Historical Sketch of Columbia College, in the City of New York, 1754-1876. Columbia College, p. 8.
- ↑ President George Washington's First Inaugural Speech, on www.archives.gov, last access 11/27/2022
- ↑ Bridges, William (1811). Map of the City of New York and Island of Manhattan with Explanatory Remarks and References.
- ↑ Lankevich (1998), pp. 67–68.
- ↑ Mushkat, Jerome Mushkat (1990). Fernando Wood: A Political Biography. Kent State University Press, p. 36. ISBN 087338413X.
- ↑ Cook, Adrian (1974). The Armies of the Streets: The New York City Draft Riots of 1863, pp. 193-195.
- ↑ The 100 Year Anniversary of the Consolidation of the 5 Boroughs into New York City, New York City. Accessed June 29, 2007.
- ↑ Cornell University Library: Triangle Factory Fire. Cornell University. Retrieved on 2007-03-12.
- ↑ Allen, Oliver E. (1993). “Chapter 9: The Decline”, The Tiger – The Rise and Fall of Tammany Hall. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company. Retrieved on 2007-05-25.
- ↑ Burns, Ric (2003-08-22). The Center of the World - New York: A Documentary Film (Transcript). PBS. Retrieved on 2006-07-20.
- ↑ World Trade Center: Frequently Asked Questions. Silverstein Properties. Retrieved on 2007-05-25.
- ↑ Washington, D.C. is 228 miles driving distance from New York City, and Boston is 217 miles driving distance from New York.
- ↑ Information about the Hudson River estuary
- ↑ Gillespie, Angus K. (1999). Twin Towers: The Life of New York City's World Trade Center. Rutgers University Press, p. 71.
- ↑ Lopate , Phillip (2004). Waterfront: A Walk Around Manhattan. Anchor Press. ISBN 0385497148.
- ↑ Land Use Facts. New York City Department of City Planning. Retrieved on 2007-03-13. New York City's total area is 468.9 mi². 159.88 mi² of this is water and 321 mi² is land.
- ↑ Lundrigan, Margaret (2004). Staten Island: Isle of the Bay, NY. Arcadia Publishing, p. 10.
- ↑ Howard, David (2002). Outside Magazine's Urban Adventure New York City. W. W. Norton & Company, p. 35. ISBN 0393322122.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 24.3 The Climate of New York. New York State Climate Office. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ Riley, Mary Elizabeth (2006). Assessing the Impact of Interannual Climate Variability on New York City's Reservoir System (PDF). Cornell University Graduate School for Atmospheric Science. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ Romm, Joseph J., Hell and High Water: Global Warming — the Solution and the Politics, pp. 44, 47 (2006) William Morrow & Co. ISBN 0-06117-212-X citing MIT's and Kerry Emanuel's research as showing that the AMO has now been supplanted by global warming as the "dominant force" in the Atlantic climate.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 Jervey, Ben (2006). The Big Green Apple: Your Guide to Eco-Friendly Living in New York City. Globe Pequot Press. ISBN 0762738359.
- ↑ Owen, David. "Green Manhattan", The New Yorker, October 18, 2004.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Inventory of New York City Greenhouse Gas Emissions (PDF). New York City Office of Long-term Planning and Sustainability (April 2007). Retrieved on 2007-04-11.
- ↑ Global Warming and Greenhouse Gases. PlaNYC / The City of New York (2006-12-06). Retrieved on 2006-12-13.
- ↑ Coburn, Jason, Jeffrey Osleeb, Michael Porter (June 2006). "Urban Asthma and the Neighbourhood Environment in New York City". Health & Place 12(2): pp. 167–179. PMID 16338632.
- ↑ DePalma, Anthony. It Never Sleeps, but It's Learned to Douse the Lights, The New York Times, December 11, 2005. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 Pogrebin, Robin. 7 World Trade Center and Hearst Building: New York's Test Cases for Environmentally Aware Office Towers, The New York Times, April 16, 2006. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Current Reservoir Levels. New York City Department of Environmental Protection. Retrieved on 2007-06-04.
- ↑ Miele, Joel A., Sr (November 20, 1998). Maintaining Water Quality that Satisfies Customers: New York City Watershed Agricultural Program. International Water Supply Symposium Tokyo 1998, New York City Department of Environmental Protection. Retrieved on 2006-11-17.
- ↑ New York City 2005 Drinking Water Supply and Quality Report (PDF). New York City Department of Environmental Protection (2005). Retrieved on 2006-07-17.
- ↑ About New York City. Emporis. Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- ↑ Fischler, Raphael (1998). "The Metropolitan Dimension of Early Zoning: Revisiting the 1916 New York City Ordinance". Journal of the American Planning Association 64(2).
- ↑ Favorites! 100 Experts Pick Their top 10 New York Towers. The Skyscraper Museum (January 22, 2006). Retrieved on 2007-04-11.
- ↑ Plunz, Richar A. (1990). “Chapters 3 [Rich and Poor] & 4 [Beyond the Tenement]”, History of Housing in New York City: Dwelling Type and Change in the American Metropolis. Columbia University Press. ISBN 0231062974.
- ↑ Lankevich (1998), pp. 82–83.
- ↑ Wilson, Rufus Rockwell (1902). New York: Old & New: Its Story, Streets, and Landmarks. J.B. Lippincott, p. 354.
- ↑ B. Diamonstein–Spielvoegel, Barbaralee (2005). The Landmarks of New York. Monacelli Press. ISBN 1580931545. See also Whyte, William H. (1939). The WPA Guide to New York City. New Press. ISBN 1565843215.
- ↑ Elliot, Debbie (2006-12-02). Wondering About Water Towers. National Public Radio. Retrieved on 2007-04-11.
- ↑ Hood, Clifton (2004). 722 Miles: The Building of the Subways and how They Transformed New York. Johns Hopkins University Press, pp. 175–177.
- ↑ Benjamin, Gerald, Richard P. Nathan (1990). Regionalism and realism: A Study of Government in the New York Metropolitan Area. Brookings Institute, p. 59.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 47.3 47.4 47.5 47.6 The Current Population of NYC (2005) (PDF). New York City Department of City Planning. Retrieved on 2007-03-13. These figures were adopted by the U.S. Census Bureau in September 2006.
- ↑ Frazier, Ian. Utopia, the Bronx, The New Yorker, June 26, 2006. Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Ward, Candace (2000). New York City Museum Guide. Dover Publications, p. 72. ISBN 0486410005.
- ↑ Toop, David (1992). Rap Attack 2: African Rap to Global Hip Hop. Serpents Tail. ISBN 1852422432.
- ↑ Immerso, Michael (2002). Coney Island: The People's Playground. Rutgers University Press, p. 3. ISBN 0813531381.
- ↑ O'Donnell, Michelle. In Queens, It's the Glorious 4th, and 6th, and 16th, and 25th..., New York Times, July 4, 2006. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Roberts, Sam. Black Incomes Surpass Whites in Queens, The New York Times, January 10, 2006. Retrieved on 2007-03-28.
- ↑ Fresh Kills Park: Lifescape - Draft Master Plan (pdf). New York City Department of City Planning (March 2006). Retrieved on 2007-06-03.
- ↑ Bruce Posner. (2005). Picturing a Metropolis: New York City Unveiled [DVD]. Unseen Cinema.
- ↑ Creative New York (PDF). Center for an Urban Future (December 2005). Retrieved on 2006-06-19.
- ↑ Welsh, Anne Marie. 2 plays + 9 nominations = good odds for locals, San Diego Union-Tribune, June 6, 2004. Retrieved on 2007-06-08.
- ↑ Summerstage: Our Mission. Summerstage.org. Retrieved on 2007-05-31.
- ↑ NYC Statistics. NYC & Company. Retrieved on 2006-08-03.
- ↑ Statue of Liberty. New York Magazine. Retrieved on 2006-06-20.
- ↑ Mayor Giuliani Announces Amount of Parkland in New York City has Passed 28,000 Acre Mark. New York City Mayor's Office (February 3, 1999). Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ Beaches. New York City Department of Parks & Recreation. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ City Park Facts. The Trust for Public Land, Center for City Park Excellence (June 2006). Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ General Information. Prospect Park Alliance. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ Bleyer, Jennifer. Kebabs on the Night Shift, The New York Times, May 14, 2006. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Collins, Glenn. Michelin Takes on the City, Giving Some a Bad Taste, The New York Times, November 3, 2005. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Request for Expressions of Interest (PDF). The Governors Island Preservation & Education Corporation (2005). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Media and Entertainment. New York City Economic Development Corporation. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Ethnic Press Booms In New York City, Editor & Publisher, July 10, 2002. Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ el diario/La Prensa: The Nation’s Oldest Spanish-Language Daily. New America Media (July 27, 2005). Retrieved on 2007-06-09.
- ↑ Community Celebrates Public Access TV's 35th Anniversary, Manhattan Neighborhood Network press release dated August 6, 2006. Accessed April 28, 2007. "Public access TV was created in the 1970s to allow ordinary members of the public to make and air their own TV shows—and thereby exercise their free speech. It was first launched in the U.S. in Manhattan July 1st 1971, on the Teleprompter and Sterling Cable systems, now Time Warner Cable."
- ↑ Top 30 Public Radio Subscribers: Spring 2006 Arbitron (PDF). Radio Research Consortium (August 28, 2006). Retrieved on 2006-11-17.
- ↑ Newman, Michael (2005) "New York Talk" in American Voices Walt Wolfram and Ben Ward (eds). p.82-87 Blackwell ISBN 1-4051-2109-2
- ↑ Postseason Overview. National Invitation Tournament. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ Saskia Sassen (2001). The Global City: New York, London, Tokyo, 2nd edition. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691070636.
- ↑ The role of metro areas in the U.S. economy (PDF). The United States Conference of Mayors (January 13, 2006). Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ NYC Business Climate - Facts & Figures. New York City Economic Development Corporation. Retrieved on 2007-06-08.
- ↑ Wylde, Kathryn. Keeping the Economy Growing, Gotham Gazette, January 23, 2006. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Quirk, James. "Bergen offices have plenty of space", The Record (Bergen County), July 5, 2007. Accessed July 5, 2007. "On Monday, a 26-year-old, 33-story office building at 450 Park Ave. sold for a stunning $1,589 per square foot, or about $510 million. The price is believed to be the most ever paid for a U.S. office building on a per-square-foot basis. That broke the previous record -- set four weeks earlier -- when 660 Madison Ave. sold for $1,476 a square foot."
- ↑ Electronic Finance: Reshaping the Financial Landscape Around the World (PDF). The World Bank (September 2000). Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ Orr, James and Giorgio Topa (Volume 12, Number 1, January 2006). Challenges Facing the New York Metropolitan Area Economy (PDF). Current Issues in Economics and Finance - Second District Highlights. New York Federal Reserve. Retrieved on 2007-06-05.
- ↑ 82.0 82.1 Tentative Assessment Roll: Fiscal Year 2008 (PDF). New York City Department of Finance (January 15, 2007). Retrieved on 2007-03-21.
- ↑ NYC Film Statistics. Mayor's Office of Film, Theatre, and Broadcasting. Retrieved on 2007-06-07.
- ↑ Currid, Elizabeth (2006). "New York as a Global Creative Hub: A Competitive Analysis of Four Theories on World Cities". Economic Development Quarterly 20(4): pp. 330–350.
- ↑ Telecommunications and Economic Development in New York City: A Plan for Action (PDF). New York City Economic Development Corporation (March 2005). Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Protecting and Growing New York City's Industrial Job Base (PDF). The Mayor's Office for Industrial and Manufacturing Business (January 2005). Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 More Than a Link in the Food Chain (PDF). The Mayor's Office for Industrial and Manufacturing Business (February 2007). Retrieved on 2007-02-14.
- ↑ Highest Density States, Counties and Cities (2022), United States Census Bureau. Accessed December 30, 2023.
- ↑ Appendix Table 5-4: Ten Largest Sources of the Foreign-Born by County New York Metropolitan Region, 2000 (PDF). New York City Department of City Planning (2005). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Jewish Community Study of New York (PDF). United Jewish Appeal-Federation of New York (2002). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Census Profile:New York City's Indian American Population (PDF). Asian American Federation of New York (2004). Retrieved on 2007-03-28.
- ↑ Socioeconomic Characteristics by Race/Hispanic Origin and Ancestry Group, 2005 American Community Survey, New York City Department of City Planning, available at
- ↑ Archive of the Mayor's Press Office, Mayor Giuliani Proclaims Puerto Rican Week in New York City, Tuesday, June 9, 1998.
- ↑ Moore LT, McEvoy B, Cape E, Simms K, Bradley DG (February 2006). "A Y-Chromosome Signature of Hegemony in Gaelic Ireland" (PDF). The American Journal of Human Genetics 78 (2): 334–338. PMID 16358217. Retrieved on 2007-06-07. See also Wade, Nicholas. If Irish Claim Nobility, Science May Approve, The New York Times, 2006-01-18. Retrieved on 2006-07-16.
- ↑ Roberts, Sam. In Manhattan, Poor Make 2 Cents for Each Dollar to the Rich, The New York Times, April 9, 2005. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ Average Weekly Wage in Manhattan at $1,453 in Second Quarter 2006 (PDF). Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor (February 20, 2007). Retrieved on 2007-02-21.
- ↑ Roberts, Sam. In Surge in Manhattan Toddlers, Rich White Families Lead Way, The New York Times, 2007-03-27. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ About the Council. New York City Council. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ 2006 Election Overview: Top Zip Codes. Opensecrets.org. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ A Fair Share of State Budget: Does Albany Play Fair with NYC?. New York City Finance Division (March 11, 2005). Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Permanent Missions to the United Nations. United Nations (October 3,2006). Retrieved on 2007-11-28.
- ↑ Foreign Consular Offices in the United States (PDF). U.S. Department of State (August 4, 2006). Retrieved on 2007-01-21.
- ↑ Don’t tell New York, but crime is going up.
- ↑ Langan, Patrick A. (October 21, 2004). The Remarkable Drop In Crime In New York City (PDF). Istituto Nazionale di Statistica (Italy). Retrieved on 2007-05-22.
- ↑ Johnson, Bruce D., Andrew Golub, Eloise Dunlap (2006). “The Rise and Decline of Hard Drugs, Drug Markets, and Violence in Inner-City New York”, Blumstein, Alfred, Joel Wallman: The Crime Drop in America. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0521862795.
- ↑ Karmen, Andrew (2000). New York Murder Mystery: The True Story Behind the Crime Crash of the 1990s. NYU Press. 0814747175.
- ↑ Lardner, James, and Thomas Reppetto (2000). NYPD: A City and Its Police. Owl Books, pp. 18–21.
- ↑ Johnson, Marilynn S. (2003). Street Justice: A History of Political Violence in New York City. Beacon Press.
- ↑ Son of Sam, David Berkowitz, famous serial killer. Crime Library / Court TV. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ School Enrollment by Level of School and Type of School for Population 3 Years and Over (MS Excel). New York City Department of City Planning (2000). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Private School Universe Survey. National Center for Education Statistics. Retrieved on 2007-06-05.
- ↑ (November 2003). New York in Focus: A Profile from Census 2000 (PDF). Brookings Institution. Retrieved on 2006-11-17.
- ↑ McGeehan, Patrick. New York Area Is a Magnet For Graduates, The New York Times, August 16, 2006. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ New York City Economic Development Corporation (November 18, 2004). Mayor Michael R. Bloomberg and Economic Development Corporation President Andrew M. Alper Unveil Plans to Develop Commercial Bioscience Center in Manhattan. Press release. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ NIH Domestic Institutions Awards Ranked by City, Fiscal Year 2003. National Institutes of Health (2003). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ 116.0 116.1 Nation's Largest Libraries. LibrarySpot. Retrieved on 2007-06-06.
- ↑ 117.0 117.1 117.2 NHTS 2001 Highlights Report, BTS03-05 (PDF). U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics (2001). Retrieved on 2006-05-21.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 118.2 118.3 The MTA Network: Public Transportation for the New York Region. Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved on 2006-05-17.
- ↑ Pisarski, Alan (October 16, 2006). Commuting in America III: Commuting Facts (PDF). Transportation Research Board. Retrieved on 2007-03-27.
- ↑ Verrazano-Narrows Bridge. Nycroads.com. Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ About the MTA Long Island Rail Road. Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ Facts at a Glance (PDF). NJ Transit (2005). Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Grand Central Demographics. Metropolitan Transportation Authority. Retrieved on 2007-03-26.
- ↑ Amtrak Facts. National Atlas. Retrieved on 2006-07-19.
- ↑ U.S. International Travel and Transportation Trends, BTS02-03. U.S. Department of Transportation, Bureau of Transportation Statistics (2002). Retrieved on 2007-02-18.
- ↑ 2005 Annual Airport Traffic Report (PDF). The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (November 2, 2006). Retrieved on 2007-02-18.
- ↑ The Port Authority of New York and New Jersey (August 29, 2005). Port Authority Leads Nation in Record-Setting Year for Travel Abroad. Press release. Retrieved on 2007-02-18.
- ↑ Schaller, Bruce. Biking It, Gotham Gazette, June 2006. Retrieved on 2006-07-20.
- ↑ U.S. Cities’ Preparedness for an Oil Crisis. SustainLane (March 2006). Retrieved on 2006-07-20.
- ↑ 2001 National Household Travel Survey: Summary of Travel Trends (PDF). U.S. Department of Transportation (December 2004). Retrieved on 2007-02-18.