J. P. Morgan: Difference between revisions
imported>Subpagination Bot m (Add {{subpages}} and remove any categories (details)) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
'''John Pierpont Morgan''' (April 17, 1837 – March 31, 1913) was an [[United States of America|American]] financier, banker, philanthropist, and art collector who dominated [[corporate finance]] and [[industrial consolidation]] from the 1890s to 1913. In 1892 Morgan arranged the merger of Edison General Electric and Thompson-Houson Electric Company to form [[General Electric]]. After financing the creation of the Federal Steel Company he merged the [[Carnegie Steel Company]] and several other steel and iron businesses to form the [[United States Steel Corporation]] in 1901. He played a key role in ending the [[Panic of 1907]]. A leading art collector he bequeathed much of his large collection to the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] in New York City. At the height of Morgan's career during the early 1900s, he and his partners had financial investments in many large corporations and was accused by critics of controlling the nation's high finance. By 1901, he was one of the wealthiest men in the world. | |||
'''John Pierpont Morgan''' (April 17, 1837 – March 31, 1913) was an [[United States|American]] financier, banker, philanthropist, and art collector who dominated [[corporate finance]] and [[industrial consolidation]] from the 1890s to 1913. In 1892 Morgan arranged the merger of Edison General Electric and Thompson-Houson Electric Company to form [[General Electric]]. After financing the creation of the Federal Steel Company he merged the [[Carnegie Steel Company]] and several other steel and iron businesses to form the [[United States Steel Corporation]] in 1901. He played a key role in ending the [[Panic of 1907]]. A leading art collector he bequeathed much of his large collection to the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] in New York City. At the height of Morgan's career during the early 1900s, he and his partners had financial investments in many large corporations and was | |||
== Early life and education == | == Early life and education == | ||
| Line 10: | Line 9: | ||
==Career== | ==Career== | ||
=== Early years === | === Early years === | ||
Morgan entered banking in his father's London branch in 1856, moving to [[New York City]] the next year where he worked at the banking house of Duncan, Sherman & Company, the American representatives of George Peabody & Company. From 1860 to 1864, as J. Pierpont Morgan & Company, he acted as agent in New York for his father's firm. By 1864-71 he was a member of the firm of Dabney, Morgan & Company; in 1871 he partnered with the Drexels of Philadelphia to form the New York firm of Drexel, Morgan & Company. | Morgan entered banking in his father's London branch in 1856, moving to [[New York, New York|New York City]] the next year where he worked at the banking house of Duncan, Sherman & Company, the American representatives of George Peabody & Company. From 1860 to 1864, as J. Pierpont Morgan & Company, he acted as agent in New York for his father's firm. By 1864-71 he was a member of the firm of Dabney, Morgan & Company; in 1871 he partnered with the Drexels of Philadelphia to form the New York firm of Drexel, Morgan & Company. | ||
In 1895 it became J. P. Morgan & Company, and retained close ties with Drexel & Company of Philadelphia, Morgan, Harjes & Company of Paris, and J. S. Morgan & Company (after 1910 Morgan, Grenfell & Company), of London. By 1900 it was one of the most powerful banking houses of the world, carrying through many deals especially reorganizations and consolidations. Morgan had many partners over the years, such as [[George W. Perkins]], but remained in firm charge.<ref>Garraty, (1960) </ref> | In 1895 it became J. P. Morgan & Company, and retained close ties with Drexel & Company of Philadelphia, Morgan, Harjes & Company of Paris, and J. S. Morgan & Company (after 1910 Morgan, Grenfell & Company), of London. By 1900 it was one of the most powerful banking houses of the world, carrying through many deals especially reorganizations and consolidations. Morgan had many partners over the years, such as [[George W. Perkins]], but remained in firm charge.<ref>Garraty, (1960) </ref> | ||
| Line 23: | Line 22: | ||
===Later years=== | ===Later years=== | ||
[[Image:JP Morgan.jpg|right|thumb|240px|J.P. Morgan, photographed by [[Edward Steichen]] in | [[Image:JP Morgan.jpg|right|thumb|240px|J.P. Morgan, photographed by [[Edward Steichen]] in 1903]] | ||
After the death of his father in 1890, Morgan took control of [[Morgan, Grenfell & Co.|J. S. Morgan & Co]] (re-named Morgan, Grenfell & Company in 1910). Morgan began talks with [[Charles M. Schwab]], president of Carnegie Co., and businessman [[Andrew Carnegie]] in 1900 with the intention of buying Carnegie's business and several other steel and iron businesses to consolidate them to create the [[United States Steel Corporation]].<ref name="steel">{{cite news |first=Peter |last= Krass |title=He Did It!(creation of U.S. Steel by J.P. Morgan) |url= |work= |publisher=Across the Board (Professional Collection) |date=May 2001}}</ref> Carnegie agreed to sell the business to Morgan for $480 million.<ref name="steel"/> The deal was closed without lawyers and without a written contract. News of the industrial consolidation arrived to newspapers in mid-January 1901. U.S. Steel was founded later that year and was the first billion-dollar company in the world with an authorized [[capitalization]] of $1.4 billion.<ref name="steel"/> | After the death of his father in 1890, Morgan took control of [[Morgan, Grenfell & Co.|J. S. Morgan & Co]] (re-named Morgan, Grenfell & Company in 1910). Morgan began talks with [[Charles M. Schwab]], president of Carnegie Co., and businessman [[Andrew Carnegie]] in 1900 with the intention of buying Carnegie's business and several other steel and iron businesses to consolidate them to create the [[United States Steel Corporation]].<ref name="steel">{{cite news |first=Peter |last= Krass |title=He Did It!(creation of U.S. Steel by J.P. Morgan) |url= |work= |publisher=Across the Board (Professional Collection) |date=May 2001}}</ref> Carnegie agreed to sell the business to Morgan for $480 million.<ref name="steel"/> The deal was closed without lawyers and without a written contract. News of the industrial consolidation arrived to newspapers in mid-January 1901. U.S. Steel was founded later that year and was the first billion-dollar company in the world with an authorized [[capitalization]] of $1.4 billion.<ref name="steel"/>{{cite web|title=History of U. S. Steel|url=http://www.ussteel.com/uss/portal/home/aboutus/history|publisher=United States Steel|accessdate=24 October 2013}}</ref> | ||
U.S. Steel aimed to achieve greater [[economies of scale]], reduce transportation and resource costs, expand product lines, and improve distribution.<ref name="steel"/> It was also planned to allow the United States to compete globally with [[ | U.S. Steel aimed to achieve greater [[economies of scale]], reduce transportation and resource costs, expand product lines, and improve distribution.<ref name="steel"/> It was also planned to allow the United States to compete globally with the [[United Kingdom]] and [[Germany]]. U.S. Steel's size was claimed by Schwab and others to allow the company to pursue distant international markets-[[globalization]].<ref name="steel"/> U.S. Steel was regarded as a [[monopoly]] by critics, as the business was attempting to dominate not only steel but also the construction of bridges, ships, railroad cars and rails, wire, nails, and a host of other products. With U.S. Steel, Morgan had captured two-thirds of the steel market, and Schwab was confident that the company would soon hold a 75 percent market share.<ref name="steel"/> However, since 1901 the businesses' market share dropped, never reaching Schwab's dream of seventy-five percent market share. | ||
Morgan also financed manufacturing and [[mining]] businesses and controlled banks, [[insurance]] companies, shipping lines, and communications systems. Through his firm came enormous funds from abroad to help develop American resources. | Morgan also financed manufacturing and [[mining]] businesses and controlled banks, [[insurance]] companies, shipping lines, and communications systems. Through his firm came enormous funds from abroad to help develop American resources. | ||
| Line 35: | Line 34: | ||
==Personal life== | ==Personal life== | ||
Morgan was a lifelong member of the [[Episcopal Church in the United States of America|Protestant Episcopal Church]], and by 1890 was one of its most influential leaders. | Morgan was a lifelong member of the [[Episcopal Church in the United States of America|Protestant Episcopal Church]], and by 1890 was one of its most influential leaders. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Anne Morgan]] (1873–1952). | * [[Anne Morgan]] (1873–1952). | ||
Morgan was physically large with massive shoulders, piercing eyes and a purple nose, because of a childhood skin disease, [[rosacea]].<ref> | Morgan was physically large with massive shoulders, piercing eyes and a purple nose, because of a childhood skin disease, [[rosacea]].<ref>{{cite news|last=Roberts|first=William|title=The Celebrity Face of Rosacea|url=http://inhealth.cnn.com/rosacea/the-celebrity-face-of-rosacea/8|work=Cable News Network|publisher=Turner Broadcasting System|accessdate=24 October 2013}}</ref> His grotesquely deformed nose was due to a disease called [[rhinophyma]], which is the end result of acne rosacea. As the deformity worsens, pits, nodules, fissures, lobulations, and pedunculation contort the nose into grotesque cosmetic problems. This condition inspired the taunt "Johny Morgan's nasal organ has a purple hue."<ref>Kennedy, David M., and Lizabeth Cohen. ''The American Pageant''. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, 2006. p541.</ref> Surgeons could have shaved away the rhinophymous growth of sebaceous tissue during Morgan's lifetime, but as a child Morgan suffered from infantile seizures, and it is suspected that he did not seek surgery for his nose because he feared the seizures would return. His social and professional self-confidence were well too established to be undermined by this affliction. It appeared as if he dared people to meet him squarely and not shrink from the sight, asserting the force of his character over the ugliness of his face.<ref>Strouse 1999, pp 265-66'''</ref> He was known to dislike publicity and hated being photographed; as a result of his self-consciousness of his rosacea, all of his professional portraits were retouched. He smoked large Havana cigars called ''Hercules' Clubs'' and often had a tremendous physical effect on people; one man said that a visit from Morgan left him feeling "as if a gale had blown through the house."<ref name="bioofamerica">[http://claver.gprep.org/fac/sjochs//jpmorgan-1.htm John Pierpont Morgan and the American Corporation], Biography of America</ref> | ||
Morgan died while traveling abroad in Rome. At the time of his death, he had an estate worth $80 million (approximately $1.2 billion today).<ref name="bioofamerica" /> His remains were interred in the Cedar Hill Cemetery in his birthplace of Hartford. His son, [[J. P. Morgan, Jr.]], inherited the banking business. | Morgan died while traveling abroad in Rome. At the time of his death, he had an estate worth $80 million (approximately $1.2 billion today).<ref name="bioofamerica" /> His remains were interred in the Cedar Hill Cemetery in his birthplace of Hartford. His son, [[J. P. Morgan, Jr.]], inherited the banking business. | ||
==Art, book and gemstone collector== | ==Art, book and gemstone collector== | ||
Morgan was a notable collector of books, pictures, and, other art objects, many loaned or given to the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] (of which he was president and was a major force in its establishment), and many housed in his London house and in his private library on 36th Street, near [[Madison Avenue]] in [[New York City]]. His son, [[J. P. Morgan, Jr.]], made the [[Pierpont Morgan Library]] a public institution in 1924 as a memorial to his father and kept Belle da Costa Greene, his father's private librarian, as its first director.<ref>Auchincloss (1990)</ref> | Morgan was a notable collector of books, pictures, and, other art objects, many loaned or given to the [[Metropolitan Museum of Art]] (of which he was president and was a major force in its establishment), and many housed in his London house and in his private library on 36th Street, near [[Madison Avenue]] in [[New York, New York|New York City]]. His son, [[J. P. Morgan, Jr.]], made the [[Pierpont Morgan Library]] a public institution in 1924 as a memorial to his father and kept Belle da Costa Greene, his father's private librarian, as its first director.<ref>Auchincloss (1990)</ref> | ||
By the turn of the century JP Morgan had become one of America's most important collectors of gems and had assembled the most important gem collection in the USA as well as of American gemstones (over 1000 pieces). | By the turn of the century JP Morgan had become one of America's most important collectors of gems and had assembled the most important gem collection in the USA as well as of American gemstones (over 1000 pieces). | ||
| Line 61: | Line 59: | ||
==Popular culture== | ==Popular culture== | ||
[[Bertold Brecht]] the German writer based the figure of Pierpont Mauler the beef tycoon in his play [[Saint Joan of the Stockyards]] on Morgan. | [[Bertold Brecht]] the German writer based the figure of Pierpont Mauler the beef tycoon in his play [[Saint Joan of the Stockyards]] on Morgan. | ||
| Line 68: | Line 65: | ||
J. P. Morgan appears in [[E. L. Doctorow]]'s novel ''[[Ragtime (novel)|Ragtime]]'', and in the [[Ragtime (musical)|broadway musical]] inspired by it of the same name. | J. P. Morgan appears in [[E. L. Doctorow]]'s novel ''[[Ragtime (novel)|Ragtime]]'', and in the [[Ragtime (musical)|broadway musical]] inspired by it of the same name. | ||
J.P. Morgan is mentioned, by name, by [[Oliver Warbucks]] in the [[broadway musical]], [[Annie]] | J.P. Morgan is mentioned, by name, by [[Oliver Warbucks]] in the [[broadway musical]], ''[[Annie]]''. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist|2}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 3 September 2024
John Pierpont Morgan (April 17, 1837 – March 31, 1913) was an American financier, banker, philanthropist, and art collector who dominated corporate finance and industrial consolidation from the 1890s to 1913. In 1892 Morgan arranged the merger of Edison General Electric and Thompson-Houson Electric Company to form General Electric. After financing the creation of the Federal Steel Company he merged the Carnegie Steel Company and several other steel and iron businesses to form the United States Steel Corporation in 1901. He played a key role in ending the Panic of 1907. A leading art collector he bequeathed much of his large collection to the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City. At the height of Morgan's career during the early 1900s, he and his partners had financial investments in many large corporations and was accused by critics of controlling the nation's high finance. By 1901, he was one of the wealthiest men in the world.
Early life and education
J.P. Morgan was born in Hartford, Connecticut to Junius Spencer Morgan (1813—1890) and Juliet Pierpont (1816—1884) of Boston, Massachusetts. Pierpont, as he preferred to be known, had a varied education due in part to interference by his father, Junius. In the autumn of 1848, Pierpont transferred to the Hartford Public School and then to the Episcopal Academy in Cheshire, boarding with the principal. In September 1851, Morgan passed the entrance exam for English High School of Boston, a school specialising in Mathematics to prepare young men for careers in commerce.
In the spring of 1852, illness that was to become more common as his life progressed struck; rheumatic fever left him in so much pain that he couldn't walk. Junius sent the boy to the Azores in order for him to recover. After convalescing for almost a year, Pierpont returned to the school in Boston to resume his studies. After graduating he attended Bellerive, a school near the Swiss village of Vevey. When Morgan had attained fluency in French, his attended the University of Göttingen in order to improve his German.
Career
Early years
Morgan entered banking in his father's London branch in 1856, moving to New York City the next year where he worked at the banking house of Duncan, Sherman & Company, the American representatives of George Peabody & Company. From 1860 to 1864, as J. Pierpont Morgan & Company, he acted as agent in New York for his father's firm. By 1864-71 he was a member of the firm of Dabney, Morgan & Company; in 1871 he partnered with the Drexels of Philadelphia to form the New York firm of Drexel, Morgan & Company.
In 1895 it became J. P. Morgan & Company, and retained close ties with Drexel & Company of Philadelphia, Morgan, Harjes & Company of Paris, and J. S. Morgan & Company (after 1910 Morgan, Grenfell & Company), of London. By 1900 it was one of the most powerful banking houses of the world, carrying through many deals especially reorganizations and consolidations. Morgan had many partners over the years, such as George W. Perkins, but remained in firm charge.[1]
Morgan's ascent to power was accompanied by dramatic financial battles. He wrested control of the Albany and Susquehanna Railroad from Jay Gould and Jim Fisk in 1869, he led the syndicate that broke the government-financing privileges of Jay Cooke, and soon became deeply involved in developing and financing a railroad empire by reorganizations and consolidations in all parts of the United States. He raised large sums in Europe but instead of only handling the funds he helped the railroads reorganize and achieve greater efficiencies. He fought against the speculators interested in speculative profits, and built a vision of an integrated transportation system. In 1885 he reorganized the New York, West Shore & Buffalo Railroad, leasing it to the New York Central. In 1886 he reorganized the Philadelphia & Reading, and in 1888 the Chesapeake & Ohio. After Congress passed the Interstate Commerce Act in 1887, Morgan set up conferences in 1889 and 1890 that brought together railroad presidents in order to help the industry follow the new laws and write agreements for the maintenance of "public, reasonable, uniform and stable rates" The conferences were the first of their kind, and by creating a community of interest among competing lines paved the way for the great consolidations of the early 20th century.
Morgan's process of taking over troubled businesses to reorganize them was known as "Morganization".[2] Morgan reorganized business structures and management in order to return them to profitability. Morgan's reputation as a banker and financier also helped bring interest from investors to the businesses he took over.[3]
In 1895, at the depths of the Panic of 1893, the Federal Treasury was nearly out of gold. President Grover Cleveland arranged for Morgan to create a private syndicate on Wall Street to supply the U.S. Treasury with $65 million in gold, half of it from Europe, to float a bond issue that restored the treasury surplus of $100 million. The episode saved the Treasury but hurt Cleveland with the agrarian wing of his Democratic party and became an issue in the election of 1896, when banks came under withering attack from William Jennings Bryan. Morgan and Wall Street bankers donated heavily to Republican William McKinley, who was elected in 1896 and reelected in 1900 on a gold standard platform. [4]
In 1902, J. P. Morgan & Co. purchased the Leyland line of Atlantic steamships and other British lines, creating an Atlantic shipping combine, the International Mercantile Marine Company, which eventually became the owner of White Star Line, builder and operator of RMS Titanic. In addition, J P Morgan & Co (or the banking houses which it succeeded) reorganized a large number of railroads between 1869 and 1899.
Later years
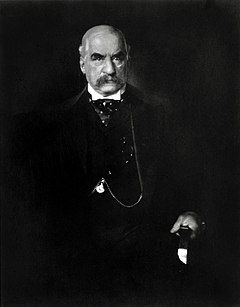
After the death of his father in 1890, Morgan took control of J. S. Morgan & Co (re-named Morgan, Grenfell & Company in 1910). Morgan began talks with Charles M. Schwab, president of Carnegie Co., and businessman Andrew Carnegie in 1900 with the intention of buying Carnegie's business and several other steel and iron businesses to consolidate them to create the United States Steel Corporation.[5] Carnegie agreed to sell the business to Morgan for $480 million.[5] The deal was closed without lawyers and without a written contract. News of the industrial consolidation arrived to newspapers in mid-January 1901. U.S. Steel was founded later that year and was the first billion-dollar company in the world with an authorized capitalization of $1.4 billion.[5]History of U. S. Steel. United States Steel. Retrieved on 24 October 2013.</ref>
U.S. Steel aimed to achieve greater economies of scale, reduce transportation and resource costs, expand product lines, and improve distribution.[5] It was also planned to allow the United States to compete globally with the United Kingdom and Germany. U.S. Steel's size was claimed by Schwab and others to allow the company to pursue distant international markets-globalization.[5] U.S. Steel was regarded as a monopoly by critics, as the business was attempting to dominate not only steel but also the construction of bridges, ships, railroad cars and rails, wire, nails, and a host of other products. With U.S. Steel, Morgan had captured two-thirds of the steel market, and Schwab was confident that the company would soon hold a 75 percent market share.[5] However, since 1901 the businesses' market share dropped, never reaching Schwab's dream of seventy-five percent market share.
Morgan also financed manufacturing and mining businesses and controlled banks, insurance companies, shipping lines, and communications systems. Through his firm came enormous funds from abroad to help develop American resources.
Enemies of banking attacked Morgan for the terms of his loan of gold to the federal government in the 1895 crisis, for his financial resolution of the Panic of 1907, and for bringing on the financial ills of the New York, New Haven & Hartford RR. In 1912, the Pujo Committee, a subcommittee of the House Banking and Currency committee, found that the partners of J.P. Morgan & Co. along with the directors of First National and National City Bank controlled aggregate resources of $22,245,000,000. Louis Brandeis, the former U.S. Supreme Court Justice, compared this sum to the value of all the property in the twenty-two states west of the Mississippi River.[6]
In 1900, Morgan financed inventor Nikola Tesla and his Wardenclyffe Tower with $150,000 for experiments in radio. Tesla was unsuccessful and, in 1904, Morgan pulled out. At the height of Morgan's career during the early 1900s, he and his partners controlled directly and indirectly assets worth $1.3 billion. [7]
Personal life
Morgan was a lifelong member of the Protestant Episcopal Church, and by 1890 was one of its most influential leaders.
In 1861, he married Amelia Sturges (1835–1862). After her death the next year, he married Frances Louise Tracy (1842–1924) on May 3, 1863 and they had the following children:
- Louisa Pierpont Morgan (1866–1946) who married Herbert
PennyLivingston Satterlee [8] (1863–1947), - Jack Pierpont Morgan (1867–1943),
- Juliet Morgan (1870–1952), and
- Anne Morgan (1873–1952).
Morgan was physically large with massive shoulders, piercing eyes and a purple nose, because of a childhood skin disease, rosacea.[9] His grotesquely deformed nose was due to a disease called rhinophyma, which is the end result of acne rosacea. As the deformity worsens, pits, nodules, fissures, lobulations, and pedunculation contort the nose into grotesque cosmetic problems. This condition inspired the taunt "Johny Morgan's nasal organ has a purple hue."[10] Surgeons could have shaved away the rhinophymous growth of sebaceous tissue during Morgan's lifetime, but as a child Morgan suffered from infantile seizures, and it is suspected that he did not seek surgery for his nose because he feared the seizures would return. His social and professional self-confidence were well too established to be undermined by this affliction. It appeared as if he dared people to meet him squarely and not shrink from the sight, asserting the force of his character over the ugliness of his face.[11] He was known to dislike publicity and hated being photographed; as a result of his self-consciousness of his rosacea, all of his professional portraits were retouched. He smoked large Havana cigars called Hercules' Clubs and often had a tremendous physical effect on people; one man said that a visit from Morgan left him feeling "as if a gale had blown through the house."[12]
Morgan died while traveling abroad in Rome. At the time of his death, he had an estate worth $80 million (approximately $1.2 billion today).[12] His remains were interred in the Cedar Hill Cemetery in his birthplace of Hartford. His son, J. P. Morgan, Jr., inherited the banking business.
Art, book and gemstone collector
Morgan was a notable collector of books, pictures, and, other art objects, many loaned or given to the Metropolitan Museum of Art (of which he was president and was a major force in its establishment), and many housed in his London house and in his private library on 36th Street, near Madison Avenue in New York City. His son, J. P. Morgan, Jr., made the Pierpont Morgan Library a public institution in 1924 as a memorial to his father and kept Belle da Costa Greene, his father's private librarian, as its first director.[13]
By the turn of the century JP Morgan had become one of America's most important collectors of gems and had assembled the most important gem collection in the USA as well as of American gemstones (over 1000 pieces).
Morgan was a benefactor of the American Museum of Natural History, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, Groton School, Harvard Medical School|medical school), the Lying-in Hospital of the City of New York and the New York trade schools. Morgan was a patron to photographer Edward S. Curtis.
Legacy
His son, J. P. Morgan, Jr. took over the business at his father's death, but was never as influential. As required by the 1933 Glass-Steagall Act, the "House of Morgan" became three entities: J.P. Morgan and Co. and its bank, Morgan Guaranty Trust; Morgan Stanley, an investment house; and Morgan Grenfell in London, an overseas securities house.
The gemstone Morganite was named in his honor. [14]
Popular culture
Bertold Brecht the German writer based the figure of Pierpont Mauler the beef tycoon in his play Saint Joan of the Stockyards on Morgan.
In the musical How to Succeed in Business Without Really Trying, the character J. Pierrepont Finch is portrayed as a rising, powerful businessman; his character is possibly an allegory to Morgan. The character Mr. Bratt alludes to the nominal similarity in the beginning of the show: "Pierrepont. Say, maybe that ought to be J. Pierrepont Finch."
J. P. Morgan appears in E. L. Doctorow's novel Ragtime, and in the broadway musical inspired by it of the same name.
J.P. Morgan is mentioned, by name, by Oliver Warbucks in the broadway musical, Annie.
References
- ↑ Garraty, (1960)
- ↑ Timmons, Heather. "J.P. Morgan: Pierpont would not approve.", BusinessWeek, Nov 18, 2002.
- ↑ Morganization: How Bankrupt Railroads were Reorganized (HTML). Retrieved on 2007-01-05.
- ↑ Chernow (2001) ch 4
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Krass, Peter. "He Did It!(creation of U.S. Steel by J.P. Morgan)", Across the Board (Professional Collection), May 2001.
- ↑ Brandeis (1995), ch. 2
- ↑ Carosso (1970) p. 42
- ↑ J. Pierpont Morgan, Satterlee, Herbert L., New York: The Macmillan Company, 1939
- ↑ Roberts, William. The Celebrity Face of Rosacea, Cable News Network, Turner Broadcasting System. Retrieved on 24 October 2013.
- ↑ Kennedy, David M., and Lizabeth Cohen. The American Pageant. Houghton Mifflin Company: Boston, 2006. p541.
- ↑ Strouse 1999, pp 265-66
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 John Pierpont Morgan and the American Corporation, Biography of America
- ↑ Auchincloss (1990)
- ↑ Morganite, International Colored Gemstone Association, accessed online January 22, 2007