Posterior tibial tendon: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
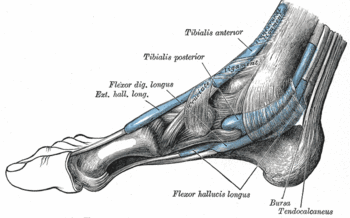
{{Image|Grays-image442.gif|right|350px|The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Medial aspect.}} | {{Image|Grays-image442.gif|right|350px|The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Medial aspect.}} | ||
In [[anatomy]], the '''posterior tibial tendon''', also call '''tibialis posterior''', is a tendon on the sole of the foot.<ref name="isbn1-58734-102-6chapt8d">{{cite book |author=Gray, Henry David |title=Anatomy of the human body |edition=20th edition|publisher=Bartleby.com |location= |year=1918|chapter=8d. The Fasciæ Around the Ankle |chapterurl=http://www.bartleby.com/107/130.html |pages= |isbn=1-58734-102-6 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> It inserts onto the plantar surface of the foot mainly at the junction of the [[navicular bone|navicular]] and first cuneiform bones with smaller insertions on the cuboid and calcaneus bones. | In [[human anatomy]], the '''posterior tibial tendon''', also call '''tibialis posterior''', is a tendon on the sole of the foot.<ref name="isbn1-58734-102-6chapt8d">{{cite book |author=Gray, Henry David |title=Anatomy of the human body |edition=20th edition|publisher=Bartleby.com |location= |year=1918|chapter=8d. The Fasciæ Around the Ankle |chapterurl=http://www.bartleby.com/107/130.html |pages= |isbn=1-58734-102-6 |oclc= |doi=}}</ref> It inserts onto the plantar surface of the foot mainly at the junction of the [[navicular bone|navicular]] and first cuneiform bones with smaller insertions on the cuboid and calcaneus bones. | ||
Rupture or dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon may cause adult [[flatfoot]].<ref name="pmid17561206">{{cite journal |author=Bluman EM, Myerson MS |title=Stage IV posterior tibial tendon rupture |journal=Foot Ankle Clin |volume=12 |issue=2 |pages=341–62, viii |year=2007 |month=June |pmid=17561206 |doi=10.1016/j.fcl.2007.03.004 |url= |issn=}}</ref> | Rupture or dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon may cause adult [[flatfoot]].<ref name="pmid17561206">{{cite journal |author=Bluman EM, Myerson MS |title=Stage IV posterior tibial tendon rupture |journal=Foot Ankle Clin |volume=12 |issue=2 |pages=341–62, viii |year=2007 |month=June |pmid=17561206 |doi=10.1016/j.fcl.2007.03.004 |url= |issn=}}</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:00, 6 October 2024
In human anatomy, the posterior tibial tendon, also call tibialis posterior, is a tendon on the sole of the foot.[1] It inserts onto the plantar surface of the foot mainly at the junction of the navicular and first cuneiform bones with smaller insertions on the cuboid and calcaneus bones.
Rupture or dysfunction of the posterior tibial tendon may cause adult flatfoot.[2]
References
- ↑ Gray, Henry David (1918). “8d. The Fasciæ Around the Ankle”, Anatomy of the human body, 20th edition. Bartleby.com. ISBN 1-58734-102-6.
- ↑ Bluman EM, Myerson MS (June 2007). "Stage IV posterior tibial tendon rupture". Foot Ankle Clin 12 (2): 341–62, viii. DOI:10.1016/j.fcl.2007.03.004. PMID 17561206. Research Blogging.