North Korea: Difference between revisions
imported>Ro Thorpe (correct names of cuddly leaders) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
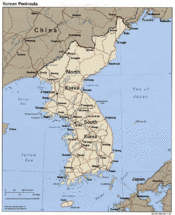
'''North Korea''' ([[Korean]]: ''Bukjoseon''<ref>According to the [[revised romanization of Korean]].</ref>), officially the '''Democratic People's Republic of Korea''' or '''DPRK''' (Korean: ''Joseon Minjujueui Inmin Gonghwaguk''<ref>According to the [[revised romanization of Korean]].</ref>), is the state comprising the northern part of [[ | {{Image|Political map of the Korean peninsula.gif|right|175px|A political map of [[Korea]].}} | ||
'''North Korea''' ([[Korean language|Korean]]: ''Bukjoseon''<ref>According to the [[revised romanization of Korean]].</ref>), officially the '''Democratic People's Republic of Korea''' or '''DPRK''' (Korean: ''Joseon Minjujueui Inmin Gonghwaguk''<ref>According to the [[revised romanization of Korean]].</ref>), is the [[state]] comprising the northern part of the [[Korean peninsula]], between China and [[South Korea]]. Its [[capital (city)|capital]] and largest city is [[Pyongyang]]. [[Korea]] was split into two states following [[World War II]], since when the North has had [[Soviet Union|Soviet]]-inspired government, first under [[Kim Il-sung]] and then under his son [[Kim Jong-il]]. The elder Kim remains "Eternal President" despite his death in 1994,<ref>This is not entirely unprecedented: Caliph Mustasim was killed by the Mongols in 1258, but the Sultans of Delhi continued stamping his name on their coins until 1325.</ref> while Kim Jong-il was Chairman of the National Defense Committee and ''de facto'' leader until his death in December 2011, when he was succeeded in turn by his son Kim Jong-un. | |||
The state follows Kim Il-sung's policy of ''juche'' or 'self-reliance,' sometimes classified as a religion. [[Communism]] was removed from the DPRK's [[constitution]] in 2009. Officially, the state is [[multiparty democracy]] which holds [[election]]s and guarantees [[human rights]]. However, the [[Workers' Party of Korea]] is responsible for most political offices and receives regular international criticism for its approach to [[democracy]] and individual freedoms. | |||
North Korea benefits from much of the peninsula's [[natural resources]] and historically was more industrialized than South Korea. It exports [[military]] hardware and foodstuffs, and hosts some [[tourism|tourist]] sites. As the DPRK has seen favorable [[trade]] relationships weaken with the decline of Communism since the 1990s, its [[economy]] under-performs compared to its southern neighbour, and the country has also suffered from [[famine]]s and [[flooding]] over the years.<ref>''CNN'': '[http://edition.cnn.com/2010/WORLD/asiapcf/09/26/north.korea.explainer/index.html What is life like inside North Korea?]' September 27, 2010.</ref> | |||
In 2006, North Korea became the world's ninth<ref>not counting former nuclear powers</ref> nuclear power. However, its nuclear arsenal is believed to be small, crude and unreliable. | |||
{{Image|Korean peninsula.jpg|left|200px|A satellite image of the [[Korean peninsula]].}} | |||
==Footnotes== | ==Footnotes== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist|2}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:01, 26 September 2024
North Korea (Korean: Bukjoseon[1]), officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea or DPRK (Korean: Joseon Minjujueui Inmin Gonghwaguk[2]), is the state comprising the northern part of the Korean peninsula, between China and South Korea. Its capital and largest city is Pyongyang. Korea was split into two states following World War II, since when the North has had Soviet-inspired government, first under Kim Il-sung and then under his son Kim Jong-il. The elder Kim remains "Eternal President" despite his death in 1994,[3] while Kim Jong-il was Chairman of the National Defense Committee and de facto leader until his death in December 2011, when he was succeeded in turn by his son Kim Jong-un.
The state follows Kim Il-sung's policy of juche or 'self-reliance,' sometimes classified as a religion. Communism was removed from the DPRK's constitution in 2009. Officially, the state is multiparty democracy which holds elections and guarantees human rights. However, the Workers' Party of Korea is responsible for most political offices and receives regular international criticism for its approach to democracy and individual freedoms.
North Korea benefits from much of the peninsula's natural resources and historically was more industrialized than South Korea. It exports military hardware and foodstuffs, and hosts some tourist sites. As the DPRK has seen favorable trade relationships weaken with the decline of Communism since the 1990s, its economy under-performs compared to its southern neighbour, and the country has also suffered from famines and flooding over the years.[4]
In 2006, North Korea became the world's ninth[5] nuclear power. However, its nuclear arsenal is believed to be small, crude and unreliable.
Footnotes
- ↑ According to the revised romanization of Korean.
- ↑ According to the revised romanization of Korean.
- ↑ This is not entirely unprecedented: Caliph Mustasim was killed by the Mongols in 1258, but the Sultans of Delhi continued stamping his name on their coins until 1325.
- ↑ CNN: 'What is life like inside North Korea?' September 27, 2010.
- ↑ not counting former nuclear powers