Clotrimazole: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
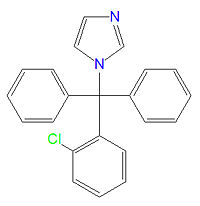
'''Clotrimazole''', also called clotrimazol and chlotrimazole, is | '''Clotrimazole''', also called clotrimazol and chlotrimazole, is a broad-spectrm [[azole]]-based antifungal drug sold under many trade names. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oropharyngeal candidiasis, and fungal infections such as [[ringworm]], [[athlete's foot]] and [[jock itch]]. It is also used in combination with [[betamethasone]] in the treatment of cutaneous tinea infections. | ||
== | == Mechanism of action == | ||
Like other azole-based antifungal drugs, clotrimazole increases cell permeability by interfering with the conversion of [[lanosterol]] to [[ergostol]], a critical component in fungal cell membranes, by inhibiting the enzyme [[14-alpha-methylase]], a P-450 enzyme. It is most effective against growing and dividing organisms. | |||
== Brand names == | |||
* Canesten® | |||
* Canestine® | |||
* Canifug® | |||
* Cimitidine® | |||
* Clotrimaderm® | |||
* Empecid® | |||
* FemCare® | |||
* Gyne-Lotrimin 3® | |||
* Gyne-Lotrimin® | |||
* Gyne-Lotrimin ® | |||
* Gynix® | |||
* Lotrimin® | |||
* Mono-baycuten | |||
* Mycelax® | |||
* Mycelex® | |||
* Mycelex 7® | |||
* Mycelex G ® | |||
* Mycelex Troches® | |||
* Mycelex-7® | |||
* Myclo® | |||
* Myclo-Gyne® | |||
* Mycosporin® | |||
* Mykosporin® | |||
* Neo-Zol Cream® | |||
* Trimysten® | |||
* Trivagizole 3® | |||
* Veltrim® | |||
== References and external links == | |||
{{CZMed}}[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 17:01, 29 July 2024
|
| |||||||
| clotrimazole | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | antifungal drug | ||||||
| Properties: | azole compound | ||||||
| Hazards: | see side effects & drug interactions | ||||||
| |||||||
Clotrimazole, also called clotrimazol and chlotrimazole, is a broad-spectrm azole-based antifungal drug sold under many trade names. It is used to treat vaginal yeast infections, oropharyngeal candidiasis, and fungal infections such as ringworm, athlete's foot and jock itch. It is also used in combination with betamethasone in the treatment of cutaneous tinea infections.
Mechanism of action
Like other azole-based antifungal drugs, clotrimazole increases cell permeability by interfering with the conversion of lanosterol to ergostol, a critical component in fungal cell membranes, by inhibiting the enzyme 14-alpha-methylase, a P-450 enzyme. It is most effective against growing and dividing organisms.
Brand names
- Canesten®
- Canestine®
- Canifug®
- Cimitidine®
- Clotrimaderm®
- Empecid®
- FemCare®
- Gyne-Lotrimin 3®
- Gyne-Lotrimin®
- Gyne-Lotrimin ®
- Gynix®
- Lotrimin®
- Mono-baycuten
- Mycelax®
- Mycelex®
- Mycelex 7®
- Mycelex G ®
- Mycelex Troches®
- Mycelex-7®
- Myclo®
- Myclo-Gyne®
- Mycosporin®
- Mykosporin®
- Neo-Zol Cream®
- Trimysten®
- Trivagizole 3®
- Veltrim®
References and external links
The most up-to-date information about Clotrimazole and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Clotrimazole - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Clotrimazole - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Clotrimazole - Detailed information from DrugBank.